SHAP説明可能性
【概要】SHAPはゲーム理論のシャプレイ値を用いて機械学習モデルの各特徴量の貢献度を定量化する手法である。医療診断支援や金融審査などで活用される。
SHAP説明可能性
目次
概要
主要技術: SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations)
論文: "A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions" (NIPS 2017)
新規性・特徴: ゲーム理論のシャプレイ値を用いて機械学習モデルの予測に対する各特徴量の貢献度を定量化する手法である。
アプリ例: 医療診断支援、金融審査、画像分類における判断根拠の説明
体験価値: 機械学習モデルの予測において、どの特徴量がどの程度影響するかを数値で確認できる。
Python開発環境,ライブラリ類
ここでは、最低限の事前準備について説明する。機械学習や深層学習を行う場合は、NVIDIA CUDA、Visual Studio、Cursorなどを追加でインストールすると便利である。これらについては別ページ https://www.kkaneko.jp/cc/dev/aiassist.htmlで詳しく解説しているので、必要に応じて参照してください。
Python 3.12 のインストール
インストール済みの場合は実行不要。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要である。
REM Python をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements
REM Python のパス設定
set "PYTHON_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312"
set "PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312\Scripts"
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_PATH%" /M >nul
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" /M >nul【関連する外部ページ】
Python の公式ページ: https://www.python.org/
AI エディタ Windsurf のインストール
Pythonプログラムの編集・実行には、AI エディタの利用を推奨する。ここでは,Windsurfのインストールを説明する。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行して、Windsurfをシステム全体にインストールする。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
winget install --scope machine --id Codeium.Windsurf -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements【関連する外部ページ】
Windsurf の公式ページ: https://windsurf.com/
ライブラリのインストール
コマンドプロンプトを管理者として実行(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する:
pip install shap>=0.45.0 scikit-learn numpy
プログラムコード
# プログラム名: SHAP機械学習説明可能性デモプログラム
# 特徴技術名: SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations)
# 出典: Lundberg, S. M., & Lee, S. I. (2017). A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 4765-4774).
# 特徴機能: ゲーム理論のシャプレイ値に基づく局所的な特徴重要度の計算。各特徴量が予測結果に与える貢献度を定量的に算出し、機械学習モデルの判断根拠を数値として可視化
# 学習済みモデル: 使用なし
# 方式設計:
# - 関連利用技術: scikit-learn (RandomForestClassifier - アンサンブル学習手法), NumPy (数値計算)
# - 入力と出力: 入力: Irisデータセット(プログラム内で自動読み込み)、出力: コンソールまたはファイルにSHAP値と予測根拠の詳細表示
# - 処理手順: 1)Irisデータセット読み込み 2)データ分割 3)RandomForestモデル学習 4)TreeExplainerでSHAP値計算 5)全クラスの特徴量貢献度を数値表示
# - 前処理、後処理: 前処理: train_test_splitによるデータ分割、後処理: SHAP値の解釈ガイド表示
# - 追加処理: 予測確率分布の表示により、モデルの確信度を可視化。全クラスのSHAP値比較分析
# - 調整を必要とする設定値: SAMPLE_IDX (解析対象サンプルのインデックス、0から始まる整数値)
# 将来方策: 全テストデータに対してSHAP値を計算し、予測精度が低いサンプルのSHAP値の傾向を自動分析する機能
# その他の重要事項: TreeExplainerは決定木系モデル専用。他のモデルではKernelExplainerを使用。SHAP 0.45.0以降の形式変更に対応
# 前準備: pip install shap>=0.45.0 scikit-learn numpy
# バージョン要件: Python>=3.9, SHAP>=0.45.0, scikit-learn>=1.0.0, numpy>=1.21.0
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import shap
import numpy as np
import argparse
import sys
# 定数定義
SEED = 42 # 乱数シード(再現性確保)
TREES = 10 # 決定木の数
MAX_DEPTH = 5 # 最大深度
TEST_RATIO = 0.5 # テストデータの割合
SAMPLE_IDX = 0 # 解析対象サンプルのインデックス
OUTPUT_FILE = 'shap_analysis_result.txt' # 出力ファイル名
ENCODING = 'utf-8' # ファイルエンコーディング
# Irisデータセットのクラス名(英語と日本語の対応)
IRIS_CLASS_NAMES = ['setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica']
IRIS_CLASS_NAMES_JP = ['セトサ', 'バーシカラー', 'バージニカ']
def setup_argparse():
"""コマンドライン引数の設定"""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='SHAP機械学習説明可能性デモプログラム')
parser.add_argument('--sample-idx', type=int, default=SAMPLE_IDX,
help=f'解析対象サンプルのインデックス (デフォルト: {SAMPLE_IDX})')
parser.add_argument('--output-mode', choices=['console', 'file', 'both'], default='console',
help='出力モード: console(コンソールのみ), file(ファイルのみ), both(両方) (デフォルト: console)')
parser.add_argument('--output-file', type=str, default=OUTPUT_FILE,
help=f'出力ファイル名 (デフォルト: {OUTPUT_FILE})')
parser.add_argument('--trees', type=int, default=TREES,
help=f'決定木の数 (デフォルト: {TREES})')
parser.add_argument('--max-depth', type=int, default=MAX_DEPTH,
help=f'決定木の最大深度 (デフォルト: {MAX_DEPTH})')
return parser
def output_manager(text, results, output_mode):
"""統一された出力管理関数"""
if output_mode in ['console', 'both']:
print(text)
if output_mode in ['file', 'both']:
results.append(text)
def check_shap_version():
"""SHAPバージョンの確認と警告"""
try:
shap_version = shap.__version__
version_parts = [int(x) for x in shap_version.split('.')]
