地形侵食シミュレーション
【概要】Python + NumPyによる物理ベースの水力侵食シミュレーション。fBmノイズで初期地形を生成し、降雨・水流・土砂運搬・堆積の物理プロセスを統合計算。128×128グリッドで100m×100mスケールの地形を数百年の侵食過程で変化させ、自然な河川パターンと谷地形を生成する。
はじめに
Three Ways of Generating Terrain with Erosion Features(GitHub: https://github.com/dandrino/terrain-erosion-3-ways)をベースとした物理シミュレーション基盤である。本システムは水力侵食による地形変化を物理法則に基づいて計算し、地形生成を行う。適用範囲は100m×100m〜数kmスケールの地形、時間スケールは数百〜数千年の侵食過程に相当し、計算精度は格子解像度(グリッドの細かさ)に依存する(128×128で約0.8m精度)。
技術仕様
実装技術:Python + NumPy
特徴:物理ベースの水力侵食シミュレーション
物理シミュレーションの原理
理論的基盤
本システムは水、土砂、地形の物理的相互作用をシミュレートする。水力侵食シミュレーションは流体運動を記述するナビエ・ストークス方程式(粘性流体の運動方程式)に基づく。質量保存則(物質の総量保存法則)により水の流れを、運動量保存則(運動量の総和保存法則)により土砂運搬を計算し、土砂運搬能力(水流強度に比例)に基づいて侵食・堆積を決定する。
物理パラメータ
各パラメータの物理的意味と単位:
- rain_rate:降雨量 [m³/s] - セル面積あたりの降水体積流量(デフォルト: 0.0008 × セル面積)
- evaporation_rate:蒸発率 [1/s] - 水の体積減少率(デフォルト: 0.0005)
- gravity:重力定数 [m/s²] - 水流速度計算用の加速度(デフォルト: 30.0)
- sediment_capacity_constant:土砂運搬能力係数 - 水流による土砂運搬量の比例定数(デフォルト: 50.0)
- dissolving_rate:溶解率 - 地形からの土砂供給率(デフォルト: 0.25)
- deposition_rate:堆積率 - 土砂の沈降堆積率(デフォルト: 0.001)
実装手法
アルゴリズム
- 有限差分法による勾配計算:中央差分により隣接セルとの高度差から水流方向を決定
- 初期地形生成:fBm(fractional Brownian motion:自己相似確率過程)ノイズを使用。ヒュルスト指数H(0 < H < 1)により地形粗さを制御し、パワーロー特性(f^-2)で地形の統計的性質を再現
- 土砂運搬処理:土砂運搬能力に基づく侵食・堆積の計算
- 境界条件:流出境界条件(グリッド端部で値を固定し、水と土砂の領域外流出を想定)
- 数値計算:時間ステップによる逐次計算、NumPyのベクトル化演算による高速化
設定例
基本設定
# グリッドサイズと空間スケール
grid_size = 128 # 128×128のグリッド
full_width = 100 # 実世界での100m×100m高解像度設定
simulator = TerrainErosionSimulator(grid_size=256, full_width=200)
final_terrain = simulator.run_simulation(iterations=500)処理フロー
↓
[fBmノイズで初期地形生成]
↓
[水力侵食シミュレーション100回反復]
↓
[最終地形の可視化・保存]
↓
[プログラム終了]
システム実装
実装コード
以下は地形侵食シミュレーションの実装コードである。Three Ways of Generating Terrain with Erosion Features をベースとした物理シミュレーション基盤として設計されている。
# 地形侵食シミュレーションプログラム
# fBmノイズ+水文学的侵食による地形生成
# 論文: "Fast Hydraulic Erosion Simulation and Visualization on GPU" (Mei et al. 2007)
# GitHub: https://github.com/dandrino/terrain-erosion-3-ways
# 特徴: fBmノイズによる初期地形生成とGrid-based侵食の組み合わせ、フラクタル自己相似性を利用
# 水流・土砂運搬・堆積の物理プロセス統合、128x128グリッドで100ステップ処理
# 前準備: pip install numpy matplotlib
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
import warnings
import platform
# 定数
GRID_SIZE = 128
FULL_WIDTH = 100
ITERATIONS = 100
# 物理パラメータ
RAIN_RATE = 0.0008
EVAPORATION_RATE = 0.0005
GRAVITY = 30.0
SEDIMENT_CAPACITY_CONSTANT = 50.0
DISSOLVING_RATE = 0.25
DEPOSITION_RATE = 0.001
MIN_HEIGHT_DELTA = 0.05
FLOW_RATE = 0.5 # 流速に基づく移動割合
# 数値安定性制限値
MAX_VELOCITY = 10.0
MAX_WATER = 1.0
MAX_SEDIMENT = 1.0
# 日本語フォント設定
system = platform.system()
font_candidates = []
if system == "Windows":
