Blender に3Dアセット(obj,mtl)の配置(ソースコードと実行結果)
【概要】Blenderに3Dアセット(OBJ/MTLファイル)を自動配置するPythonプログラムについて解説する。ランダム配置では衝突回避アルゴリズムを用いて複数オブジェクトを配置し、Blenderをバックグラウンドで実行して結果を保存する。
プログラム利用ガイド
1. このプログラムの利用シーン
Blenderのシーンに複数の3Dオブジェクトを配置するためのツールである。手作業で一つずつ配置する代わりに、ランダム配置またはJSON指定による一括配置を行うことができる。森林、都市景観、群衆など、同一オブジェクトを多数配置するシーン制作に適している。
2. 主な機能
- ランダム配置: 指定範囲内でオブジェクト同士が重ならないよう自動配置する。
- カスタム配置: JSONファイルで位置と回転を指定し、任意の配置パターンを実現する。
- 配置プレビュー: 実行前にOpenCVウィンドウで配置計画を確認できる。
- 複数オブジェクト形式: OBJ/MTLファイルまたはプリミティブ形状(立方体、球、円柱、六角柱)を選択できる。
- 既存ファイルへの追加: 既存のBlenderファイルを開き、オブジェクトを追加して別名保存する。
3. 基本的な使い方
- 起動とBlender選択:
プログラムを実行すると、検出されたBlenderのインストール一覧が表示される。使用するBlenderの番号を入力する。
- Blenderファイル選択:
オブジェクトを配置する既存のBlenderファイルを選択する。
- オブジェクト選択:
1(OBJ/MTLファイル)または2(プリミティブ形状)を選択する。OBJ/MTLファイルの場合はファイルダイアログで選択する。
- 配置方法選択:
1(ランダム配置)または2(カスタム配置)を選択する。ランダム配置では範囲、最小距離、配置数を設定できる。
- プレビュー確認:
配置プレビューウィンドウが表示される。任意のキーを押して続行するか、nを入力して再生成する。
- 保存:
保存先のBlenderファイル名を指定する。元のファイルとは別名で保存することを推奨する。
4. 便利な機能
- 配置の再生成: ランダム配置のプレビュー後、nを入力すると新しい配置パターンを生成できる。
- JSONによる配置指定: 以下の形式でJSONファイルを作成し、任意の配置を指定できる。
[ {"x": 0, "y": 0, "z": 0, "rotation": 0}, {"x": 5, "y": 5, "z": 0, "rotation": 1.57} ] - MTLファイル自動検出: OBJファイルと同名のMTLファイルが存在する場合、自動的に検出して使用を提案する。
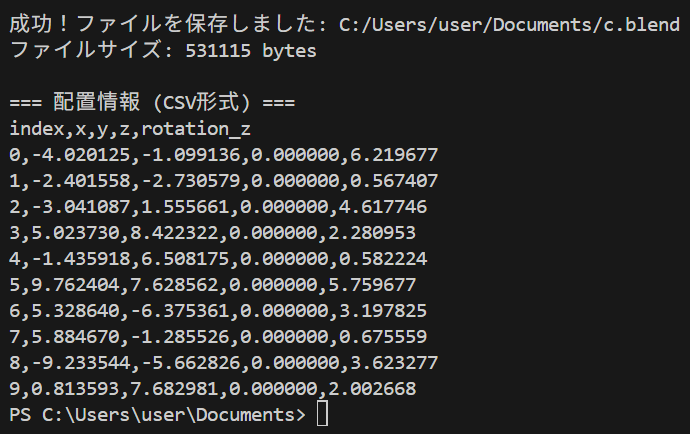
- CSV形式での配置情報出力: 処理完了後、配置座標と回転角がCSV形式でコンソールに出力される。
Python開発環境,ライブラリ類
ここでは、最低限の事前準備について説明する。機械学習や深層学習を行う場合は、NVIDIA CUDA、Visual Studio、Cursorなどを追加でインストールすると便利である。これらについては別ページ https://www.kkaneko.jp/cc/dev/aiassist.htmlで詳しく解説しているので、必要に応じて参照してください。
Python 3.12 のインストール
インストール済みの場合は実行不要。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要である。
REM Python をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements
REM Python のパス設定
set "PYTHON_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312"
set "PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312\Scripts"
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_PATH%" /M >nul
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" /M >nul【関連する外部ページ】
Python の公式ページ: https://www.python.org/
AI エディタ Windsurf のインストール
Pythonプログラムの編集・実行には、AI エディタの利用を推奨する。ここでは,Windsurfのインストールを説明する。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行して、Windsurfをシステム全体にインストールする。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
winget install --scope machine --id Codeium.Windsurf -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements【関連する外部ページ】
Windsurf の公式ページ: https://windsurf.com/
その他の前準備
Blenderをインストールしておく.
