face_recognition による顔のクラスタリングを行う Python プログラム(Dlib,ageitgey/face_recognition,Python を使用)(Windows 上)
【サイト内の関連ページ】
- 説明資料: Dlib の機能概要 [PDF], [パワーポイント]
- 顔情報処理の Python プログラム(Dlib,face_recognition を使用) について: 別ページ »にまとめ
- Windows で動く人工知能関係 Pythonアプリケーション,オープンソースソフトウエア): 別ページ »にまとめている.
【用語説明】
- Dlib
Dlibは,数多くの機能を持つ C++ ライブラリ.機能には,機械学習,数値計算,グラフィカルモデル推論,画像処理,スレッド,通信,GUI,データ圧縮・一貫性,テスト,さまざまなユーティリティなどがある.Python API もある.
【関連する外部ページ】
ageitgey/face_recognition のページ: https://github.com/ageitgey/face_recognition
前準備
Python のインストール(Windows上)
注:既にPython(バージョン3.12を推奨)がインストール済みの場合は,この手順は不要である.
winget(Windowsパッケージマネージャー)を使用してインストールを行う
- Windowsで,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - winget(Windowsパッケージマネージャー)が利用可能か確認する:
winget --version
- Pythonのインストール(下のコマンドにより Python 3.12 がインストールされる).
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem" /v LongPathsEnabled /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f REM Python をシステム領域にインストール winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 -e --silent REM Python のパス set "INSTALL_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312" echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%INSTALL_PATH%" >nul if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%INSTALL_PATH%" /M >nul echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%INSTALL_PATH%\Scripts" >nul if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%INSTALL_PATH%\Scripts" /M >nul
- Python詳細ガイド:Pythonまとめ »
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - 次のコマンドを実行する.
python -m pip install -U dlib
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - Dlib のソースコード等のダウンロード
次のコマンドを実行.
cd C:\ rmdir /s /q dlib git clone https://github.com/davisking/dlib
- Dlib の学習済みモデルのダウンロード
次のコマンドを実行.
cd C:\dlib cd python_examples curl -O http://dlib.net/files/mmod_human_face_detector.dat.bz2 curl -O http://dlib.net/files/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat.bz2 curl -O http://dlib.net/files/shape_predictor_5_face_landmarks.dat.bz2 curl -O http://dlib.net/files/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2 "c:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe" x mmod_human_face_detector.dat.bz2 "c:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe" x dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat.bz2 "c:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe" x shape_predictor_5_face_landmarks.dat.bz2 "c:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe" x shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2 del mmod_human_face_detector.dat.bz2 del dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat.bz2 del shape_predictor_5_face_landmarks.dat.bz2 del shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2
- Windows のコマンドプロンプトを開く
- Python プログラムファイルの作成
ここでは,ファイル名は cluster.py とする.
cd /d c:%HOMEPATH% cd face_recognition notepad cluster.py
ソースコードは次の通り.
次のソースコードは,Dlib に付属の python_examples\face_clustering.py (パブリックドメイン)を書き替えたもの.
太字が書き換え部分.顔画像のすべてを出力するように変更.