if version_parts[0] == 0 and version_parts[1] < 45:
print(f"警告: SHAP バージョン {shap_version} は古いバージョンです。")
print("SHAP 0.45.0以降の使用を推奨します。")
print("アップグレード: pip install --upgrade shap")
return shap_version
except Exception as e:
print(f"SHAPバージョンの確認中にエラーが発生しました: {e}")
return "不明"
def get_shap_values_safely(explainer, X_sample):
"""SHAPバージョンに対応した安全なSHAP値取得"""
try:
shap_values = explainer.shap_values(X_sample)
# デバッグ情報:実際の形状を確認
if isinstance(shap_values, np.ndarray):
# print(f"Debug: SHAP values shape: {shap_values.shape}")
# print(f"Debug: SHAP values ndim: {shap_values.ndim}")
if shap_values.ndim == 3:
# 多くの場合、形状は (n_outputs, n_samples, n_features) または (n_samples, n_features, n_outputs)
# 最初の次元が3(クラス数)の場合は既に正しい形式
if shap_values.shape[0] == 3: # (classes, samples, features)
pass # 既に正しい形式
elif shap_values.shape[2] == 3: # (samples, features, classes)
shap_values = np.transpose(shap_values, (2, 0, 1))
elif shap_values.shape[1] == 3: # (samples, classes, features)
shap_values = np.transpose(shap_values, (1, 0, 2))
elif isinstance(shap_values, list):
# リスト形式の場合は通常正しい形式(各要素が各クラスのSHAP値)
pass
return shap_values
except Exception as e:
print(f"SHAP値の計算中にエラーが発生しました: {e}")
return None
def analyze_class_comparison(shap_values, feature_names, class_names):
"""全クラスのSHAP値比較分析"""
analysis_results = []
analysis_results.append("\n=== 全クラスのSHAP値比較分析 ===")
# 各特徴量について、クラス間でのSHAP値を比較
for i, feature_name in enumerate(feature_names):
analysis_results.append(f"\n【{feature_name}】")
for j, class_name in enumerate(class_names):
if isinstance(shap_values, (list, tuple)):
shap_val = shap_values[j][0, i] # 常に最初のサンプル(インデックス0)
else: # np.ndarray
shap_val = shap_values[j, 0, i] # 常に最初のサンプル(インデックス0)
impact = "正の寄与" if shap_val > 0 else "負の寄与" if shap_val < 0 else "中立"
analysis_results.append(f" {class_name}: {shap_val:.4f} ({impact})")
# クラス間での最も影響の大きい特徴量を特定
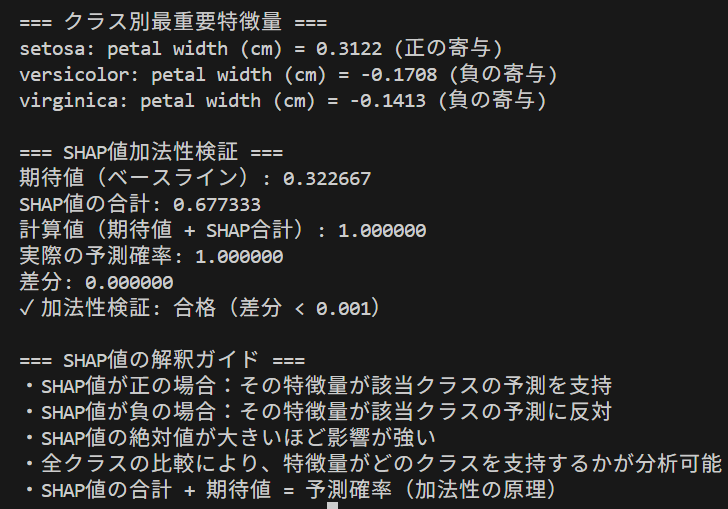
analysis_results.append(f"\n=== クラス別最重要特徴量 ===")
for j, class_name in enumerate(class_names):
if isinstance(shap_values, (list, tuple)):
class_shap = shap_values[j][0, :] # 常に最初のサンプル(インデックス0)
else: # np.ndarray
class_shap = shap_values[j, 0, :] # 常に最初のサンプル(インデックス0)
abs_shap = np.abs(class_shap)
most_important_idx = np.argmax(abs_shap)
most_important_feature = feature_names[most_important_idx]
most_important_value = class_shap[most_important_idx]
impact = "正の寄与" if most_important_value > 0 else "負の寄与"
analysis_results.append(f"{class_name}: {most_important_feature} = {most_important_value:.4f} ({impact})")