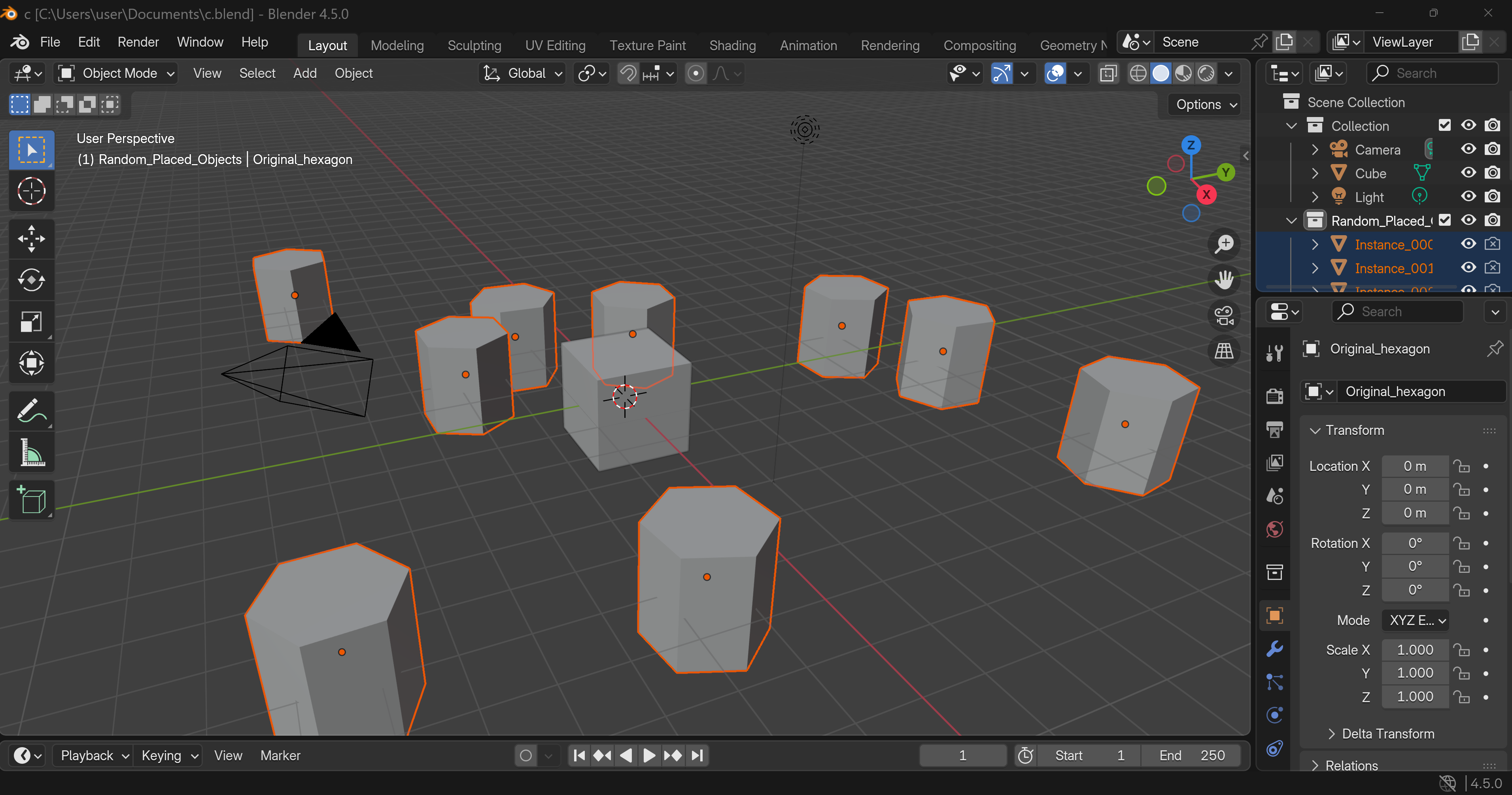
Blender への3Dアセット(obj,mtl)の配置プログラム
概要
このプログラムは、Blenderに3Dアセット(OBJ/MTLファイル)を自動配置する。ランダム配置ではサンプリングベースの衝突回避アルゴリズムにより、オブジェクト間の最小距離を保証しながら配置位置を決定する。Blenderをバックグラウンドで実行し、配置結果をBlenderファイルとして保存する。
主要技術
サンプリングベースの配置探索
LaValleが提唱したサンプリングベースの動作計画手法[1]に基づき、ランダムな候補位置を生成し、既存オブジェクトとの距離判定により有効な配置を探索する。各オブジェクトについて最大100回の試行を行い、設定された最小距離以上を保証する位置を決定する。
Blender Python API
Blender公式のPython API(bpy)[2]を使用し、OBJファイルのインポート、コレクション管理、インスタンス化、ファイル保存を実行する。バックグラウンドモードでBlenderを起動し、GUIなしで処理を完結する。
技術的特徴
- 2D平面での衝突判定
Z座標を0に固定し、XY平面上でユークリッド距離を計算することで衝突判定を行う。NumPyのlinalg.normを使用して距離計算を実装している。
- インスタンス化によるメモリ共有
オリジナルオブジェクトのメッシュデータを複製せず参照することで、多数のオブジェクト配置時のメモリ使用量を抑制する。
- 座標系変換
OBJファイル(Y-up座標系)からBlender(Z-up座標系)への変換を、インポート時のaxis_forwardおよびaxis_upパラメータで処理する。
- 配置プレビュー
OpenCVを使用して配置計画を2D画像として可視化し、実行前に確認できる。Blenderと同一の座標系で表示し、Z座標に応じた色分けと回転方向の矢印表示を行う。
実装の特色
- Windowsレジストリおよび標準インストールパスからBlender実行ファイルを自動検出
- tkinterによるGUIファイル選択とコマンドライン入力の両方に対応
- JSON形式によるカスタム配置データの読み込み
- プリミティブ形状(立方体、球、円柱、六角柱)の生成機能
- コレクションによるオブジェクト階層管理とカスタムプロパティによるメタデータ付与
- マテリアル統合とテクスチャパス修正による重複排除
参考文献
[1] LaValle, S. M. (2006). Planning Algorithms. Cambridge University Press. Chapter 5: Sampling-Based Motion Planning, pp. 185-280. https://lavalle.pl/planning/
[2] Blender Foundation. Blender Python API Documentation. https://docs.blender.org/api/current/
ソースコード
# Blender への3Dアセット(obj,mtl)の配置プログラム
# Blender Python API (bpy) の基本構造
# コンテキストとデータ構造
#
# bpy.context: 現在のシーン、選択オブジェクト等のコンテキスト情報
# bpy.data: メッシュ、マテリアル、テクスチャ等の全データブロック
# bpy.ops: オペレーター(インポート、変換等の操作)
# bpy.types: クラス定義(オブジェクト、メッシュ等)
# 座標系
#
# Blenderは右手系Z-up座標系を使用
# OBJファイル(通常Y-up)からの変換が必要な場合あり
# OBJ/MTLインポート
#
# 軸変換の重要性
#
# TripoSR等のAI生成モデルは座標系が異なる場合が多い
# axis_forwardとaxis_upパラメータで適切に設定
# 一般的な設定パターン:
# Y-up to Z-up: axis_forward='-Z', axis_up='Y'
# Z-up維持: axis_forward='Y', axis_up='Z'
# 大量アセット管理のベストプラクティス
# コレクション(Collection)による階層管理
#
# コレクション作成
# collection = bpy.data.collections.new("3D_Assets")
# bpy.context.scene.collection.children.link(collection)
#
# オブジェクトをコレクションに追加
# obj = bpy.context.selected_objects[0]
# collection.objects.link(obj)
# bpy.context.scene.collection.objects.unlink(obj)
# 命名規則とメタデータ
#
# 一貫した命名規則(例:Asset_Category_Number_Variant)
# カスタムプロパティによるメタデータ付与
# obj["asset_type"] = "prop"
# obj["source"] = "tripoSR"
# obj["import_date"] = "2024-01-01"
# パフォーマンス最適化
# インスタンス化(Instancing)
#
# リンク複製によるメモリ効率化
# original = bpy.data.objects['original_object']
# for i in range(100):
# instance = original.copy()
# instance.data = original.data # メッシュデータを共有
# instance.location = (i * 2, 0, 0)
# collection.objects.link(instance)
# マテリアルとテクスチャの最適化
# マテリアルの統合
#
# def consolidate_materials(obj):
# 重複マテリアルの削除
# materials = {}
# for slot in obj.material_slots:
# if slot.material:
# mat_name = slot.material.name.split('.')[0]
# if mat_name not in materials:
# materials[mat_name] = slot.material
# else:
# slot.material = materials[mat_name]
# テクスチャパスの管理
#
# import os
#
# def fix_texture_paths(base_path):
# for image in bpy.data.images:
# if image.source == 'FILE':
# filename = os.path.basename(image.filepath)
# new_path = os.path.join(base_path, filename)
# if os.path.exists(new_path):
# image.filepath = new_path
# ランダム配置with衝突回避
#
# import random
# from mathutils import Vector
#
# def random_placement_with_collision(objects, bounds=(-10, 