EfficientADによる床面異常検出
Python開発環境,ライブラリ類
ここでは、最低限の事前準備について説明する。機械学習や深層学習を行う場合は、NVIDIA CUDA、Visual Studio、Cursorなどを追加でインストールすると便利である。これらについては別ページ https://www.kkaneko.jp/cc/dev/aiassist.htmlで詳しく解説しているので、必要に応じて参照してください。
Python 3.12 のインストール
インストール済みの場合は実行不要。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要である。
REM Python をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements
REM Python のパス設定
set "PYTHON_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312"
set "PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312\Scripts"
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_PATH%" /M >nul
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" /M >nul【関連する外部ページ】
Python の公式ページ: https://www.python.org/
AI エディタ Windsurf のインストール
Pythonプログラムの編集・実行には、AI エディタの利用を推奨する。ここでは,Windsurfのインストールを説明する。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行して、Windsurfをシステム全体にインストールする。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
winget install --scope machine --id Codeium.Windsurf -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements【関連する外部ページ】
Windsurf の公式ページ: https://windsurf.com/
必要なライブラリをシステム領域にインストール
コマンドプロンプトを管理者として実行(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する
pip install -U torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126
pip install opencv-python numpy scipy scikit-image matplotlib pillow
EfficientADによる床面異常検出プログラム
概要
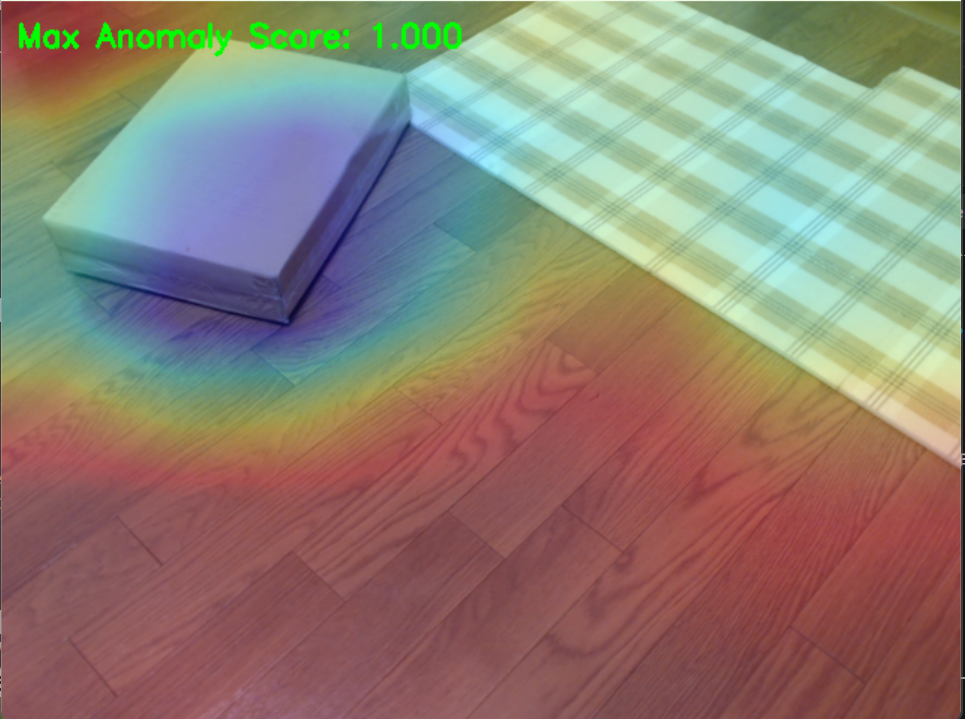
カメラから取得した画像を分析し、正常パターンとの差異を検出することで床面の異常を認識する。 EfficientADを用いた異常検出プログラムは、正常な床面画像のパターンを学習し、新たに入力された画像との差異を検出する能力を持つ。教師-生徒アーキテクチャにより、正常パターンからの逸脱を数値化し、視覚的にヒートマップとして表示する。この手法により、事前に異常パターンを定義することなく、正常データのみから異常を検出できる。
主要技術
- EfficientAD [1]
教師-生徒アーキテクチャを用いた異常検出手法である。軽量な特徴抽出器から抽出された特徴を生徒ネットワークが予測するよう学習し、テスト時に正常画像の特徴予測に失敗することで異常を検出する。さらに論理的異常検出のためにオートエンコーダを組み込んでいる。 - WideResNet [2]
ResNetアーキテクチャの幅を拡張したCNNモデルである。各層のチャンネル数を増やすことで、深さを抑えながら表現力を向上させている。ImageNetで事前学習されたモデルは、特徴抽出器として転移学習に広く利用される。
参考文献
[1] Batzner, K., Heckler, L., & König, R. (2024). EfficientAD: Accurate Visual Anomaly Detection at Millisecond-Level Latencies. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (pp. 128-138). https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/WACV2024/html/Batzner_EfficientAD_Accurate_Visual_Anomaly_Detection_at_Millisecond-Level_Latencies_WACV_2024_paper.html
[2] Zagoruyko, S., & Komodakis, N. (2016). Wide residual networks. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC) (pp. 87.1-87.12). https://bmva-archive.org.uk/bmvc/2016/papers/paper087/index.html
ソースコード
# EfficientADによる異常検出プログラム
# 特徴技術名: EfficientAD
# 出典: Batzner, K., Heckler, L., & König, R. (2024). EfficientAD: Accurate Visual Anomaly Detection at Millisecond-Level Latencies. In WACV (pp. 128-138).