#!/usr/bin/python # The contents of this file are in the public domain. See LICENSE_FOR_EXAMPLE_PROGRAMS.txt # # This example shows how to use dlib's face recognition tool for clustering using chinese_whispers. # This is useful when you have a collection of photographs which you know are linked to # a particular person, but the person may be photographed with multiple other people. # In this example, we assume the largest cluster will contain photos of the common person in the # collection of photographs. Then, we save extracted images of the face in the largest cluster in # a 150x150 px format which is suitable for jittering and loading to perform metric learning (as shown # in the dnn_metric_learning_on_images_ex.cpp example. # https://github.com/davisking/dlib/blob/master/examples/dnn_metric_learning_on_images_ex.cpp # # COMPILING/INSTALLING THE DLIB PYTHON INTERFACE # You can install dlib using the command: # pip install dlib # # Alternatively, if you want to compile dlib yourself then go into the dlib # root folder and run: # python setup.py install # # Compiling dlib should work on any operating system so long as you have # CMake installed. On Ubuntu, this can be done easily by running the # command: # sudo apt -y install cmake # # Also note that this example requires Numpy which can be installed # via the command: # pip install numpy import sys import os import dlib import glob if len(sys.argv) != 5: print( "Call this program like this:\n" " ./face_clustering.py shape_predictor_5_face_landmarks.dat dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat ../examples/faces output_folder\n" "You can download a trained facial shape predictor and recognition model from:\n" " http://dlib.net/files/shape_predictor_5_face_landmarks.dat.bz2\n" " http://dlib.net/files/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat.bz2") exit() predictor_path = sys.argv[1] face_rec_model_path = sys.argv[2] faces_folder_path = sys.argv[3] output_folder_path = sys.argv[4] # Load all the models we need: a detector to find the faces, a shape predictor # to find face landmarks so we can precisely localize the face, and finally the # face recognition model. detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector() sp = dlib.shape_predictor(predictor_path) facerec = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1(face_rec_model_path) descriptors = [] images = [] # Now find all the faces and compute 128D face descriptors for each face. for f in glob.glob(os.path.join(faces_folder_path, "*.jpg")): print("Processing file: {}".format(f)) img = dlib.load_rgb_image(f) # Ask the detector to find the bounding boxes of each face. The 1 in the # second argument indicates that we should upsample the image 1 time. This # will make everything bigger and allow us to detect more faces. dets = detector(img, 1) print("Number of faces detected: {}".format(len(dets))) # Now process each face we found. for k, d in enumerate(dets): # Get the landmarks/parts