10), min_distance=2.0):
# placed_positions = []
#
# for obj in objects:
# valid_position = False
# attempts = 0
#
# while not valid_position and attempts < 100:
# pos = Vector((
# random.uniform(bounds[0], bounds[1]),
# random.uniform(bounds[0], bounds[1]),
# 0
# ))
#
# valid_position = True
# for placed_pos in placed_positions:
# if (pos - placed_pos).length < min_distance:
# valid_position = False
# break
#
# attempts += 1
#
# if valid_position:
# obj.location = pos
# placed_positions.append(pos)
import os
import sys
import json
import random
import math
import numpy as np
import cv2
import tempfile
import subprocess
from datetime import datetime
import winreg
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
try:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog, messagebox
except ImportError:
print("tkinterが利用できません。ファイルパスを手動入力してください。")
tk = None
class BlenderObjectPlacer:
def __init__(self):
self.bounds = (-10, 10)
self.min_distance = 2.0
self.num_objects = 10
self.obj_path = None
self.mtl_path = None
self.use_primitive = False
self.primitive_type = 'cube'
self.placements = []
self.blender_path = None
self.placement_mode = 'random' # 'random' or 'custom'
self.input_blend_path = None # 既存のBlenderファイル
def find_blender_windows(self):
"""Windows環境でBlenderのパスを検索"""
possible_paths = []
# レジストリから検索
try:
reg_paths = [
(winreg.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, r"SOFTWARE\Blender Foundation"),
(winreg.HKEY_CURRENT_USER, r"SOFTWARE\Blender Foundation"),
]
for hkey, subkey in reg_paths:
try:
with winreg.OpenKey(hkey, subkey) as key:
for i in range(winreg.QueryInfoKey(key)[0]):
version = winreg.EnumKey(key, i)
with winreg.OpenKey(key, version) as version_key:
install_path = winreg.QueryValue(version_key, "")
blender_exe = os.path.join(install_path, "blender.exe")
if os.path.exists(blender_exe):
possible_paths.append(blender_exe)
except:
pass
except:
pass
# 一般的なインストール場所を確認
common_paths = [
r"C:\Program Files\Blender Foundation",
r"C:\Program Files (x86)\Blender Foundation",
os.path.expanduser(r"~\AppData\Local\Blender Foundation"),
]
for base_path in common_paths:
if os.path.exists(base_path):
for item in os.listdir(base_path):
blender_exe = os.path.join(base_path, item, "blender.exe")
if os.path.exists(blender_exe):
possible_paths.append(blender_exe)
# PATH環境変数を確認
for path in os.environ.get("PATH", "").split(os.pathsep):
blender_exe = os.path.join(path, "blender.exe")
if os.path.exists(blender_exe):
possible_paths.append(blender_exe)
# 重複を削除
return list(set(possible_paths))
def select_blender_path(self):
"""Blenderの実行パスを選択"""
found_paths = self.find_blender_windows()
if found_paths:
print("\n検出されたBlenderのインストール:")
for i, path in enumerate(found_paths):
print(f"{i+1}: {path}")
choice = input(f"\n使用するBlenderを選択 (1-{len(found_paths)}) または手動入力は0: ").strip()
try:
idx = int(choice)
if 1 <= idx <= len(found_paths):
self.blender_path = found_paths[idx-1]
return True
except:
pass
# 手動入力
if tk:
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
self.blender_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
title="blender.exeを選択",
filetypes=[("Executable", "*.exe"), ("All files", "*.*")]
)
root.destroy()
else:
self.blender_path = input("\nblender.exeのフルパスを入力: ").strip()
if self.blender_path and os.path.exists(self.blender_path):
