R システムのパッケージに付属のデータセットから SQLite 3 データベースを生成(R システム,SQLite3 を使用)
- 一般: iris, diamonds, Indometh
- 時系列: Lai2005fig4, meteoandes, economics , nhtemp
- 緯度・経度: seals
◆ 作成するSQLite 3 データベース:rdataset
前準備
使用するソフトウェア
- R システムのインストールが済んでいること
- SQLite 3 のインストール: SQLite 3インストール,データベース作成,テーブル定義,レコード挿入(Windows 上)別ページ »で説明
- python のインストール、python のパッケージ sqlite3, rpy2, numpy, pandas のインストールが済んでいること
あらかじめ決めておく事項
このページでは,SQLite 3 データベースの生成を行う. 生成するSQLite 3 データベースのデータベース名を決めておくこと. このページでは,次のように書く.
- データベース名: rdataset
データベース名は,自由に決めてよいが,半角文字(つまり英字と英記号)を使い,スペースを含まないこと,
一般のデータ
iris
- テーブル定義
- iris(Sepal_Length, Sepal_Width, Petal_Length, Petal_Width, Species)
◆ bash プログラム
#!/usr/bin/python import sqlite3 conn = sqlite3.connect('rdataset') sql = u""" drop table iris; """ conn.execute(sql) sql = u""" create table iris ( Sepal_Length real, Sepal_Width real, Petal_Length real, Petal_Width real, Species text ); """ conn.execute(sql) conn.close()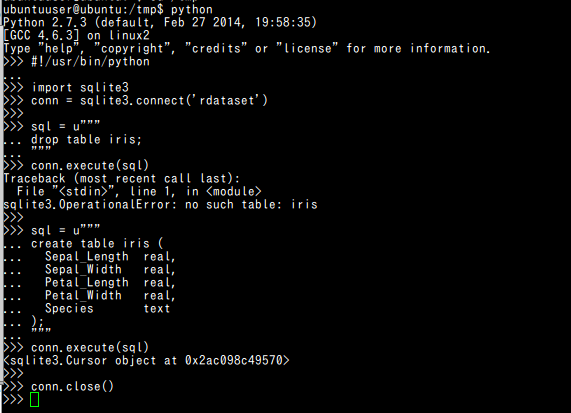
- テーブルの作成
◆ bash プログラム
#!/usr/bin/python import rpy2.robjects import pandas.rpy.common x = pandas.rpy.common.load_data('iris') for i in x: print '===' print i cat /tmp/a.$$.r | R --no-save cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL .mode csv .import /tmp/a.$$.csv iris vacuum; SQL # tail -n +2 /tmp/iris.csv > /tmp/a.$$.csv cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # echo 'select * from iris limit 10;' | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset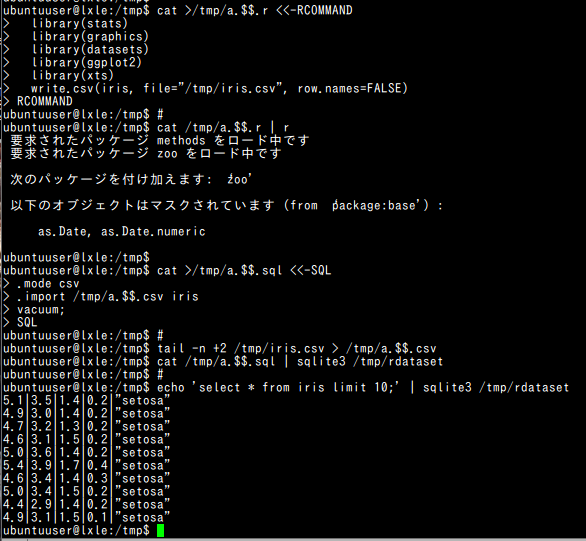
diamonds
- テーブル定義
- diamonds(carat, cut, color, clarity, depth, table, price, x, y, z)
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash # rm -f /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL drop table diamonds; SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL create table diamonds ( carat real, cut text, color text, clarity text, depth real, tbl real, price integer, x real, y real, z real ); SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset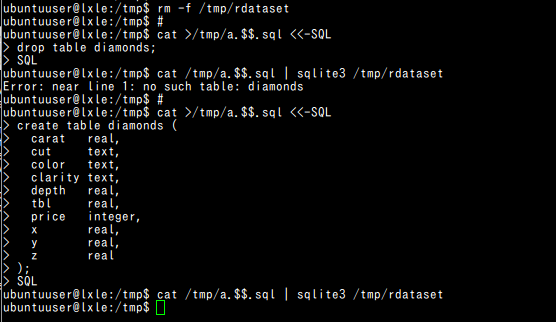
