Ubuntu, Fedora で,パッケージを用いて Octave をインストール
このページでは, Ubuntu, Fedora で,パッケージを用いて Octave をインストールする手順を図解などで説明します.
- Ubuntu 12.04 で, パッケージを用いて octave バージョン 3.2.4 をインストール
- Fedora 16 で, パッケージを用いて octave バージョン 3.4.3 をインストール
貴重な情報源: http://www40.atwiki.jp/gnuoctavejp (Octave for Windows メモの著者様による Wiki)
(参考)
* liboctave の使い方については,別の Web ページで説明しています.liboctave を使って,Octave の行列関係の機能を呼び出すような C++ のプログラムを簡単に作ることができます.
* Octave に BLAS (GotoBLAS あるいは ATLAS) と LAPACK を組み込みたい. あるいは Intel Math Kernel Library (インテル・マス・カーネル・ライブラリ) とリンクさせたい場合には, ソースコードを使って Octave をビルドする必要があるでしょう. その手順は,別の Web ページで説明しています.
【関連する外部ページ】
- Octave オンラインマニュアル: https://www.gnu.org/software/octave/
Octave のインストールの手順
* Ubuntu 12.04 の場合の操作手順(例)
Ubuntu の他のバージョンでも同様の手順になります
- アップデート操作
端末で次のように操作する。
◆ Ubuntu の場合の操作手順(例)
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get -yV upgrade sudo shutdown -r now - パッケージを用いてインストール
◆ Ubuntu の場合の操作手順(例)
sudo apt-get -yV install libatlas* sudo apt-get -yV install octave sudo apt-get -yV install octave-pkg-dev sudo apt-get -yV install octave-* sudo apt-get -yV install gmt sudo apt-get -yV install gmt-examples sudo apt-get -yV install gmt-tutorial-pdf sudo apt-get -yV install gmt-doc-pdf sudo apt-get -yV install gmt-coast-low sudo apt-get -yV install pfstools sudo apt-get -yV install libplplot11 sudo apt-get -yV install qtoctave - 試しに起動してみる.
インストールはこれで終了.
* Fedora バージョン 16 での手順(例)
'yum を使ってインストールします.
* 自前で atlas をビルドした場合には「yum install atlas*」は無視して下さい.
- yum を使ってインストール
yum install atlas* yum install octave* yum install *octave*
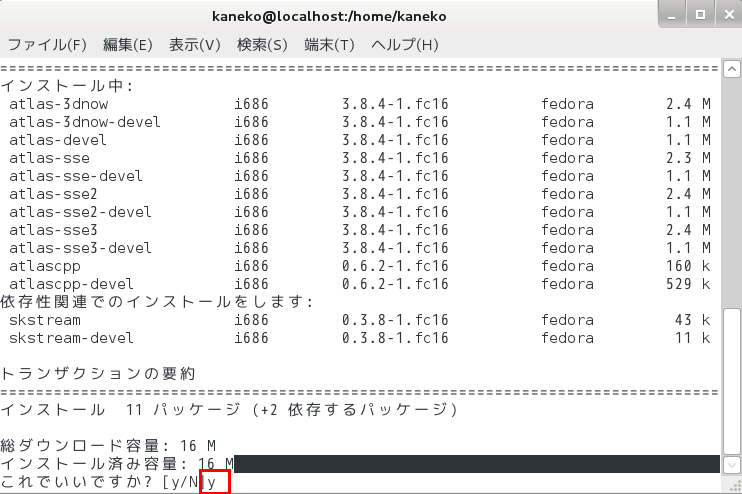

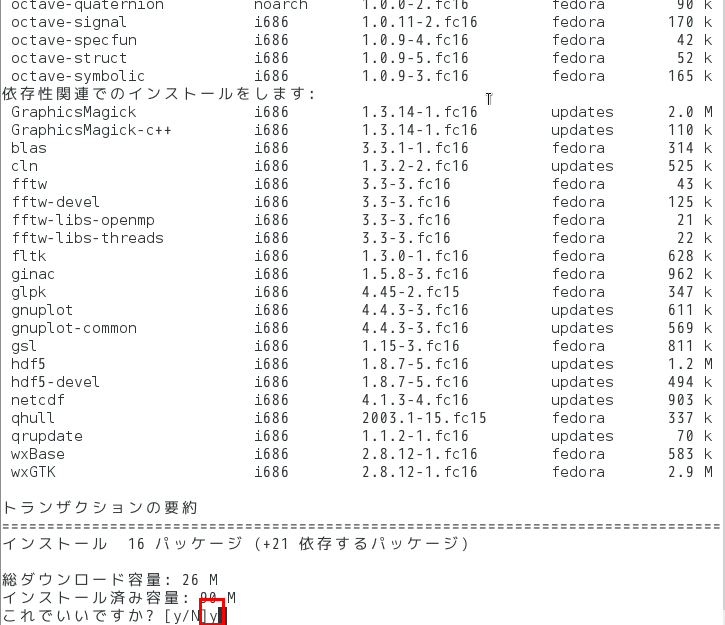

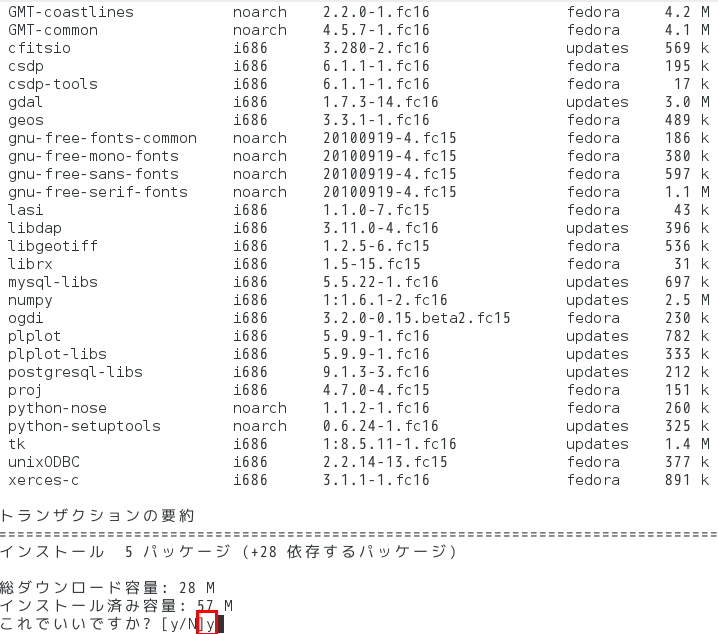
- 試しに起動してみる.