return True
else:
print("エラー: Blenderが見つかりません")
return False
def load_custom_placement(self):
"""カスタム配置JSONファイルを読み込み"""
# サンプルJSON表示
print("\nJSONファイルのサンプル:")
sample = '''[
{"x": 0, "y": 0, "z": 0, "rotation": 0},
{"x": 5, "y": 5, "z": 0, "rotation": 1.57},
{"x": -5, "y": 3, "z": 0, "rotation": 3.14}
]'''
print(sample)
print("\nJSONファイルの指定")
# ファイル選択
if tk:
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
json_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
title="配置JSONファイルを選択",
filetypes=[("JSON files", "*.json"), ("All files", "*.*")]
)
root.destroy()
else:
json_path = input("JSONファイルのパスを入力: ").strip().replace('"', '')
if not json_path or not os.path.exists(json_path):
print("ファイルが見つかりません")
return False
# JSON読み込み
try:
with open(json_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
if not isinstance(data, list):
print("エラー: JSONはリスト形式である必要があります")
return False
# 各エントリを検証
valid_placements = []
for i, entry in enumerate(data):
try:
# 必須フィールドチェック
if not all(key in entry for key in ['x', 'y', 'z', 'rotation']):
print(f"行 {i+1}: {entry}")
print("スキップ")
continue
# 数値チェック
x = float(entry['x'])
y = float(entry['y'])
z = float(entry['z'])
rotation = float(entry['rotation'])
valid_placements.append({
'position': [x, y, z],
'rotation': rotation
})
except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
print(f"行 {i+1}: {entry}")
print("スキップ")
continue
if not valid_placements:
print("有効な配置データがありません")
return False
self.placements = valid_placements
print(f"\n{len(self.placements)}個の配置データを読み込みました")
return True
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"JSONパースエラー: {e}")
return False
except Exception as e:
print(f"ファイル読み込みエラー: {e}")
return False
def get_user_inputs(self):
"""ユーザーからの入力を取得"""
print("\n=== 3Dオブジェクト配置ツール (Windows版) ===")
print("\n[概要説明]")
print("Blenderファイルに3Dオブジェクトを自動配置するツールです")
print("OBJ/MTLファイルまたはプリミティブ形状を複数配置できます")
print("\n[操作方法]")
print("1. Blenderの実行ファイルを選択")
print("2. 既存のBlenderファイルを選択")
print("3. 配置するオブジェクトを選択")
print("4. 配置方法を選択(ランダムまたはJSON指定)")
print("\n[注意事項]")
print("- 元のBlenderファイルは変更されません")
print("- 新しいファイル名で保存されます")
print("- Blender 4.5対応")
# Blenderパス設定
if not self.select_blender_path():
return False
# 既存Blenderファイル選択
print("\n既存のBlenderファイルを選択")
if tk:
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
messagebox.showinfo("ファイル選択", "オブジェクトを配置する既存のBlenderファイルを選択してください")
self.input_blend_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
title="既存のBlenderファイルを選択(配置を追加するファイル)",
filetypes=[("Blend files", "*.blend"), ("All files", "*.*")]
)
root.destroy()
else:
self.input_blend_path = input("\n既存のBlenderファイルのパスを入力: ").strip().replace('"', '')
if not self.input_blend_path or not os.path.exists(self.input_blend_path):
print("エラー: Blenderファイルが見つかりません")
return False
# オブジェクトタイプ選択
choice = input("\n1: OBJ/MTLファイルを使用\n2: プリミティブ形状を使用\n選択してください (1 or 2) [1]: ").strip()
if choice == '2':
self.use_primitive = True
print("\nプリミティブ形状:")
print("1: 立方体 (Cube)")
print("2: 球 (Sphere)")
print("3: 円柱 (Cylinder)")
print("4: 六角柱 (Hexagonal Prism)")
prim_choice = input("選択してください [1]: ").strip()
prim_map = {'1': 'cube', '2': 'sphere', '3': 'cylinder', '4': 'hexagon'}
self.primitive_type = prim_map.get(prim_choice, 'cube')
else:
# ファイル選択
if tk:
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
print("\nOBJファイルを選択してください...")