- テーブルの作成
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash cat >/tmp/a.$$.r <<-RCOMMAND library(stats) library(graphics) library(datasets) library(ggplot2) library(xts) library(chron) write.csv(diamonds, file="/tmp/diamonds.csv", row.names=FALSE) RCOMMAND # cat /tmp/a.$$.r | R --no-save cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL .mode csv .import /tmp/a.$$.csv diamonds vacuum; SQL # tail -n +2 /tmp/diamonds.csv > /tmp/a.$$.csv cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # echo 'select * from diamonds limit 10;' | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset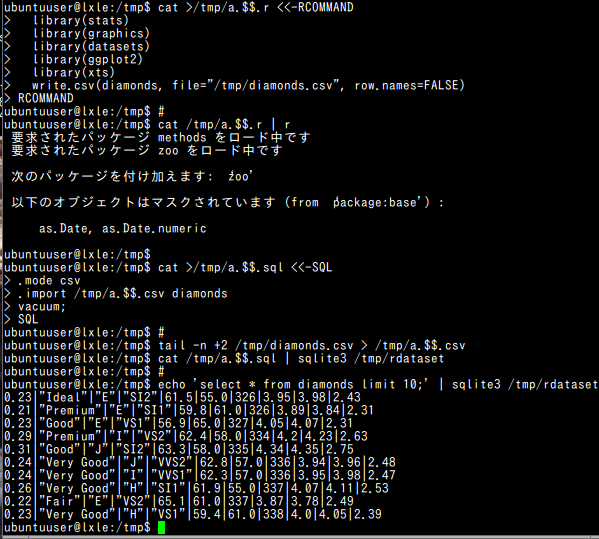
Indometh
- テーブル定義
- Indometh(Subject, t, conc)
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash # rm -f /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL drop table Indometh; SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL create table Indometh ( Subject integer, t real, conc real ); SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset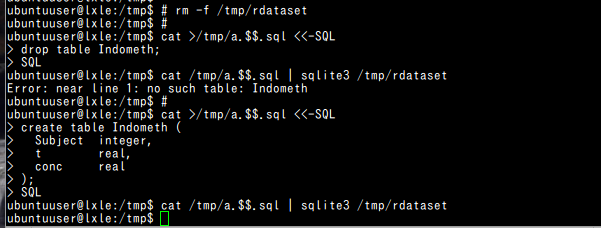
- テーブルの作成
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash cat >/tmp/a.$$.r <<-RCOMMAND library(stats) library(graphics) library(datasets) library(ggplot2) library(xts) library(chron) write.csv(Indometh, file="/tmp/Indometh.csv", row.names=FALSE) RCOMMAND # cat /tmp/a.$$.r | R --no-save cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL .mode csv .import /tmp/a.$$.csv Indometh vacuum; SQL # tail -n +2 /tmp/Indometh.csv > /tmp/a.$$.csv cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # echo 'select * from Indometh limit 10;' | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset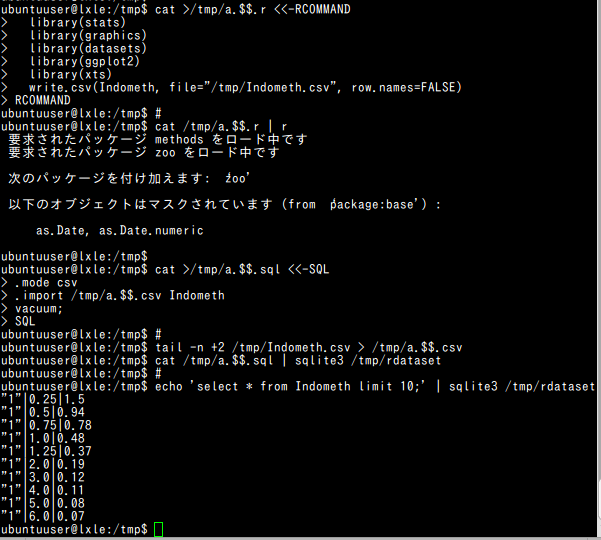
時系列 (time series)
wind
ここでの wind は gstat パッケージ内の風向データ