return analysis_results
def verify_shap_additivity(explainer, shap_values, pred_class, model, X_sample, X_train):
"""SHAP値の加法性検証"""
try:
# 期待値(ベースライン)を取得
expected_value = None
if hasattr(explainer, 'expected_value'):
if isinstance(explainer.expected_value, (list, np.ndarray)):
# 多クラス分類の場合
if len(explainer.expected_value) > pred_class:
expected_value = explainer.expected_value[pred_class]
else:
# 二値分類または回帰の場合(Irisでは使用されないが互換性のため)
expected_value = explainer.expected_value
# 期待値が取得できない場合は、訓練データ全体での特定クラスの平均予測確率を使用
if expected_value is None:
expected_value = model.predict_proba(X_train)[:, pred_class].mean()
# SHAP値の合計を計算(常に最初のサンプル)
if isinstance(shap_values, (list, tuple)):
shap_sum = np.sum(shap_values[pred_class][0, :])
else: # np.ndarray
shap_sum = np.sum(shap_values[pred_class, 0, :])
# 実際の予測値を取得
actual_prediction = model.predict_proba(X_sample)[0, pred_class]
# 検証結果
calculated_prediction = expected_value + shap_sum
verification_results = []
verification_results.append(f"\n=== SHAP値加法性検証 ===")
verification_results.append(f"期待値(ベースライン): {expected_value:.6f}")
verification_results.append(f"SHAP値の合計: {shap_sum:.6f}")
verification_results.append(f"計算値(期待値 + SHAP合計): {calculated_prediction:.6f}")
verification_results.append(f"実際の予測確率: {actual_prediction:.6f}")
# 差分の計算
difference = abs(calculated_prediction - actual_prediction)
verification_results.append(f"差分: {difference:.6f}")
if difference < 0.001:
verification_results.append("✓ 加法性検証: 合格(差分 < 0.001)")
elif difference < 0.01:
verification_results.append("⚠ 加法性検証: 警告(差分 < 0.01)")
else:
verification_results.append("✗ 加法性検証: 失敗(差分 >= 0.01)")
verification_results.append("注意: TreeExplainerのデフォルト設定では完全な加法性は保証されません")
return verification_results
except Exception as e:
return [f"加法性検証中にエラーが発生しました: {e}"]
def main():
# コマンドライン引数の解析
parser = setup_argparse()
args = parser.parse_args()
# 結果保存用リスト
results = []
# プログラム開始時の表示
output_manager('=== SHAP機械学習説明可能性デモプログラム ===', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('概要: 機械学習モデルの予測根拠をSHAP値で分析します', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('操作方法: --sample-idx でサンプル番号を指定、--output-mode で出力先を選択', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('注意事項: TreeExplainerは決定木系モデル専用です', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('', results, args.output_mode)
# SHAPバージョン確認
shap_version = check_shap_version()
output_manager(f'SHAP バージョン: {shap_version}', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('', results, args.output_mode)
try:
# データ準備
iris = load_iris()
X, y = iris.data, iris.target
feature_names = iris.feature_names # 標準的な英語名を使用
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=TEST_RATIO, random_state=SEED, stratify=y
)
# サンプルインデックスの妥当性チェック
if args.sample_idx >= len(X_test):
output_manager(f"エラー: サンプルインデックス {args.sample_idx} は範囲外です(最大: {len(X_test)-1})", results, args.output_mode)
sys.exit(1)
# モデル学習
model = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=args.trees,
max_depth=args.max_depth,
random_state=SEED,
min_samples_split=2,
min_samples_leaf=1
)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# TreeExplainerの作成(デフォルト設定)
explainer = shap.TreeExplainer(model)
# SHAP値の安全な取得
shap_values = get_shap_values_safely(explainer, X_test[args.sample_idx:args.sample_idx+1])
if shap_values is None:
output_manager("エラー: SHAP値の計算に失敗しました", results, args.output_mode)
sys.exit(1)
# 予測結果
pred_class = model.predict(X_test[args.sample_idx:args.sample_idx+1])[0]
pred_proba = model.predict_proba(X_test[args.sample_idx:args.sample_idx+1])[0]
# 結果出力
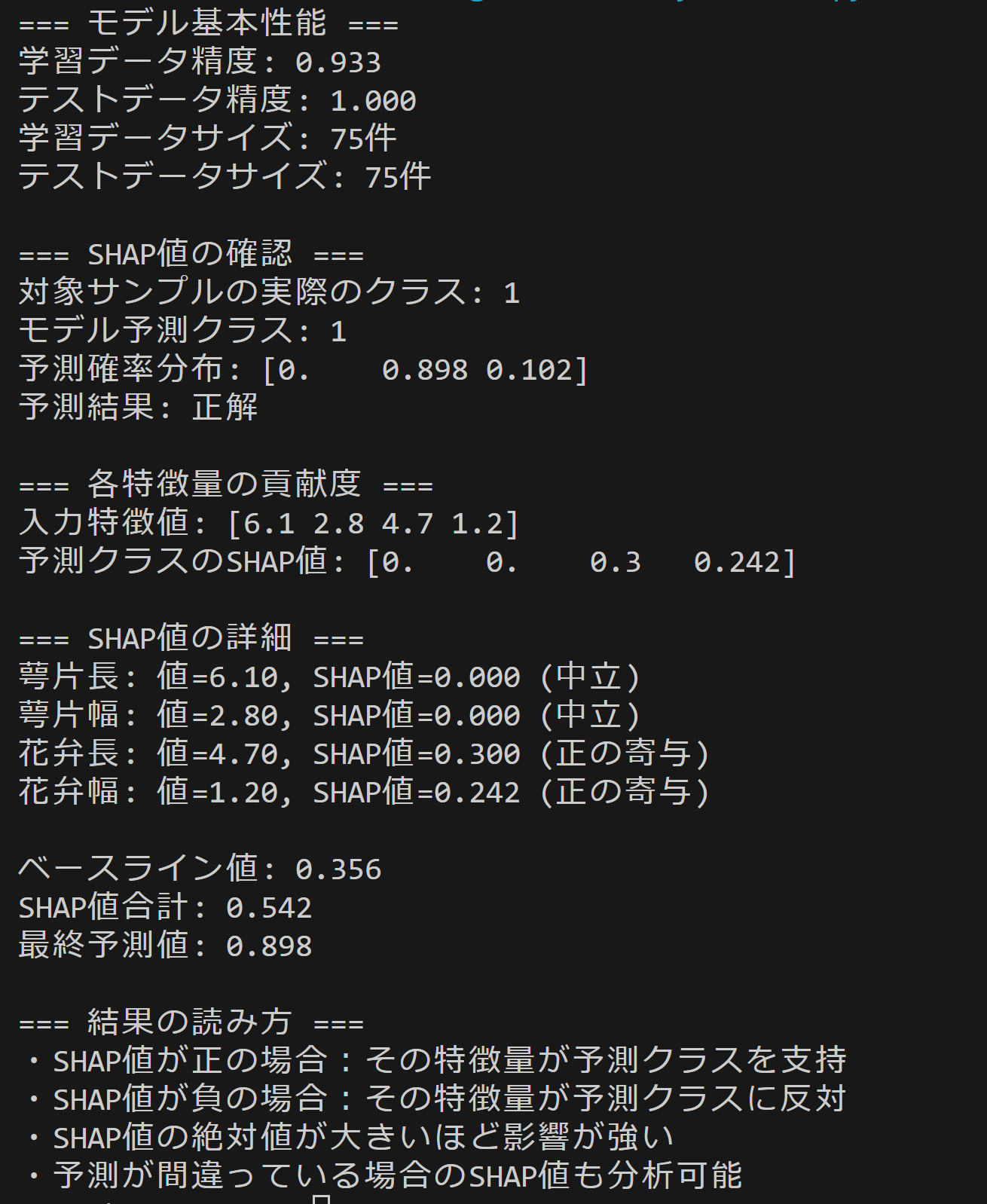
output_manager('=== モデル基本性能 ===', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager(f'使用パラメータ: 木の数={args.trees}, 最大深度={args.max_depth}', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager(f'学習データ精度: {model.score(X_train, y_train):.3f}', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager(f'テストデータ精度: {model.score(X_test, y_test):.3f}', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager(f'学習データサイズ: {len(X_train)}件', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager(f'テストデータサイズ: {len(X_test)}件', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('\n=== 対象サンプルの分析 ===', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager(f'サンプルインデックス: {args.sample_idx}', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager(f'実際のクラス: {y_test[args.sample_idx]} ({IRIS_CLASS_NAMES[y_test[args.sample_idx]]})', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager(f'予測クラス: {pred_class} ({IRIS_CLASS_NAMES[pred_class]})', results, args.output_mode)
# 全クラスの予測確率を表示
output_manager('予測確率分布:', results, args.output_mode)
for i, (class_name, prob) in enumerate(zip(IRIS_CLASS_NAMES, pred_proba)):
marker = " ← 予測" if i == pred_class else ""
output_manager(f' {class_name}: {prob:.4f}{marker}', results, args.output_mode)
result = '正解' if y_test[args.sample_idx] == pred_class else '不正解'
output_manager(f'予測結果: {result}', results, args.output_mode)
# 特徴量値の表示
output_manager(f'\n入力特徴値:', results, args.output_mode)