font_candidates = ['MS Gothic', 'Meiryo', 'Yu Gothic', 'NotoSansCJK']
elif system == "Darwin":
font_candidates = ['Hiragino Sans', 'Arial Unicode MS', 'NotoSansCJK']
else:
font_candidates = ['Noto Sans CJK JP', 'DejaVu Sans', 'Liberation Sans']
use_english_titles = True
for font_name in font_candidates:
font_files = fm.findSystemFonts(fontpaths=None, fontext='ttf')
available_fonts = [fm.FontProperties(fname=fname).get_name() for fname in font_files]
if any(font_name.lower() in font.lower() for font in available_fonts):
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = font_name
use_english_titles = False
break
if use_english_titles:
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore', category=UserWarning, message='Glyph .* missing from font.*')
cell_width = FULL_WIDTH / GRID_SIZE
cell_area = cell_width ** 2
rain_rate = RAIN_RATE * cell_area
# fBmノイズによる初期地形生成
shape = (GRID_SIZE, GRID_SIZE)
freqs = tuple(np.fft.fftfreq(n, d=1.0/n) for n in shape)
freq_radial = np.hypot(*np.meshgrid(*freqs))
envelope = np.power(freq_radial, -2.0, where=freq_radial!=0)
envelope[0, 0] = 0.0
phase_noise = np.exp(2j * np.pi * np.random.rand(*shape))
terrain = np.real(np.fft.ifft2(np.fft.fft2(phase_noise) * envelope))
terrain_range = terrain.max() - terrain.min()
if terrain_range > 0:
terrain = (terrain - terrain.min()) / terrain_range
else:
terrain = np.zeros_like(terrain)
water = np.zeros_like(terrain)
sediment = np.zeros_like(terrain)
velocity = np.zeros_like(terrain)
# メイン処理
print("地形侵食シミュレーション開始")
print("操作方法: プログラムは自動実行されます。終了時にグラフが表示されます。")
print(f"設定: グリッドサイズ {GRID_SIZE}x{GRID_SIZE}, 反復回数 {ITERATIONS}")
print("注意: 処理には数秒かかる場合があります。")
for i in range(ITERATIONS):
# 降雨
rain_amount = np.random.rand(GRID_SIZE, GRID_SIZE) * rain_rate
water += rain_amount
water = np.clip(water, 0, MAX_WATER)
# 勾配計算(有限差分法、物理的距離を考慮、下り方向を正とする)
water_terrain = np.nan_to_num(water + terrain, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
water_terrain = np.clip(water_terrain, -1e6, 1e6)
# 下り勾配を取得(符号反転)
dx = -(np.roll(water_terrain, -1, axis=1) - np.roll(water_terrain, 1, axis=1)) / (2.0 * cell_width)
dy = -(np.roll(water_terrain, -1, axis=0) - np.roll(water_terrain, 1, axis=0)) / (2.0 * cell_width)
dx = np.nan_to_num(dx, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
dy = np.nan_to_num(dy, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
dx = np.clip(dx, -1e6, 1e6)
dy = np.clip(dy, -1e6, 1e6)
gradient = dx + 1j * dy
gradient_magnitude = np.abs(gradient)
# ゼロ勾配の処理
zero_mask = gradient_magnitude < 1e-10