self.obj_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
title="OBJファイルを選択",
filetypes=[("OBJ files", "*.obj"), ("All files", "*.*")]
)
if self.obj_path:
# MTLファイルを自動検索
base_name = os.path.splitext(self.obj_path)[0]
auto_mtl = base_name + ".mtl"
if os.path.exists(auto_mtl):
use_auto = input(f"\nMTLファイルを検出: {os.path.basename(auto_mtl)}\nこれを使用しますか? (Y/n): ").strip().lower()
if use_auto != 'n':
self.mtl_path = auto_mtl
if not self.mtl_path:
print("\nMTLファイルを選択してください...")
self.mtl_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
title="MTLファイルを選択",
initialdir=os.path.dirname(self.obj_path),
filetypes=[("MTL files", "*.mtl"), ("All files", "*.*")]
)
root.destroy()
else:
self.obj_path = input("\nOBJファイルのパスを入力: ").strip().replace('"', '')
self.mtl_path = input("MTLファイルのパスを入力: ").strip().replace('"', '')
# 配置方法選択
print("\n配置方法を選択:")
print("1: ランダム配置")
print("2: カスタム配置(JSONファイル)")
placement_choice = input("選択してください (1 or 2) [1]: ").strip()
if placement_choice == '2':
self.placement_mode = 'custom'
if not self.load_custom_placement():
return False
else:
self.placement_mode = 'random'
# ランダム配置のパラメータ
print(f"\n現在の設定:")
print(f"配置範囲: {self.bounds[0]} ~ {self.bounds[1]}")
print(f"最小距離: {self.min_distance}")
print(f"配置数: {self.num_objects}")
if input("\n設定を変更しますか? (y/N): ").strip().lower() == 'y':
try:
range_input = input(f"配置範囲 (min max) [{self.bounds[0]} {self.bounds[1]}]: ").strip()
if range_input:
min_val, max_val = map(float, range_input.split())
self.bounds = (min_val, max_val)
dist_input = input(f"最小距離 [{self.min_distance}]: ").strip()
if dist_input:
self.min_distance = float(dist_input)
num_input = input(f"配置数 [{self.num_objects}]: ").strip()
if num_input:
self.num_objects = int(num_input)
except ValueError:
print("無効な入力です。デフォルト値を使用します。")
return True
def generate_placements(self):
"""ランダム配置を生成"""
self.placements = []
placed_positions = []
for i in range(self.num_objects):
valid_position = False
attempts = 0
while not valid_position and attempts < 100:
x = random.uniform(self.bounds[0], self.bounds[1])
y = random.uniform(self.bounds[0], self.bounds[1])
z = 0
pos = np.array([x, y, z])
valid_position = True
for placed_pos in placed_positions:
# 2D平面での衝突判定(Z座標は0で固定のため)
if np.linalg.norm(pos[:2] - placed_pos[:2]) < self.min_distance:
valid_position = False
break
attempts += 1
if valid_position:
rotation = random.uniform(0, 2 * math.pi)
self.placements.append({
'position': pos.tolist(),
'rotation': rotation
})
placed_positions.append(pos)
def preview_placement(self):
"""OpenCVで配置をプレビュー(Blenderと同じ座標系)"""
if not self.placements:
print("配置データがありません")
return False
# 配置範囲を計算
positions = [p['position'] for p in self.placements]
x_coords = [p[0] for p in positions]
y_coords = [p[1] for p in positions]
if self.placement_mode == 'custom':
# カスタム配置の場合は範囲を自動計算
margin = 5
min_x, max_x = min(x_coords) - margin, max(x_coords) + margin
min_y, max_y = min(y_coords) - margin, max(y_coords) + margin
# 正方形にするため、大きい方の範囲を使用
x_range = max_x - min_x
y_range = max_y - min_y
max_range = max(x_range, y_range)
center_x = (min_x + max_x) / 2
center_y = (min_y + max_y) / 2
bounds_min = min(center_x - max_range/2, center_y - max_range/2)
bounds_max = max(center_x + max_range/2, center_y + max_range/2)
bounds = (bounds_min, bounds_max)
else:
bounds = self.bounds
img_size = 800
scale = img_size / (bounds[1] - bounds[0])
img = np.ones((img_size, img_size, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 255
# グリッド描画
grid_step = max(int(scale), 1) # ゼロ除算防止
for i in range(0, img_size, grid_step):
cv2.line(img, (i, 0), (i, img_size), (200, 200, 200), 1)
cv2.line(img, (0, i), (img_size, i), (200, 200, 200), 1)
# 原点線(Blenderと同じ座標系: X軸右、Y軸上)
origin_x = int((0 - bounds[0]) * scale)
origin_y = int(img_size - (0 - bounds[0]) * scale)
cv2.line(img, (origin_x, 0), (origin_x, img_size), (100, 100, 100), 2)
cv2.line(img, (0, origin_y), (img_size, origin_y), (100, 100, 100), 2)
# オブジェクト描画
for i, placement in enumerate(self.placements):
pos = placement['position']
rotation = placement['rotation']
# Blenderと同じ座標系での表示(Y軸上向きが正)
px = int((pos[0] - bounds[0]) * scale)
py = int(img_size - (pos[1] - bounds[0]) * scale)
# Z座標に応じて色を変える
if pos[2] > 0:
color = (255, 0, 0) # 青(浮いている)
else:
color = (0, 0, 255) # 赤(地面)
radius = int(self.min_distance * scale / 2) if self.placement_mode == 'random' else 20
radius = max(radius, 5) # 最小半径を保証
cv2.circle(img, (px, py), radius, color, -1)
cv2.circle(img, (px, py), radius, (0, 0, 0), 2)
# 方向を矢印で表現(Blenderと同じ向き)
arrow_length = radius
arrow_end_x = px + int(arrow_length * math.cos(rotation))
arrow_end_y = py - int(arrow_length * math.sin(rotation))
cv2.arrowedLine(img, (px, py), (arrow_end_x, arrow_end_y), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# インデックス表示(日本語フォント対応)
FONT_PATH = 'C:/Windows/Fonts/meiryo.ttc'
FONT_SIZE = 12
try:
font = ImageFont.truetype(FONT_PATH, FONT_SIZE)
img_pil = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img_pil)
draw.text((px-10, py-5), str(i), font=font, fill=(255, 255, 255))
img = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(img_pil), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
except:
# フォールバック: OpenCVのデフォルトフォント
cv2.putText(img, str(i), (px-10, py+5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255, 255, 255), 1)
# 情報テキスト表示(日本語対応)
info_text = [
f"配置モード: {self.placement_mode.upper()}",
f"オブジェクト数: {len(self.placements)}",
f"範囲: {bounds[0]:.1f} ~ {bounds[1]:.1f}",
"任意のキーで続行..."