for i, (feature_name, value) in enumerate(zip(feature_names, X_test[args.sample_idx])):
output_manager(f' {feature_name}: {value:.2f}', results, args.output_mode)
# 予測クラスのSHAP値詳細分析
output_manager(f'\n=== 予測クラス ({IRIS_CLASS_NAMES[pred_class]}) のSHAP値詳細 ===', results, args.output_mode)
for i, feature_name in enumerate(feature_names):
if isinstance(shap_values, (list, tuple)):
shap_val = shap_values[pred_class][0, i]
else: # np.ndarray
shap_val = shap_values[pred_class, 0, i]
feature_value = X_test[args.sample_idx, i]
impact = '正の寄与' if shap_val > 0 else '負の寄与' if shap_val < 0 else '中立'
output_manager(f'{feature_name}: 値={feature_value:.2f}, SHAP値={shap_val:.4f} ({impact})', results, args.output_mode)
# 全クラス比較分析
class_analysis = analyze_class_comparison(shap_values, feature_names, IRIS_CLASS_NAMES)
for line in class_analysis:
output_manager(line, results, args.output_mode)
# SHAP値の加法性検証
additivity_check = verify_shap_additivity(explainer, shap_values, pred_class, model,
X_test[args.sample_idx:args.sample_idx+1], X_train)
for line in additivity_check:
output_manager(line, results, args.output_mode)
# 解釈ガイド
output_manager('\n=== SHAP値の解釈ガイド ===', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('・SHAP値が正の場合:その特徴量が該当クラスの予測を支持', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('・SHAP値が負の場合:その特徴量が該当クラスの予測に反対', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('・SHAP値の絶対値が大きいほど影響が強い', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('・全クラスの比較により、特徴量がどのクラスを支持するかが分析可能', results, args.output_mode)
output_manager('・SHAP値の合計 + 期待値 = 予測確率(加法性の原理)', results, args.output_mode)
# ファイル出力(必要に応じて)
if args.output_mode in ['file', 'both']:
try:
with open(args.output_file, 'w', encoding=ENCODING) as f:
for line in results:
f.write(line + '\n')
print(f'\n結果を {args.output_file} に保存しました')
except Exception as e:
print(f'ファイル保存中にエラーが発生しました: {e}')
except Exception as e:
error_msg = f"プログラム実行中にエラーが発生しました: {e}"
output_manager(error_msg, results, args.output_mode)
sys.exit(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
使用方法
- 上記のプログラムを実行
- 実行結果では、各特徴量のSHAP値が表示される。正の値は予測クラスを支持し、負の値は反対する。
実験・探求のアイデア
AIモデルを変えて追加実験:
RandomForestClassifierをLogisticRegressionやSVCに変更n_estimatorsの値を変更してSHAP値の変化を観察
追加実験:
- 異なるサンプル(
TEST_SAMPLE_INDEXを変更)でのSHAP値比較 - 訓練データサイズの変更による影響確認
- 異なるランダムシード値での結果の安定性検証
体験・実験・探求のアイデア:
- 予測が間違っているサンプルのSHAP値を分析
- SHAP値の絶対値が最も大きい特徴量を特定し、その特徴量のみでの予測精度を検証
- 複数のサンプルのSHAP値を比較し、クラス別の特徴量重要度パターンを調査
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)