- テーブル定義
- wind(year, month, day, RPT, VAL, ROS, KIL, SHA, BIR, DUB, CLA, MUL, CLO, BEL, MAL)
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash # rm -f /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL drop table wind; SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL create table wind ( at date, year integer, month integer, day integer, RPT real, VAL real, ROS real, KIL real, SHA real, BIR real, DUB real, CLA real, MUL real, CLO real, BEL real, MAL real ); SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset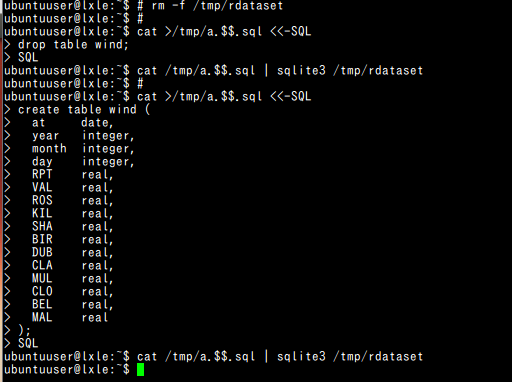
- テーブルの作成
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash cat >/tmp/a.$$.r <<-RCOMMAND library(stats) library(graphics) library(datasets) library(ggplot2) library(xts) library(chron) library(insol) library(gstat) data(wind) wind\$at = as.Date( ISOdate(wind\$year + 1900, wind\$month, wind\$day) ) # 列順序の入れ替え wind <- wind[,c(16,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15)] str(wind) write.csv(wind, file="/tmp/wind.csv", row.names=FALSE) RCOMMAND # cat /tmp/a.$$.r | R --no-save cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL .mode csv .import /tmp/a.$$.csv wind vacuum; SQL # tail -n +2 /tmp/wind.csv > /tmp/a.$$.csv cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # echo 'select * from wind limit 10;' | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset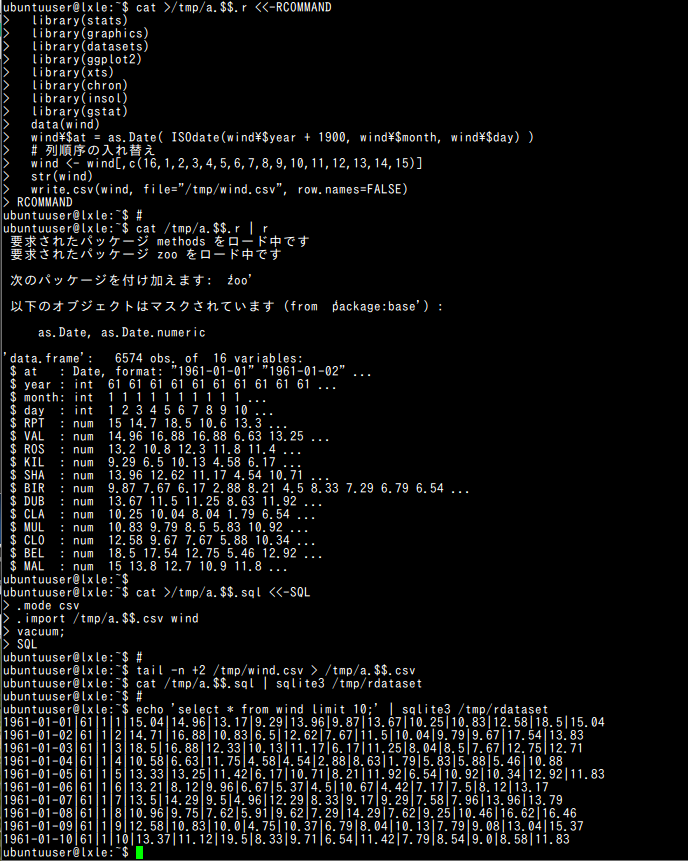
◆ ggplot() を使用 (R プログラム)
library(ggplot2)
library(RSQLite)
library(xts)
library(chron)
fetch_table <- function(sqlite3dbname, tablename) {
drv <- dbDriver("SQLite", max.con = 1)
conn <- dbConnect(drv, dbname=sqlite3dbname)
rs <- dbSendQuery( conn, paste("SELECT * from", tablename, ";") )
T <- fetch(rs, n = -1)
return(T)
}
T <- fetch_table("/tmp/rdataset", "wind")
#
table_to_melt <- function(T, tsvec, tsformat) {
# 先に xts 型に変換しておく
D <- as.xts( read.zoo( T, tsformat ) )