# 特徴機能: PDN(Patch Description Network)と教師-生徒アーキテクチャ、オートエンコーダによる構造的・論理的異常の検出
# 学習済みモデル: 教師モデルはPDNを用いる
# 方式設計:
# - 関連利用技術: PDN(特徴抽出)、教師-生徒モデル(知識蒸留)、オートエンコーダ(論理的異常検出)
# - 入力と出力: 入力: 画像(256x256)、出力: 異常検出結果(構造的+論理的異常の統合スコア)
# - 前処理、後処理: ImageNet統計で正規化、ガウシアンフィルタ、画像ごとのmin-max正規化(判定は上位10%平均値)
# - 追加処理: Hard negative mining、penalty loss
# 調整可能な設定: 閾値、学習率、ガウシアンsigma、上位割合
# 前準備: pip install -U torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126
# pip install opencv-python numpy scipy scikit-image matplotlib pillow
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import cv2
import numpy as np
from scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
import urllib.request
import os
import time
from datetime import datetime
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
# GPU/CPU自動選択
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(f'デバイス: {str(device)}')
# GPU使用時の最適化
if device.type == 'cuda':
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
# ===== 設定値 =====
# 基本設定
MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES = 3
SAMPLE_PREFIX = 'sample_'
RESULT_FILE = 'result.txt'
# モデル設定
IMAGE_SIZE = 256
OUT_CHANNELS = 384
TEACHER_INIT_EPOCHS = 10
STUDENT_EPOCHS = 70
AE_EPOCHS = 70
# 学習設定
LEARNING_RATE = 1e-4
BATCH_SIZE = 8
HARD_RATIO = 0.999
# 後処理・判定
GAUSSIAN_SIGMA = 4
ANOMALY_THRESHOLD = 0.7 # 固定閾値(画像ごとのmin-max正規化後に適用)
TOPK_RATIO = 0.10 # 上位10%平均値で判定
# 日本語フォント設定
FONT_PATH = 'C:/Windows/Fonts/meiryo.ttc'
FONT_SIZE = 20
# サンプル画像URL
SAMPLE_URLS = [
'https://github.com/opencv/opencv/raw/master/samples/data/fruits.jpg',
'https://github.com/opencv/opencv/raw/master/samples/data/messi5.jpg',
'https://github.com/opencv/opencv/raw/master/samples/data/aero3.jpg'
]
# ===== PDN (Patch Description Network) =====
class PDN(nn.Module):
"""Patch Description Network"""
def __init__(self, out_channels=384):
super(PDN, self).__init__()
self.pdn = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 128, kernel_size=4, stride=1, padding=3),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=4, stride=1, padding=3),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, out_channels, kernel_size=4, stride=1, padding=0)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.pdn(x)
# ===== オートエンコーダ(GroupNorm) =====
class Autoencoder(nn.Module):
"""論理的異常検出用の軽量オートエンコーダ"""
def __init__(self, in_channels=384, latent_dim=64):
super(Autoencoder, self).__init__()
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 256, kernel_size=1),
nn.GroupNorm(32, 256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=1),
nn.GroupNorm(16, 128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, latent_dim, kernel_size=1)
)
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(latent_dim, 128, kernel_size=1),
nn.GroupNorm(16, 128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=1),
nn.GroupNorm(32, 256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, in_channels, kernel_size=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
z = self.encoder(x)
x_recon = self.decoder(z)
return x_recon
# ===== 日本語テキスト描画ユーティリティ =====
class TextRenderer:
"""日本語テキスト描画の統一処理"""
def __init__(self, font_path=FONT_PATH, font_size=FONT_SIZE):
self.font_path = font_path
self.font_size = font_size
self.font = None
self.use_japanese = False
try:
self.font = ImageFont.truetype(self.font_path, self.font_size)
self.use_japanese = True
except:
self.use_japanese = False
def draw_text(self, image, text, position, color, font_scale=1.0):