for the face in box d. shape = sp(img, d) # Compute the 128D vector that describes the face in img identified by # shape. face_descriptor = facerec.compute_face_descriptor(img, shape) descriptors.append(face_descriptor) images.append((img, shape)) # Now let's cluster the faces. labels = dlib.chinese_whispers_clustering(descriptors, 0.5) num_classes = len(set(labels)) print("Number of clusters: {}".format(num_classes)) if not os.path.isdir(output_folder_path): os.makedirs(output_folder_path) # Find biggest class biggest_class = None biggest_class_length = 0 for i in range(0, num_classes): print(i) indices = [] for k, label in enumerate(labels): if label == i: indices.append(k) for k, index in enumerate(indices): img, shape = images[index] file_path = os.path.join(output_folder_path, "face_" + str(i) + "_" + str(k)) dlib.save_face_chip(img, shape, file_path, size=150, padding=0.25) - Python プログラムの実行
python cluster.py ..\dlib\python_examples\shape_predictor_5_face_landmarks.dat ..\dlib\python_examples\dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat ..\examples\faces output_folder
- 結果を確認
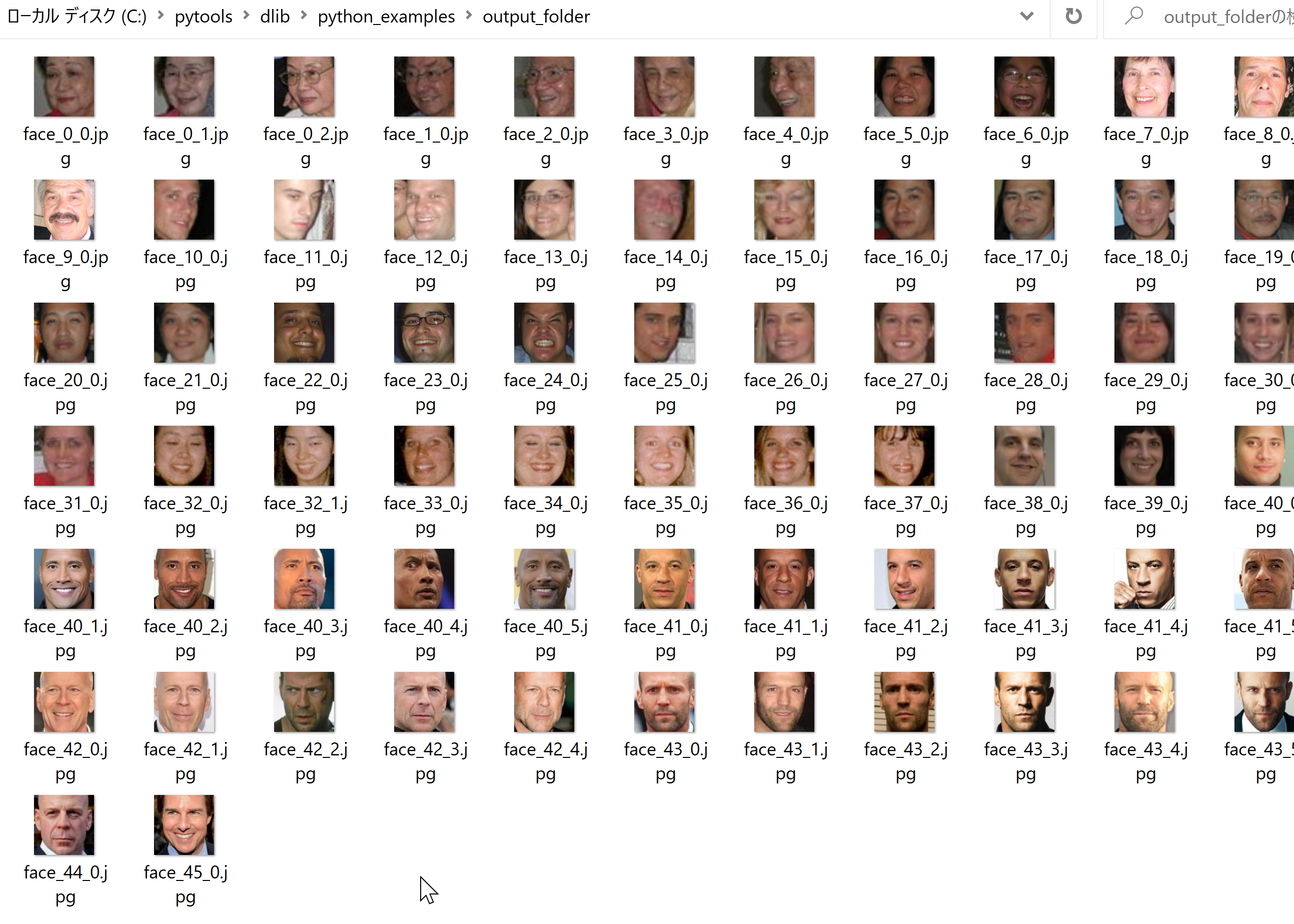
「..\examples\faces」の下にあったすべてのファイルについて顔が抽出され,Dlib の chinese_whispers_clustering によりクラスタリングが行われる.
結果の画像ファイル名は output_folder に入る. 画像ファイル名は「face_<クラスタ番号>_<クラスタ内での番号>」になる.
次のような結果が得られる.
【関連する外部サイト】
【サイト内の関連ページ】
Visual Studio 2022 Build Toolsとランタイムのインストール
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要である。
REM Visual Studio 2022 Build Toolsとランタイムのインストール
winget install --scope machine --wait --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements Microsoft.VisualStudio.2022.BuildTools Microsoft.VCRedist.2015+.x64
REM インストーラーとインストールパスの設定
set VS_INSTALLER="C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\Installer\vs_installer.exe"
set VS_PATH="C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\BuildTools"
REM C++開発ワークロードのインストール(次のコマンドは全体で1行である)
%VS_INSTALLER% modify --installPath %VS_PATH% --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Workload.VCTools --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Tools.x86.x64 --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.Windows11SDK.22621 --includeRecommended --quiet --norestart
Git のインストール(Windows 上)
Gitは,バージョン管理システム.ソースコードの管理や複数人での共同に役立つ.
【サイト内の関連ページ】 Windows での Git のインストール: 別ページ »で説明
【関連する外部ページ】 Git の公式ページ: https://git-scm.com/
Gitのインストール
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
REM Git をシステム領域にインストール
7-Zip のインストール
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
REM 7-Zip をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id 7zip.7zip -e --silent
REM 7-Zip のパス設定
set "SEVENZIP_PATH=C:\Program Files\7-Zip"
if exist "%SEVENZIP_PATH%" (
echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%SEVENZIP_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%SEVENZIP_PATH%" /M >nul
)
Dlib のインストール
Dlib のソースコード等と,Dlib の学習済みモデルのダウンロード
顔のクラスタリング
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)