# melt(Date, AttrNum, Value).
Date <- rep(strptime(tsvec, tsformat, tz=""), ncol(D))
AttrNum <- rep(1:ncol(D), each=nrow(D))
Value <- as.numeric(as.vector(D))
return( data.frame(Date=Date, AttrNum=AttrNum, Value=Value) )
}
M <- table_to_melt(T, T$at, "%Y-%m-%d")
#
# ggplot(M, aes(x=Date, y=Value, colour=factor(AttrNum))) + geom_point(size=1);
ggplot(subset(M, AttrNum==10), aes(x=Date, y=Value, colour=factor(AttrNum))) + geom_point(size=1);
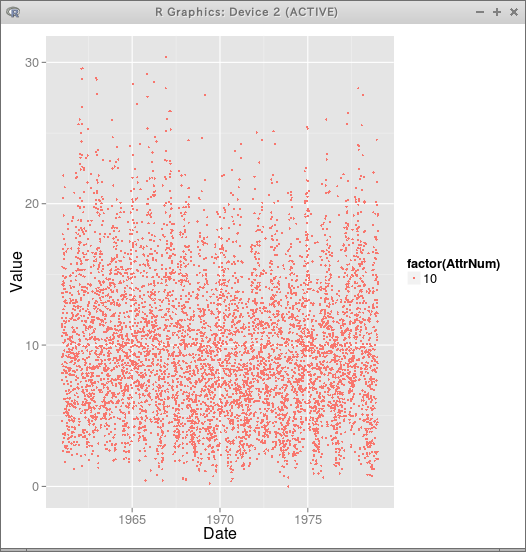
◆ 追加プログラム (R プログラム) (書きかけ)
http://www.inside-r.org/packages/cran/gstat/docs/wind
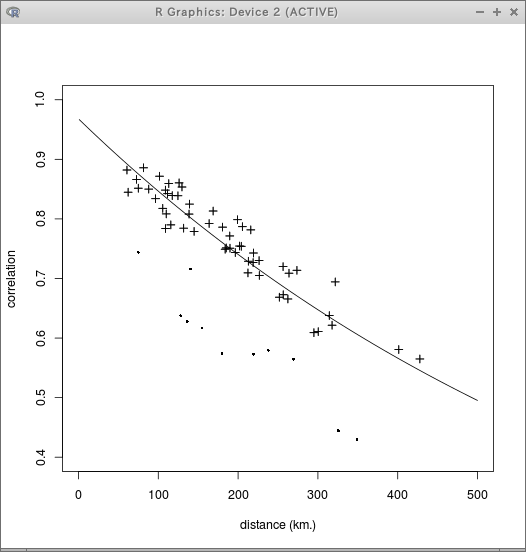
# 1月1日を基点とする日数(月日の情報を使う.年は無視) j <- as.numeric(format(as.Date(T$at), '%j') ) winsqrt = sqrt( 0.5148 * ( as.matrix(T[5:16]) ) ) plot(winsqrt) winsqrt = winsqrt - mean(winsqrt) a <- sapply( split(winsqrt, j), mean ) plot(a) lines( lowess(a, f=0.1) )
meteoandes
- テーブル定義
- meteoandes(year, doy, hh, mm, Tair, pyra1, pyra2, windspeed, winddir, RH)
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash # rm -f /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL drop table meteoandes; SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL create table meteoandes ( meteodate datetime, year integer, doy integer, hh integer, mm integer, Tair real, pyra1 real, pyra2 real, windspeed real, winddir real, RH real ); SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset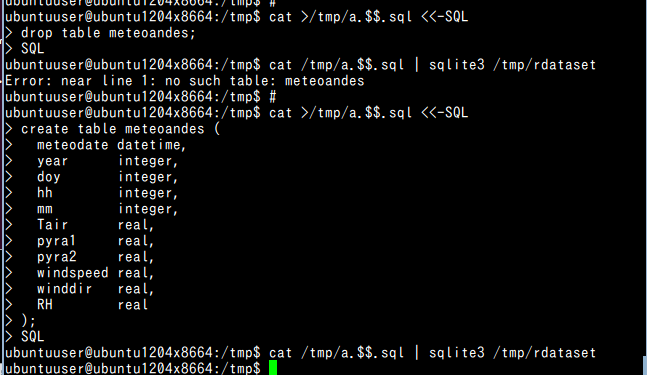
- テーブルの作成
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash cat >/tmp/a.$$.r <<-RCOMMAND library(stats) library(graphics) library(datasets) library(ggplot2) library(xts) library(chron) library(insol) data(meteoandes) meteoandes\$meteodate = strptime(paste(meteoandes\$year,meteoandes\$doy,meteoandes\$hh,meteoandes\$mm),format="%Y %j %H %M",tz="America/Santiago") # 列順序の入れ替え meteoandes <- meteoandes[,c(11,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10)] str(meteoandes) write.csv(meteoandes, file="/tmp/meteoandes.csv", row.names=FALSE) RCOMMAND # cat /tmp/a.$$.r | R --no-save cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL .mode csv .import /tmp/a.$$.csv meteoandes vacuum; SQL # tail -n +2 /tmp/meteoandes.csv > /tmp/a.$$.csv cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # echo 'select * from meteoandes limit 10;' | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset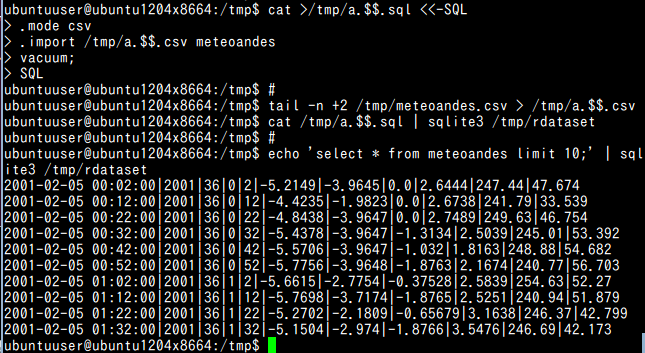