if self.use_japanese and self.font:
img_pil = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img_pil)
rgb_color = color[::-1] if len(color) == 3 else color # BGR→RGB
draw.text(position, text, font=self.font, fill=rgb_color)
return cv2.cvtColor(np.array(img_pil), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
else:
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
thickness = max(1, int(2 * font_scale))
cv2.putText(image, text, position, font, 0.7 * font_scale, color, thickness)
return image
# ===== EfficientADモデル =====
class EfficientAD:
def __init__(self):
self.device = device
self.teacher = PDN(OUT_CHANNELS).to(self.device)
self.student = PDN(OUT_CHANNELS).to(self.device)
self.autoencoder = Autoencoder(OUT_CHANNELS).to(self.device)
self.transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToPILImage(),
transforms.Resize((IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
self.text_renderer = TextRenderer()
self.normal_images = []
self.teacher_outputs = [] # 学習済み教師出力(デバッグ・分析用途で保持)
self.results_log = []
# ---- 補助関数 ----
def _bgr_to_rgb(self, img_bgr: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
return cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
def channel_standardize(self, x: torch.Tensor, eps: float = 1e-6) -> torch.Tensor:
"""各サンプル・各チャネルで空間平均0・分散1に標準化"""
mu = x.mean(dim=(2, 3), keepdim=True)
std = x.std(dim=(2, 3), keepdim=True) + eps
return (x - mu) / std
def prepare_batch_data(self, images):
tensors = []
for img in images:
img_rgb = self._bgr_to_rgb(img)
img_tensor = self.transform(img_rgb)
tensors.append(img_tensor)
return torch.stack(tensors)
def extract_features(self, images, model):
if isinstance(images, list):
batch_tensor = self.prepare_batch_data(images).to(self.device)
elif isinstance(images, np.ndarray):
img_rgb = self._bgr_to_rgb(images)
img_tensor = self.transform(img_rgb).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device)
batch_tensor = img_tensor
else:
batch_tensor = images.to(self.device)
with torch.no_grad():
features = model(batch_tensor)
return features
# ---- 学習 ----
def compute_hard_loss(self, teacher_output, student_output, hard_ratio=HARD_RATIO):
distance = (teacher_output - student_output) ** 2
distance_flat = distance.view(-1)
if distance_flat.numel() < 100:
return torch.mean(distance)
# Hard negative mining: 損失が大きい(難しい)サンプルを選択
hard_threshold = torch.quantile(distance_flat, 1.0 - hard_ratio)
hard_mask = distance >= hard_threshold
return torch.mean(distance[hard_mask]) if hard_mask.sum() > 0 else torch.mean(distance)
def train_teacher(self, images):
if TEACHER_INIT_EPOCHS == 0:
return
print(f"教師モデルを{TEACHER_INIT_EPOCHS}エポック初期学習中...")
image_tensors = self.prepare_batch_data(images)
dataset = TensorDataset(image_tensors)
dataloader = build_dataloader(dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
optimizer = optim.Adam(self.teacher.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE)
self.teacher.train()
for epoch in range(TEACHER_INIT_EPOCHS):
total_loss = 0
batch_count = 0
for batch_images, in dataloader:
batch_images = batch_images.to(self.device)
features = self.teacher(batch_images)
# 特徴量の多様性を促進
loss = -torch.mean(torch.std(features, dim=0))
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
batch_count += 1
avg_loss = total_loss / batch_count
log_epoch('教師モデル', epoch, TEACHER_INIT_EPOCHS, avg_loss, interval=5)
self.teacher.eval()
print("教師モデルの初期学習完了")
def train_student(self, images):
print(f"\n生徒モデルを{STUDENT_EPOCHS}エポック学習中...")