gradient[zero_mask] = 0
# 勾配の正規化
non_zero_mask = gradient_magnitude >= 1e-10
gradient_normalized = np.zeros_like(gradient)
gradient_normalized[non_zero_mask] = gradient[non_zero_mask] / gradient_magnitude[non_zero_mask]
# 下流隣接セルの高さ取得
terrain_safe = np.nan_to_num(terrain, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
terrain_safe = np.clip(terrain_safe, -1e6, 1e6)
coords_y, coords_x = np.meshgrid(np.arange(GRID_SIZE), np.arange(GRID_SIZE), indexing='ij')
# 勾配方向(下流)のセルを取得(グリッド座標系で1セル分移動)
gradient_real = gradient_normalized.real
gradient_imag = gradient_normalized.imag
# 下流方向のセル座標(1セル分の移動)
offset_x = coords_x + gradient_real
offset_y = coords_y + gradient_imag
offset_x = np.clip(offset_x, 0, GRID_SIZE-1)
offset_y = np.clip(offset_y, 0, GRID_SIZE-1)
x_int = np.clip(np.round(offset_x).astype(int), 0, GRID_SIZE-1)
y_int = np.clip(np.round(offset_y).astype(int), 0, GRID_SIZE-1)
# 高さの差分計算
neighbor_height = terrain_safe[y_int, x_int]
height_delta = terrain - neighbor_height
height_delta = np.nan_to_num(height_delta, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
height_delta = np.clip(height_delta, -1e6, 1e6)
# 流速計算
velocity = np.sqrt(GRAVITY * np.maximum(height_delta, 0) / cell_width)
velocity = np.clip(velocity, 0, MAX_VELOCITY)
# 土砂容量計算
height_factor = np.maximum(height_delta, MIN_HEIGHT_DELTA) / cell_width
height_factor = np.clip(height_factor, 0, 100)
velocity_factor = np.clip(velocity, 0, MAX_VELOCITY)
water_factor = np.clip(water, 0, MAX_WATER)
sediment_capacity = height_factor * velocity_factor * water_factor * SEDIMENT_CAPACITY_CONSTANT
sediment_capacity = np.clip(sediment_capacity, 0, 1000)
excess_sediment = sediment - sediment_capacity
# 土砂の堆積と侵食
deposited_sediment = np.where(
excess_sediment > 0,
DEPOSITION_RATE * excess_sediment,
-DISSOLVING_RATE * np.minimum(terrain, -excess_sediment)
)
deposited_sediment = np.clip(deposited_sediment, -0.1, 0.1)
sediment = np.clip(sediment - deposited_sediment, 0, MAX_SEDIMENT)
terrain += deposited_sediment
terrain = np.nan_to_num(terrain, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
terrain = np.clip(terrain, -1e6, 1e6)
# 水と土砂の移動(流速に基づく部分移動)
sediment_safe = np.nan_to_num(sediment, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
sediment_safe = np.clip(sediment_safe, -1e6, 1e6)
water_safe = np.nan_to_num(water, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
water_safe = np.clip(water_safe, -1e6, 1e6)
# 流出量の計算(流速に基づく)
flow_factor = np.minimum(FLOW_RATE * velocity / MAX_VELOCITY, 1.0)