- R のプログラム例を用いてプロット
◆ ggplot() を使用 (R プログラム) (書きかけ)(動作未確認)
library(ggplot2) library(RSQLite) library(xts) library(chron) fetch_table <- function(sqlite3dbname, tablename) { drv <- dbDriver("SQLite", max.con = 1) conn <- dbConnect(drv, dbname=sqlite3dbname) rs <- dbSendQuery( conn, paste("SELECT * from", tablename, ";") ) T <- fetch(rs, n = -1) return(T) } T <- fetch_table("/tmp/rdataset", "meteoandes") # table_to_melt <- function(T, tsvec, tsformat) { # 先に xts 型に変換しておく D <- as.xts( read.zoo( T, tsformat ) ) # melt(Date, AttrNum, Value). Date <- rep(strptime(tsvec, tsformat, tz=""), ncol(D)) AttrNum <- rep(1:ncol(D), each=nrow(D)) Value <- as.numeric(as.vector(D)) return( data.frame(Date=Date, AttrNum=AttrNum, Value=Value) ) } M <- table_to_melt(T, T$meteodate, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") # ggplot(M, aes(x=Date, y=Value, colour=factor(AttrNum))) + geom_point(size=1); # ggplot(subset(M, AttrNum==3), aes(x=Date, y=Value, colour=factor(AttrNum))) + geom_point(size=1);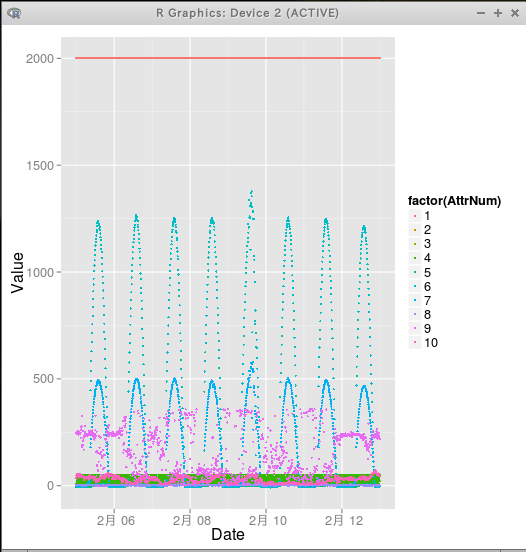
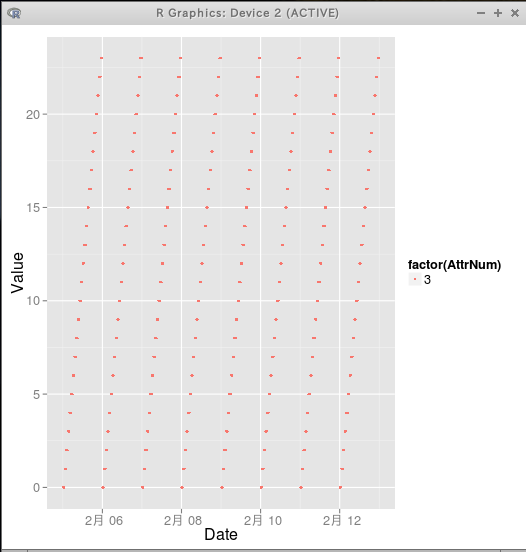
◆ plot() を使用 (R プログラム)
library(RSQLite) library(xts) library(chron) drv <- dbDriver("SQLite", max.con = 1) conn <- dbConnect(drv, dbname="/tmp/rdataset") rs <- dbSendQuery( conn, "SELECT * from meteoandes;" ) T <- fetch(rs, n = -1) # plot pyra1, pyra2 plot(strptime(T$meteodate, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", tz=""), T$pyra1, 'l', col=2, xlab='Date', xaxt="n", ylab=expression(paste('Solar radiation [ ',Wm^-2,' ]')), main='Insolation at Loma Larga glacier') r <- as.POSIXct(round(range(strptime(T$meteodate, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", tz="")), "days")) lines(strptime(T$meteodate, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", tz=""), T$pyra2, col=4) axis.POSIXct(1, at=seq(r[1],r[2], by="1 week"), format="%d日 0時")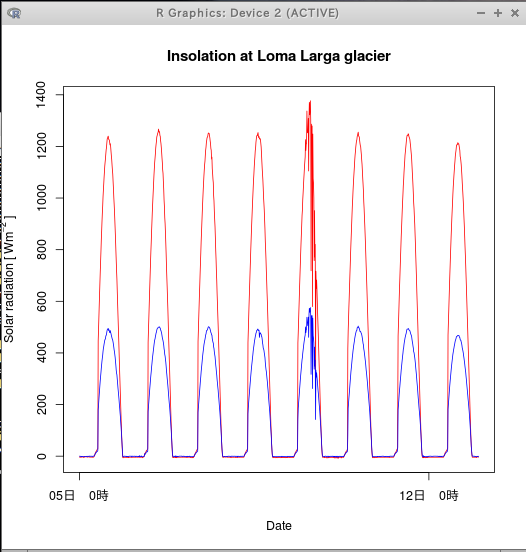