image_tensors = self.prepare_batch_data(images)
self.teacher.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
teacher_outputs = self.extract_features(image_tensors, self.teacher)
dataset = TensorDataset(image_tensors, teacher_outputs.cpu())
dataloader = build_dataloader(dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
optimizer = optim.Adam(self.student.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE)
self.student.train()
for epoch in range(STUDENT_EPOCHS):
total_loss = 0
batch_count = 0
for batch_images, batch_teacher_outputs in dataloader:
batch_images = batch_images.to(self.device)
batch_teacher_outputs = batch_teacher_outputs.to(self.device)
student_out = self.student(batch_images)
loss_hard = self.compute_hard_loss(batch_teacher_outputs, student_out, HARD_RATIO)
if epoch % 10 == 0:
noise = torch.randn_like(batch_images) * 0.1
noisy_input = batch_images + noise
student_out_noise = self.student(noisy_input)
loss_penalty = torch.mean(student_out_noise ** 2) * 0.1
else:
loss_penalty = 0
loss = loss_hard + loss_penalty
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
batch_count += 1
avg_loss = total_loss / batch_count
log_epoch('生徒モデル', epoch, STUDENT_EPOCHS, avg_loss, interval=10)
self.student.eval()
print("生徒モデルの学習完了")
self.teacher_outputs = teacher_outputs # 学習済み教師出力を保持(解析用途)
def train_autoencoder(self, images):
print(f"\nオートエンコーダを{AE_EPOCHS}エポック学習中...")
image_tensors = self.prepare_batch_data(images)
self.teacher.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
features = self.extract_features(image_tensors, self.teacher)
features_norm = self.channel_standardize(features)
dataset = TensorDataset(features_norm.cpu())
dataloader = build_dataloader(dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
optimizer = optim.Adam(self.autoencoder.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE)
self.autoencoder.train()
for epoch in range(AE_EPOCHS):
total_loss = 0
batch_count = 0
for batch_features_norm, in dataloader:
batch_features_norm = batch_features_norm.to(self.device)
recon = self.autoencoder(batch_features_norm)
loss = F.mse_loss(recon, batch_features_norm)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
batch_count += 1
avg_loss = total_loss / batch_count
log_epoch('オートエンコーダ', epoch, AE_EPOCHS, avg_loss, interval=10)
self.autoencoder.eval()
print("オートエンコーダの学習完了")
def train_on_normal(self, normals):
self.normal_images = normals
self.train_teacher(normals)
self.train_student(normals)
self.train_autoencoder(normals)
print("\n全ての学習が完了しました")
# ---- 推論 ----
def detect_anomaly(self, image):
img_rgb = self._bgr_to_rgb(image)
img_tensor = self.transform(img_rgb).unsqueeze(0)
with torch.no_grad():
teacher_feat = self.extract_features(img_tensor, self.teacher)
student_feat = self.extract_features(img_tensor, self.student)
# AEは標準化した教師特徴を再構成
teacher_norm = self.channel_standardize(teacher_feat)
ae_recon = self.autoencoder(teacher_norm)
# 構造的異常(教師-生徒)
structural_diff = torch.abs(teacher_feat - student_feat)
structural_score = torch.mean(structural_diff, dim=1).squeeze().cpu().numpy()
# 論理的異常(標準化後教師 - 再構成)
logical_diff = torch.abs(teacher_norm - ae_recon)
logical_score = torch.mean(logical_diff, dim=1).squeeze().cpu().numpy()
# 統合(構造0.7, 論理0.3)
combined_score = 0.7 * structural_score + 0.3 * logical_score
# リサイズと平滑化
h, w = image.shape[:2]
combined_map = cv2.resize(combined_score, (w, h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
combined_map = gaussian_filter(combined_map, sigma=GAUSSIAN_SIGMA)
# 画像ごとのmin-max正規化
if combined_map.max() > combined_map.min():
combined_map = (combined_map - combined_map.min()) / (combined_map.max() - combined_map.min())
return combined_map, structural_score, logical_score
# ===== ユーティリティ関数 =====
def download_samples(prefix=SAMPLE_PREFIX, urls=None):
images = []
temp_files = []
urls = urls if urls is not None else SAMPLE_URLS
for i, url in enumerate(urls):
filename = f'{prefix}{i}.jpg'
try:
print(f'サンプル画像をダウンロード中: {url}')
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)
temp_files.append(filename)
img = cv2.imread(filename)
if img is not None:
images.append(img)
except Exception as e:
print(f'画像のダウンロードに失敗しました: {url}')
print(f'エラー: {e}')
continue