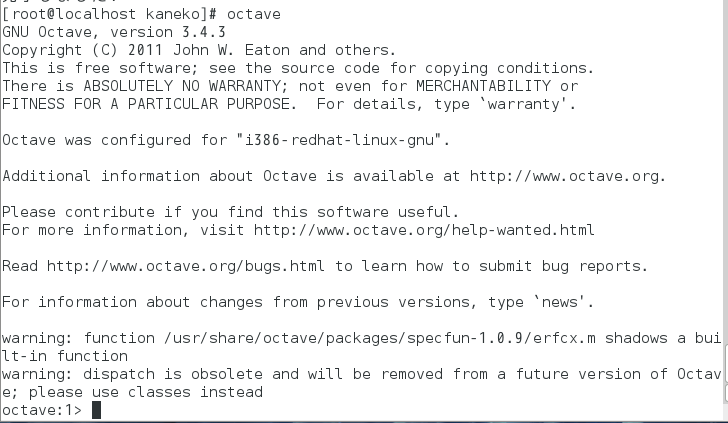
インストールはこれで終了.
ATLAS をインストールする理由
性能が向上します。インストール操作は簡単で、効果は高いです。
- CPU: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-3770K CPU @ 3.50GHz
- OS: Ubuntu 12.04 64 bit
- OS: Ubuntu 12.04 64 bit
- Octave バージョン 3.2.4 (パッケージを用いてインストール)
* 「sudo apt-get -yV install libatlas*」を行った場合
* 「sudo apt-get -yV install libatlas*」を行わなかった場合
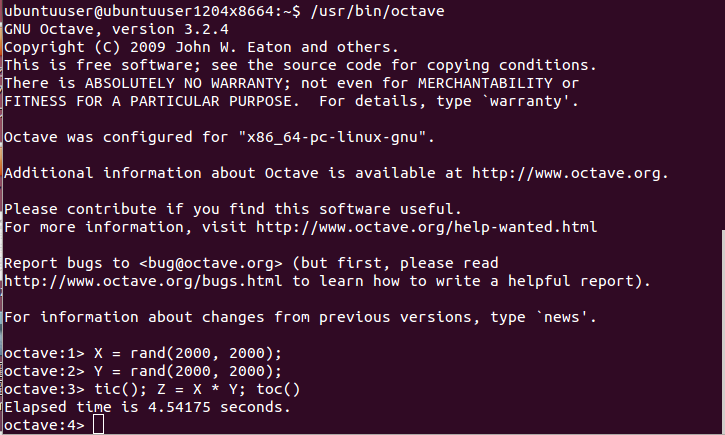
性能測定の例
| (a) | 行列と行列の積 | X = rand(2000,2000); Y = rand(2000,2000); Z = X * Y | 1.25 sec |
| (b) | LU 分解 (LU decomposition) | X = rand(2000,2000); [L, U, P] = lu(X) | 0.67 sec |
| (c) | 正方行列の逆行列 | X = rand(2000,2000); [Z, RCOND] = inv(X) | 1.72 sec |
| (d) | 行列式 (determinant) | X = rand(2000,2000); [D, RCOND] = det(X) | 0.63 sec |
| (e) | Singular Value Decomposition (SVD), X = U*S*V | X = rand(2000,2000); [U, S, V] = svd(X) | 72 sec |
| (f) | QR factorization | X = rand(2000,2000); [Q, R, P] = qr(X) | 4.2 sec |
| (g) | 分散共分散行列 | X = rand(2000,2000), Y = rand(2000,2000); Z = cov(X, Y) | 1.34 sec |
| (h) | 分散共分散行列の固有値と固有ベクトル(主成分分析) | X = rand(2000,2000); [v, L] = eig( cov(X) ) | 13.3 sec |
| (i) | 2次元の畳み込み(コンボリューション) | X = rand(2000,2000); B = rand(21); Z = conv2(X, B, 'full') | 4.1 sec |
| (j) | 2次元の高速フーリエ変換 (FFT) | X = rand(2000,2000); Z = fft2(X, 2000, 2000) | 0.105 sec |
| (k) | convex hull | x = rand(1000000,1); y = rand(1000000,1); H = convhull(x, y) | 0.51 sec |
- ハードウェア
- CPU: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-3770K CPU @ 3.50GHz
- ソフトウェア
- OS: Ubuntu 12.04 64 bit
- Octave バージョン 3.2.4 (パッケージを用いてインストール)
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)