economics
- テーブル定義
- economics(dt, pce, pop, psavert, uempmed, unemploy)
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash # rm -f /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL drop table economics; SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL create table economics ( dt datetime, pce real, pop integer, psavert real, uempmed real, unemploy integer ); SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset
- テーブルの作成
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash cat >/tmp/a.$$.r <<-RCOMMAND library(stats) library(graphics) library(datasets) library(ggplot2) library(xts) library(chron) write.csv(economics, file="/tmp/economics.csv", row.names=FALSE) RCOMMAND # cat /tmp/a.$$.r | R --no-save cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL .mode csv .import /tmp/a.$$.csv economics vacuum; SQL # tail -n +2 /tmp/economics.csv > /tmp/a.$$.csv cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # echo 'select * from economics limit 10;' | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset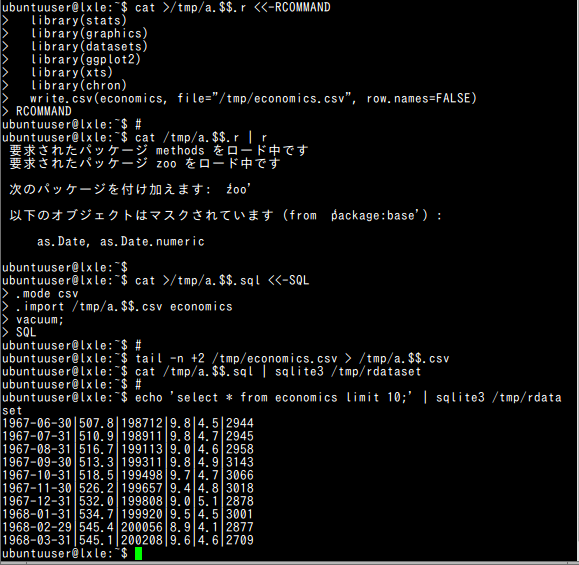
- R のプログラム例を用いてプロット
◆ ggplot() を使用 (R プログラム)
library(ggplot2) library(RSQLite) library(xts) library(chron) fetch_table <- function(sqlite3dbname, tablename) { drv <- dbDriver("SQLite", max.con = 1) conn <- dbConnect(drv, dbname=sqlite3dbname) rs <- dbSendQuery( conn, paste("SELECT * from", tablename, ";") ) T <- fetch(rs, n = -1) return(T) } T <- fetch_table("/tmp/rdataset", "economics") # table_to_melt <- function(T, tsvec, tsformat) { # 先に xts 型に変換しておく D <- as.xts( read.zoo( T, tsformat ) ) # melt(Date, AttrNum, Value). Date <- rep(strptime(tsvec, tsformat, tz=""), ncol(D)) AttrNum <- rep(1:ncol(D), each=nrow(D)) Value <- as.numeric(as.vector(D)) return( data.frame(Date=Date, AttrNum=AttrNum, Value=Value) ) } M <- table_to_melt(T, T$dt, "%Y-%m-%d") # ggplot(M, aes(x=Date, y=Value, colour=factor(AttrNum))) + geom_point(size=1); # ggplot(subset(M, AttrNum==3), aes(x=Date, y=Value, colour=factor(AttrNum))) + geom_point(size=1);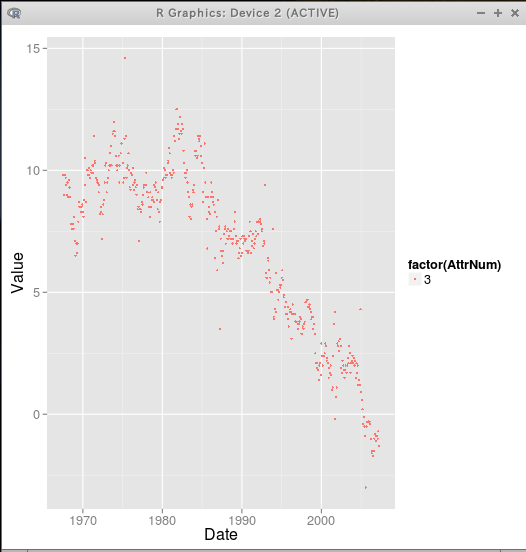