return images, temp_files
def cleanup_files(files):
for filename in files:
try:
os.remove(filename)
except OSError:
pass
def build_dataloader(dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True):
return DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=shuffle)
def log_epoch(label, epoch, total_epochs, avg_loss, interval):
if (epoch + 1) % interval == 0:
print(f'エポック {epoch+1}/{total_epochs}, 平均損失: {avg_loss:.6f}')
def open_camera():
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0, cv2.CAP_DSHOW)
if not cap.isOpened():
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_BUFFERSIZE, 1)
return cap
def run_camera_loop(mode, model, normal_images=None, min_required=None):
cap = open_camera()
text_renderer = model.text_renderer
try:
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
display_frame = frame.copy()
# テキスト描画
if mode == 'capture':
display_frame = text_renderer.draw_text(
display_frame,
f'正常画像: {len(normal_images)}枚 (最低{MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES}枚必要)',
(10, 10),
(0, 255, 0)
)
display_frame = text_renderer.draw_text(
display_frame,
'スペース: 撮影, Q: 終了',
(10, 40),
(0, 255, 0)
)
else:
display_frame = text_renderer.draw_text(
display_frame,
'スペース: 検出実行, Q: 終了',
(10, 10),
(255, 255, 0)
)
cv2.imshow('Camera', display_frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if key == ord(' '):
if mode == 'capture':
normal_images.append(frame.copy())
print(f'正常画像 {len(normal_images)} 枚目を撮影した')
else:
processed_img, result, current_time = image_processing(frame, model)
cv2.imshow('異常検出結果', processed_img)
print(result)
model.results_log.append(result)
elif key == ord('q'):
if mode == 'capture' and min_required is not None:
if len(normal_images) >= min_required:
break
else:
break
finally:
cap.release()
# ===== メイン処理 =====
def image_processing(image, model):
current_time = time.time()
amap, structural, logical = model.detect_anomaly(image)
# 可視化とテキスト描画
heatmap_rgb = (plt.cm.jet(amap)[:, :, :3] * 255).astype(np.uint8)
heatmap_bgr = cv2.cvtColor(heatmap_rgb, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
overlay = cv2.addWeighted(image, 0.7, heatmap_bgr, 0.3, 0)
flat = amap.reshape(-1)
k = max(1, int(TOPK_RATIO * flat.size))
topk = np.partition(flat, -k)[-k:]
topk_mean = float(np.mean(topk))
is_anomaly = topk_mean > ANOMALY_THRESHOLD
text_renderer = model.text_renderer
if text_renderer.use_japanese:
status_text = '異常検出' if is_anomaly else '正常'
score_line = f'上位{int(TOPK_RATIO*100)}%平均: {topk_mean:.3f} - {status_text}'
thr_line = f'閾値: {ANOMALY_THRESHOLD:.3f}'
detail_prefix_struct = '構造的異常'
detail_prefix_logic = '論理的異常'
else:
status_text = 'ANOMALY' if is_anomaly else 'NORMAL'
score_line = f'Top-{int(TOPK_RATIO*100)}% mean: {topk_mean:.3f} - {status_text}'
thr_line = f'Threshold: {ANOMALY_THRESHOLD:.3f}'
detail_prefix_struct = 'Structural'
detail_prefix_logic = 'Logical'
status_color = (0, 0, 255) if is_anomaly else (0, 255, 0)
overlay = text_renderer.draw_text(overlay, score_line, (10, 10), status_color)
overlay = text_renderer.draw_text(overlay, thr_line, (10, 40), (255, 255, 255))
if structural is not None and logical is not None:
struct_max = float(np.max(structural))
logic_max = float(np.max(logical))
detail_text = f'{detail_prefix_struct}: {struct_max:.3f}, {detail_prefix_logic}: {logic_max:.3f}'
overlay = text_renderer.draw_text(overlay, detail_text, (10, 70), (255, 255, 255))
# 結果の記録
if current_time is not None:
timestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(current_time).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f")[:-3]
else:
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f")[:-3]
if text_renderer.use_japanese:
result_text = f'{timestamp} - 上位{int(TOPK_RATIO*100)}%平均: {topk_mean:.3f}, 判定: {"異常" if is_anomaly else "正常"}'
else:
result_text = f'{timestamp} - Top-{int(TOPK_RATIO*100)}% mean: {topk_mean:.3f}, Result: {"ANOMALY" if is_anomaly else "NORMAL"}'
if structural is not None and logical is not None:
result_text += f' (Struct: {float(np.max(structural)):.3f}, Logic: {float(np.max(logical)):.3f})'
return overlay, result_text, current_time
def process_and_display_images(image_sources, source_type, model):
display_index = 1
results_log_ref = model.results_log