]
FONT_PATH = 'C:/Windows/Fonts/meiryo.ttc'
FONT_SIZE = 16
try:
font = ImageFont.truetype(FONT_PATH, FONT_SIZE)
img_pil = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img_pil)
y_offset = 20
for text in info_text:
draw.text((10, y_offset), text, font=font, fill=(0, 0, 0))
y_offset += 25
img = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(img_pil), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
except:
# フォールバック
y_offset = 20
for text in info_text:
cv2.putText(img, text, (10, y_offset), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 0), 1)
y_offset += 25
cv2.imshow("Placement Preview", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
return input("\nこの配置で続行しますか? (Y/n): ").strip().lower() != 'n'
def create_blender_script(self, json_path, input_blend_path, output_path):
"""Blender内で実行するスクリプトを作成(Blender 4.5対応)"""
# Windowsパスの処理
output_path = os.path.normpath(output_path)
input_blend_path = os.path.normpath(input_blend_path)
json_path = os.path.normpath(json_path)
script = f'''
import bpy
import json
import os
from mathutils import Vector, Euler
from datetime import datetime
# JSONファイルから設定を読み込み
with open(r"{json_path}", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
config = json.load(f)
placements = config["placements"]
use_primitive = config["use_primitive"]
primitive_type = config["primitive_type"]
obj_path = config.get("obj_path", "")
mtl_path = config.get("mtl_path", "")
# 既存のBlenderファイルを開く
bpy.ops.wm.open_mainfile(filepath=r"{input_blend_path}")
def consolidate_materials(obj):
"""重複マテリアルの削除"""
materials = {{}}
for slot in obj.material_slots:
if slot.material:
mat_name = slot.material.name.split('.')[0]
if mat_name not in materials:
materials[mat_name] = slot.material
else:
slot.material = materials[mat_name]
def fix_texture_paths(base_path):
"""テクスチャパスの管理"""
for image in bpy.data.images:
if image.source == 'FILE':
filename = os.path.basename(image.filepath)
new_path = os.path.join(base_path, filename)
if os.path.exists(new_path):
image.filepath = new_path
image.reload()
print(f"テクスチャパス修正: {{filename}}")
def create_primitive(name, prim_type='cube'):
"""プリミティブ形状を作成"""
if prim_type == 'cube':
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cube_add(size=2)
elif prim_type == 'sphere':
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_uv_sphere_add(radius=1)
elif prim_type == 'cylinder':
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cylinder_add(radius=1, depth=2)
elif prim_type == 'hexagon':
bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_cylinder_add(vertices=6, radius=1, depth=2)
obj = bpy.context.active_object
obj.name = name
return obj
def import_obj_file():
"""OBJファイルをインポート(Blender 4.5対応)"""
before_import = set(bpy.data.objects)
# Blender 4.0以降の新しいAPI
bpy.ops.wm.obj_import(
filepath=obj_path,
forward_axis='NEGATIVE_Z',
up_axis='Y'
)
imported_objects = list(set(bpy.data.objects) - before_import)
# テクスチャパスの修正
if obj_path:
texture_base_path = os.path.dirname(obj_path)
fix_texture_paths(texture_base_path)
# マテリアルの統合
for obj in imported_objects:
if obj.type == 'MESH':
consolidate_materials(obj)
return imported_objects[0] if imported_objects else None
# コレクション作成または取得
collection_name = "Random_Placed_Objects"
if collection_name in bpy.data.collections:
collection = bpy.data.collections[collection_name]
else:
collection = bpy.data.collections.new(collection_name)
bpy.context.scene.collection.children.link(collection)
# レイヤーコレクションをアクティブに
layer_collection = bpy.context.view_layer.layer_collection.children[collection_name]
bpy.context.view_layer.active_layer_collection = layer_collection
# オリジナルオブジェクトを取得/作成
if use_primitive:
original = create_primitive("Original_" + primitive_type, primitive_type)
else:
original = import_obj_file()
if not original:
raise Exception("Failed to import object")
# オリジナルをコレクションに追加(デフォルトコレクションから移動)
if original.name not in collection.objects:
if original.name in bpy.context.scene.collection.objects:
bpy.context.scene.collection.objects.unlink(original)
collection.objects.link(original)
# オリジナルを非表示
original.hide_set(True)
original.hide_render = True
# 配置実行
for i, placement in enumerate(placements):
pos = placement['position']
rotation = placement['rotation']
# インスタンス作成
instance = original.copy()
instance.data = original.data # メッシュデータを共有
instance.name = f"Instance_{{i:03d}}"
# 位置と回転設定
instance.location = Vector((pos[0], pos[1], pos[2]))
instance.rotation_euler = Euler((0, 0, rotation), 'XYZ')
# コレクションに追加
collection.objects.link(instance)
# メタデータ追加
instance["placement_index"] = i
instance["source"] = "tripoSR" if not use_primitive else "primitive"
instance["import_date"] = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
# マテリアル統計情報
material_count = len([m for m in bpy.data.materials if m.users > 0])
texture_count = len([i for i in bpy.data.images if i.users > 0])
print(f"マテリアル数: {{material_count}}")
print(f"テクスチャ数: {{texture_count}}")
print(f"配置オブジェクト数: {{len(placements)}}")
# ファイル保存
bpy.ops.wm.save_as_mainfile(filepath=r"{output_path}")
'''
return script
def execute_blender(self):
"""Blenderをバックグラウンドで実行"""
# 一時ファイル作成
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode='w', suffix='.json', delete=False, encoding='utf-8') as f:
# パスをWindowsフォーマットに変換
config = {
"placements": self.placements,
"use_primitive": self.use_primitive,
"primitive_type": self.primitive_type,
"obj_path": os.path.normpath(self.obj_path) if self.obj_path else "",
"mtl_path": os.path.normpath(self.mtl_path) if self.mtl_path else ""
}
json.dump(config, f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
json_path = f.name
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode='w', suffix='.py', delete=False, encoding='utf-8') as f:
# 出力ファイルパス
if tk:
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
messagebox.showinfo("保存先選択",
"配置後のBlenderファイルの保存先を指定してください\n" +
"(元のファイルとは別名で保存することを推奨します)")
default_name = "配置後_" + os.path.basename(self.input_blend_path)
output_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(
title="保存するBlenderファイル名(配置後のファイル)",
defaultextension=".blend",
initialfile=default_name,
filetypes=[("Blend files", "*.blend"), ("All files", "*.*")]
)
root.destroy()
# .lnkファイルの場合の処理
if output_path and output_path.endswith('.lnk'):
output_path = output_path[:-4] # .lnkを削除
else:
print("\n保存するBlenderファイルのパス")
print(f"推奨: 配置後_{os.path.basename(self.input_blend_path)}")
output_path = input("パスを入力 (.blend): ").strip().replace('"', '')
if not output_path:
print("キャンセルされました")
return
if not output_path.endswith('.blend'):
output_path += '.blend'
# デバッグ情報
print(f"\n保存先パス: {output_path}")
print(f"保存先ディレクトリ: {os.path.dirname(output_path)}")
# スクリプト作成
script_content = self.create_blender_script(json_path, self.input_blend_path, output_path)
f.write(script_content)
script_path = f.name
try:
# Blender実行
cmd = [
self.blender_path,
"--background",
"--python", script_path
]
print(f"\nBlenderを実行中...")
print(f"コマンド: {' '.join(cmd)}")
# エンコーディングを指定して実行
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True, errors='replace')
# 結果確認
if result.returncode == 0:
# ファイルの存在確認
if os.path.exists(output_path):
print(f"\n成功!ファイルを保存しました: {output_path}")
print(f"ファイルサイズ: {os.path.getsize(output_path)} bytes")
# 出力から統計情報を表示
for line in result.stdout.split('\n'):
if 'マテリアル数:' in line or 'テクスチャ数:' in line or '配置オブジェクト数:' in line:
print(line)
else:
print(f"\nエラー: ファイルが作成されませんでした: {output_path}")
else:
print(f"\nエラーが発生しました (return code: {result.returncode})")
print("エラー詳細:")
print(result.stderr)
finally:
# 一時ファイル削除
try:
os.unlink(json_path)
os.unlink(script_path)
except:
pass
def run(self):
"""メイン実行"""
if not self.get_user_inputs():
return
# 配置生成とプレビュー
if self.placement_mode == 'random':
while True:
self.generate_placements()
if self.preview_placement():
break
print("\n配置を再生成します...")