nhtemp
- テーブル定義
- nhtemp(ts, temperature)
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash # rm -f /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL drop table nhtemp; SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL create table nhtemp ( ts datatime, temperature real ); SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset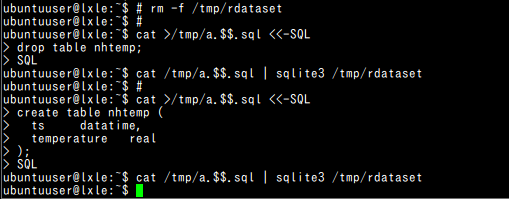
- テーブルの作成
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash cat >/tmp/a.$$.r <<-RCOMMAND library(stats) library(graphics) library(datasets) library(ggplot2) library(xts) library(chron) data(nhtemp) D <- as.xts(nhtemp) # write.csv(as.data.frame(D), file="/tmp/nhtemp.csv", row.names=TRUE) RCOMMAND # cat /tmp/a.$$.r | R --no-save cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL .mode csv .import /tmp/a.$$.csv nhtemp vacuum; SQL # tail -n +2 /tmp/nhtemp.csv > /tmp/a.$$.csv cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # echo 'select * from nhtemp limit 10;' | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset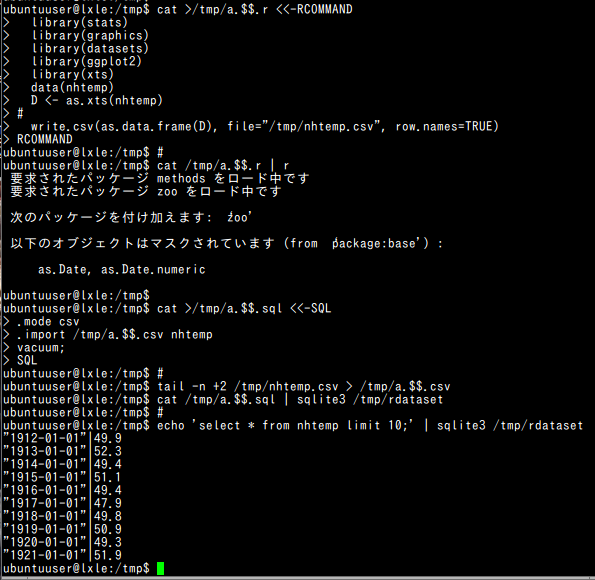
- R のプログラム例を用いてプロット
◆ ggplot() を使用 (R プログラム)
library(ggplot2) library(RSQLite) library(xts) library(chron) fetch_table <- function(sqlite3dbname, tablename) { drv <- dbDriver("SQLite", max.con = 1) conn <- dbConnect(drv, dbname=sqlite3dbname) rs <- dbSendQuery( conn, paste("SELECT * from", tablename, ";") ) T <- fetch(rs, n = -1) return(T) } T <- fetch_table("/tmp/rdataset", "nhtemp") # table_to_melt <- function(T, tsvec, tsformat) { # 先に xts 型に変換しておく D <- as.xts( read.zoo( T, tsformat ) ) # melt(Date, AttrNum, Value). Date <- rep(strptime(tsvec, tsformat, tz=""), ncol(D)) AttrNum <- rep(1:ncol(D), each=nrow(D)) Value <- as.numeric(as.vector(D)) return( data.frame(Date=Date, AttrNum=AttrNum, Value=Value) ) } M <- table_to_melt(T, T$ts, "\"%Y-%m-%d\"") # ggplot(M, aes(x=Date, y=Value, colour=factor(AttrNum))) + geom_point(size=2);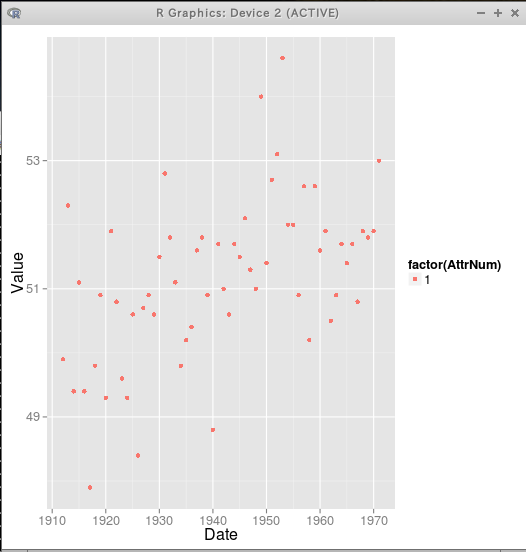
配列
Lai2005fig4
Lai2005fig4 は changepoint パッケージ内の配列データ.