flow_factor[height_delta <= 0] = 0 # 上り勾配では流れない
sediment_outflow = sediment_safe * flow_factor
water_outflow = water_safe * flow_factor
# 流入と流出の計算
sediment_new = sediment_safe - sediment_outflow
water_new = water_safe - water_outflow
# 各セルから下流への流入を計算
for j in range(GRID_SIZE):
for k in range(GRID_SIZE):
if flow_factor[j, k] > 0 and gradient_magnitude[j, k] > 1e-10:
# 下流セルの座標
target_x = x_int[j, k]
target_y = y_int[j, k]
# 境界チェック
if 0 <= target_x < GRID_SIZE and 0 <= target_y < GRID_SIZE:
if target_x != k or target_y != j: # 自分自身への流入は除外
sediment_new[target_y, target_x] += sediment_outflow[j, k]
water_new[target_y, target_x] += water_outflow[j, k]
sediment = np.clip(sediment_new, 0, MAX_SEDIMENT)
water = np.clip(water_new, 0, MAX_WATER)
# 蒸発
water *= (1 - EVAPORATION_RATE)
water = np.clip(water, 0, MAX_WATER)
# 数値安定性の確保
terrain = np.nan_to_num(terrain, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
terrain = np.clip(terrain, -1e6, 1e6)
water = np.nan_to_num(water, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
water = np.clip(water, -1e6, 1e6)
sediment = np.nan_to_num(sediment, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
sediment = np.clip(sediment, -1e6, 1e6)
velocity = np.nan_to_num(velocity, nan=0.0, posinf=0.0, neginf=0.0)
velocity = np.clip(velocity, -1e6, 1e6)
if (i + 1) % 10 == 0:
print(f'ステップ {i+1}/{ITERATIONS} 完了')
# 結果出力
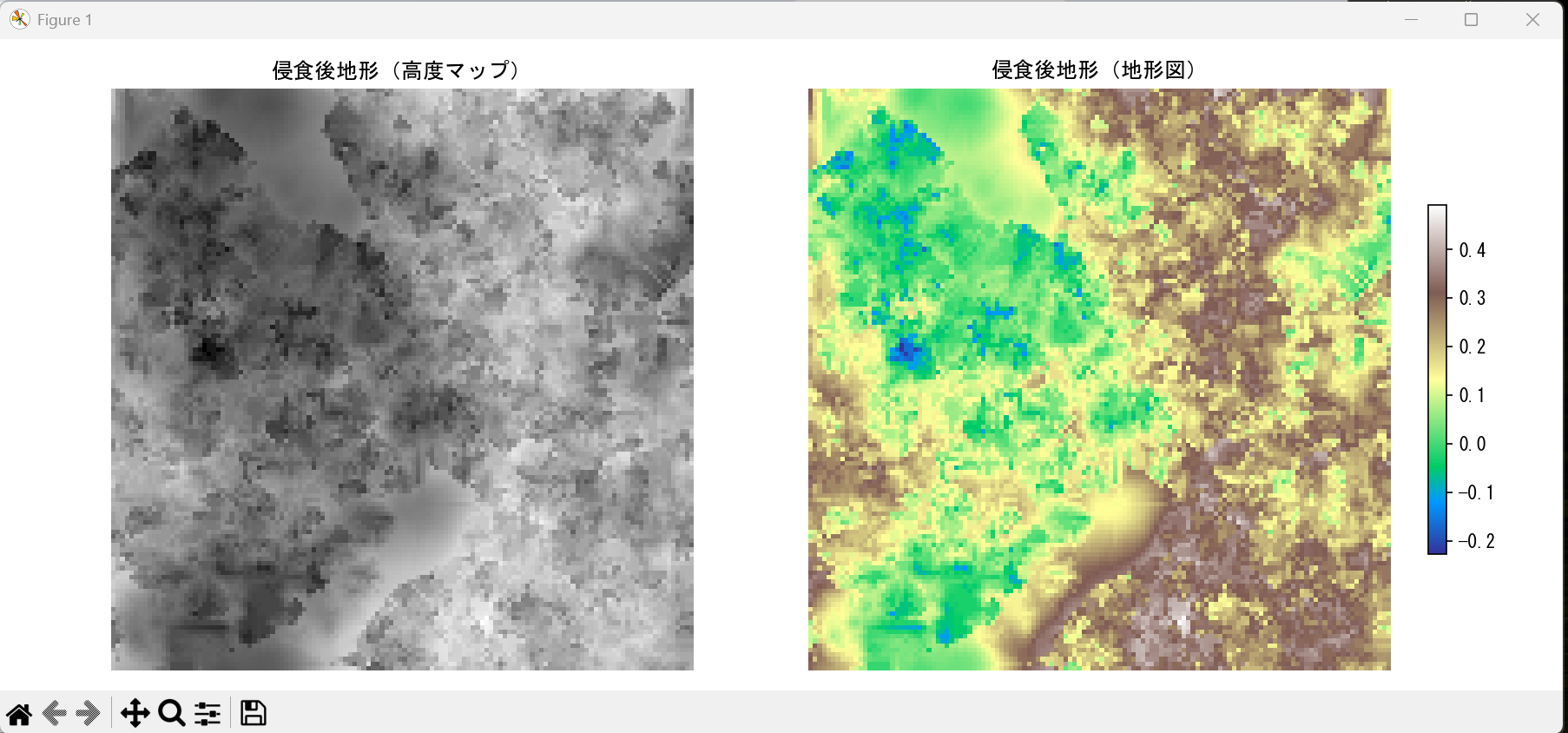
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
if use_english_titles:
title1 = 'Eroded Terrain (Height Map)'
title2 = 'Eroded Terrain (Topographic Map)'
else:
title1 = '侵食後地形(高度マップ)'
title2 = '侵食後地形(地形図)'
axes[0].imshow(terrain, cmap='gray', origin='lower')
axes[0].set_title(title1)
axes[0].axis('off')
im = axes[1].imshow(terrain, cmap='terrain', origin='lower')
axes[1].set_title(title2)
axes[1].axis('off')
plt.colorbar(im, ax=axes[1], shrink=0.6)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
np.save('eroded_terrain.npy', terrain)
print("結果を 'eroded_terrain.npy' に保存しました")
print(f"最終地形サイズ: {terrain.shape[0]}x{terrain.shape[1]} ピクセル")
print(f"高度範囲: {terrain.min():.3f} - {terrain.max():.3f}")
print("シミュレーション完了")
出力データと実行
データ形式
- NumPy配列:最終地形の高度データ(128×128の2次元配列、0.0〜1.0の正規化値)
- 可視化:グレースケール画像、カラー地形図
- 保存ファイル:'eroded_terrain.npy'(NumPyバイナリ形式)
実行方法
python terrain_erosion_simple.py生成される地形特徴と品質評価
定量的評価指標として河川密度(単位面積あたりの河川長)、分岐比(河川分岐パターンを表す数値)、高度分布の標準偏差(高度のばらつき)等により品質を測定できる。
主要な地形特徴
- 侵食パターン:初期のランダムな山地が水流により侵食され、自然な尾根と谷を形成
- 河川の切り込み:水流が地形を削り込んで河川パターンを形成し、上流から下流への連続的な流路を生成
- 滑らかな谷:土砂堆積(侵食土砂の低地蓄積)による谷底の平坦化とU字谷のような自然な谷形状