else:
# カスタム配置の場合はプレビューのみ
if not self.preview_placement():
return
# Blender実行
self.execute_blender()
# 配置情報をCSV形式で表示
print("\n=== 配置情報 (CSV形式) ===")
print("index,x,y,z,rotation_z")
for i, placement in enumerate(self.placements):
pos = placement['position']
rotation = placement['rotation']
print(f"{i},{pos[0]:.6f},{pos[1]:.6f},{pos[2]:.6f},{rotation:.6f}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
placer = BlenderObjectPlacer()
placer.run()
実験・研究スキルの基礎:Windows で学ぶ3Dオブジェクト配置実験
1. 実験・研究のスキル構成要素
実験や研究を行うには、以下の5つの構成要素を理解する必要がある。
1.1 実験用データ
このプログラムでは3Dアセットファイル(OBJ/MTLファイル)または プリミティブ形状が実験用データである。配置先となる既存のBlenderファイルも実験環境の一部となる。
1.2 実験計画
何を明らかにするために実験を行うのかを定める。
計画例:
- 配置範囲がオブジェクト密度に与える影響を確認する
- 最小距離パラメータが衝突回避の成功率に与える影響を確認する
- 配置数と配置成功率の関係を調べる
- 異なるプリミティブ形状での配置結果の違いを比較する
- カスタム配置とランダム配置の再現性を比較する
1.3 プログラム
実験を実施するためのツールである。このプログラムはサンプリングベースの衝突回避アルゴリズムとBlender Python API(bpy)を使用している。
- プログラムの機能を理解して活用することが基本である
- 基本となるプログラムを出発点として、将来、様々な機能を自分で追加することができる
1.4 プログラムの機能
このプログラムは3つの主要パラメータで配置を制御する。
入力パラメータ:
- 配置範囲:オブジェクトを配置するXY平面の範囲(デフォルト:-10~10)
- 最小距離:オブジェクト間の最小距離(デフォルト:2.0)
- 配置数:配置するオブジェクトの数(デフォルト:10)
出力情報:
- OpenCVによる配置プレビュー画像(位置、回転方向、Z座標による色分け)
- 配置結果を含むBlenderファイル
- CSV形式の配置座標データ(index, x, y, z, rotation_z)
配置モード:
- ランダム配置:指定範囲内でランダムに位置を決定し、衝突回避を行う
- カスタム配置:JSONファイルで指定した位置と回転に配置する
1.5 検証(結果の確認と考察)
プログラムの実行結果を観察し、パラメータの影響を考察する。
基本認識:
- パラメータを変えると結果が変わる。その変化を観察することが実験である
- 「良い結果」「悪い結果」は目的によって異なる
観察のポイント:
- 指定した配置数に対して実際に配置されたオブジェクト数はいくつか
- オブジェクト間の距離は最小距離以上が保たれているか
- 配置の分布は均一か、偏りがあるか
- プレビュー画像とBlenderでの実際の配置は一致しているか
- パラメータを変えたときの配置パターンの変化はどうか
2. 間違いの原因と対処方法
2.1 プログラムのミス(人為的エラー)
Blenderが見つからない
- 原因:Blenderがインストールされていない、またはパスが正しく設定されていない
- 対処方法:Blenderをインストールし、手動でblender.exeのパスを入力する
OBJファイルのインポートに失敗する
- 原因:ファイルパスに日本語や特殊文字が含まれている、またはファイル形式が正しくない
- 対処方法:ファイルを英数字のみのパスに移動して再実行する
プレビューウィンドウが表示されない
- 原因:OpenCVが正しくインストールされていない
- 対処方法:pip install opencv-pythonでOpenCVをインストールする
2.2 期待と異なる結果が出る場合
指定した数のオブジェクトが配置されない
- 原因:配置範囲に対して最小距離が大きすぎる、または配置数が多すぎる
- 対処方法:配置範囲を広げる、最小距離を小さくする、または配置数を減らす
オブジェクトが重なって配置される
- 原因:最小距離がオブジェクトのサイズより小さい
- 対処方法:オブジェクトの実際のサイズを確認し、最小距離を適切に設定する
配置が偏っている
- 原因:ランダム配置の特性として偏りが生じることがある
- 対処方法:配置を再生成する(プレビュー後にnを入力)、またはカスタム配置を使用する
Blenderファイルが保存されない
- 原因:保存先のパスに書き込み権限がない、またはディスク容量が不足している
- 対処方法:別のディレクトリを指定して保存する
3. 実験レポートのサンプル
配置密度と衝突回避成功率の関係
実験目的:
限られた配置範囲内で、衝突回避を維持しながら配置できるオブジェクト数の上限を見つける。
実験計画:
配置範囲を-10~10(20×20の領域)、最小距離を2.0に固定し、配置数を変化させて配置成功率を調べる。
実験方法:
プログラムを実行し、以下の基準で評価する:
- 配置成功数:実際に配置されたオブジェクトの数
- 配置成功率:配置成功数 ÷ 指定配置数 × 100
- 配置の均一性:プレビュー画像での目視確認
実験結果:
| 指定配置数 | 配置成功数 | 配置成功率 | 配置の均一性 | 備考 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| xxxx | x | x% | x | x |
| xxxx | x | x% | x | x |
| xxxx | x | x% | x | x |
| xxxx | x | x% | x | x |
考察:
- (例文)配置数xxxxでは配置成功率が100%であり、すべてのオブジェクトが衝突なく配置された
- (例文)配置数xxxxを超えると配置成功率が低下し始めた。これは配置可能な空間が減少したためと考えられる
- (例文)配置数xxxxでは配置成功率がxxxx%まで低下し、多くのオブジェクトが配置されなかった
- (例文)最大試行回数(100回)の制限により、理論上の最大配置数より少ない数で配置が困難になる傾向が見られた
結論:
(例文)配置範囲20×20、最小距離2.0の条件では、配置数xxxxまでは安定して配置が可能であった。これを超える配置が必要な場合は、配置範囲の拡大または最小距離の縮小が必要である。また、均一な配置を求める場合はカスタム配置の使用が適切である。
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)