- テーブル定義
- Lai2005fig4(Spot, CH, POS_start, POS_end, GBM29)
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash # rm -f /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL drop table Lai2005fig4; SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL create table Lai2005fig4 ( Spot integer, CH integer, POS_start integer, POS_end integer, GBM29 real ); SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset
- テーブルの作成
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash cat >/tmp/a.$$.r <<-RCOMMAND library(stats) library(graphics) library(datasets) library(ggplot2) library(xts) library(chron) library(changepoint) data(Lai2005fig4) write.csv(Lai2005fig4, file="/tmp/Lai2005fig4.csv", row.names=FALSE) RCOMMAND # cat /tmp/a.$$.r | R --no-save cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL .mode csv .import /tmp/a.$$.csv Lai2005fig4 vacuum; SQL # tail -n +2 /tmp/Lai2005fig4.csv > /tmp/a.$$.csv cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # echo 'select * from Lai2005fig4 limit 10;' | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset
緯度・経度
wind.loc
ここでの wind.loc は gstat パッケージ内の風向データ
- テーブル定義
- wind_loc(lat, lon, Station, Code, Latitude, Longitude, MeanWind)
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash # rm -f /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL drop table wind_loc; SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL create table wind_loc ( Station text, Code text, Latitude text, Longitude text, MeanWind real, lat real, lon real ); SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset
- テーブルの作成
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash cat >/tmp/a.$$.r <<-RCOMMAND library(stats) library(graphics) library(datasets) library(ggplot2) library(xts) library(chron) library(insol) library(gstat) library(sp) data(wind) wind.loc\$y = as.numeric(char2dms(as.character(wind.loc[['Latitude']]))) wind.loc\$x = as.numeric(char2dms(as.character(wind.loc[['Longitude']]))) coordinates(wind.loc) = ~x+y write.csv(wind.loc, file="/tmp/wind.loc.csv", row.names=FALSE) RCOMMAND # cat /tmp/a.$$.r | R --no-save cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL .mode csv .import /tmp/a.$$.csv wind_loc vacuum; SQL # tail -n +2 /tmp/wind.loc.csv > /tmp/a.$$.csv cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # echo 'select * from wind_loc limit 10;' | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset
seals
- テーブル定義
- seals(lat, long, delta_long, delta_lat)
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash # rm -f /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL drop table seals; SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL create table seals ( lat real, long real, delta_long real, delta_lat real ); SQL cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset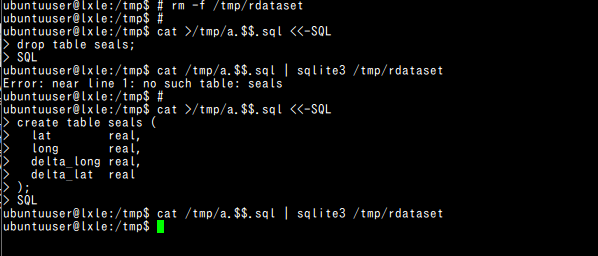
- テーブルの作成
◆ bash プログラム
#!/bin/bash cat >/tmp/a.$$.r <<-RCOMMAND library(stats) library(graphics) library(datasets) library(ggplot2) library(xts) library(chron) write.csv(seals, file="/tmp/seals.csv", row.names=FALSE) RCOMMAND # cat /tmp/a.$$.r | R --no-save cat >/tmp/a.$$.sql <<-SQL .mode csv .import /tmp/a.$$.csv seals vacuum; SQL # tail -n +2 /tmp/seals.csv > /tmp/a.$$.csv cat /tmp/a.$$.sql | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset # echo 'select * from seals limit 10;' | sqlite3 /tmp/rdataset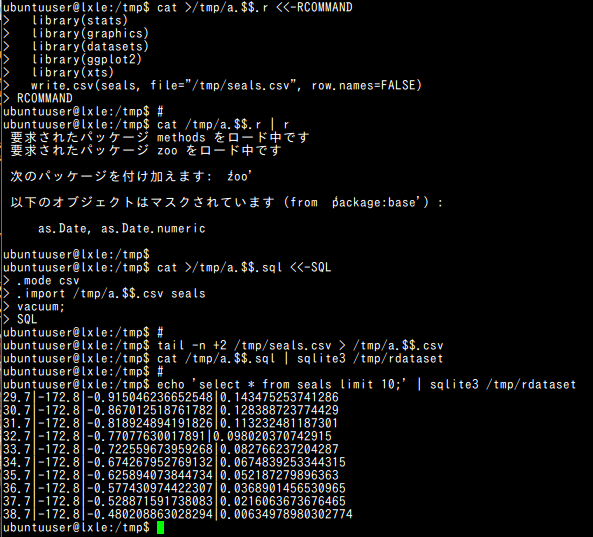
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)