for source in image_sources:
img = cv2.imread(source) if source_type == 'file' else source
if img is None:
continue
cv2.imshow(f'Image_{display_index}', img)
processed_img, result, current_time = image_processing(img, model)
cv2.imshow(f'異常検出結果_{display_index}', processed_img)
print(result)
results_log_ref.append(result)
display_index += 1
return results_log_ref
def write_results(results_log, device, result_file=RESULT_FILE):
with open(result_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write('=== 結果 ===\n')
f.write(f'使用デバイス: {str(device).upper()}\n')
if device.type == 'cuda':
f.write(f'GPU: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)}\n')
f.write('\n')
f.write('\n'.join(results_log))
print(f'\n処理結果を{result_file}に保存しました')
def print_stats(results_log):
anomaly_count = sum(1 for r in results_log if ('異常' in r and '判定' in r) or ('ANOMALY' in r and 'Result' in r))
normal_count = len(results_log) - anomaly_count
print(f'\n【検出統計】')
print(f'総検出数: {len(results_log)}')
print(f'異常検出: {anomaly_count}')
print(f'正常判定: {normal_count}')
if len(results_log) > 0:
print(f'異常率: {anomaly_count/len(results_log)*100:.1f}%')
def main():
print('=== EfficientAD(論文準拠版)による異常検出プログラム ===')
print('\n【プログラム概要】')
print('PDN(Patch Description Network)と教師-生徒アーキテクチャ、')
print('オートエンコーダを組み合わせた異常検出を行う。')
print('\n【操作方法】')
print('1. 正常画像を3枚以上入力して学習')
print('2. テスト画像で異常検出を実行')
print('3. カメラモード: スペースキーで撮影/検出、Qキーで終了')
print('\n【注意事項】')
print('- 正常画像は同じカテゴリの画像を使用する')
print('- 学習には時間がかかる場合がある')
print(f'- 異常判定閾値: {ANOMALY_THRESHOLD:.3f}')
print(f'- バッチサイズ: {BATCH_SIZE}')
model = EfficientAD()
print('\n=== 正常画像の学習フェーズ ===')
print(f'正常パターンを学習するため、{MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES}枚以上の正常画像が必要である。')
print('\n0: 画像ファイル')
print('1: カメラ')
print('2: サンプル画像')
choice = input('\n正常画像の入力方法を選択: ')
normal_images = []
if choice == '0':
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
print(f'正常画像ファイルを{MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES}枚以上選択する')
paths = filedialog.askopenfilenames()
if not paths or len(paths) < MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES:
print(f'{MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES}枚以上の画像が必要である')
return
for path in paths:
img = cv2.imread(path)
if img is not None:
normal_images.append(img)
elif choice == '1':
print(f'\nカメラから正常画像を{MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES}枚以上撮影する')
print(f'スペースキー: 撮影、Qキー: 撮影終了({MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES}枚以上撮影後)')
run_camera_loop(mode='capture', model=model, normal_images=normal_images, min_required=MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES)
elif choice == '2':
normal_images, temp_files = download_samples()
cleanup_files(temp_files)
if len(normal_images) < MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES:
print(f'正常画像が{MIN_NORMAL_IMAGES}枚未満のため終了する')
return
model.train_on_normal(normal_images)
print('\n=== 異常検出フェーズ ===')
print('構造的異常と論理的異常の両方を検出する。')
print('\n0: 画像ファイル')
print('1: カメラ')
print('2: サンプル画像')
choice = input('\nテスト画像の入力方法を選択: ')
try:
if choice == '0':
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
if not (paths := filedialog.askopenfilenames()):
return
process_and_display_images(paths, 'file', model)
cv2.waitKey(0)
elif choice == '1':
print('\nカメラモード: スペースキーで検出実行、Qキーで終了')
run_camera_loop(mode='detect', model=model)
else:
urls = [
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/opencv/opencv/master/samples/data/fruits.jpg",
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/opencv/opencv/master/samples/data/messi5.jpg",
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/opencv/opencv/master/samples/data/aero3.jpg",
"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/3a/Cat03.jpg"
]
images, downloaded_files = download_samples(prefix=SAMPLE_PREFIX, urls=urls)
process_and_display_images(downloaded_files, 'file', model)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cleanup_files(downloaded_files)
finally:
print('\n=== プログラム終了 ===')
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if model.results_log:
write_results(model.results_log, device, RESULT_FILE)
print_stats(model.results_log)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)