IMDb データセットによる学習と分類(TensorFlow データセット,TensorFlow,Python を使用)(Windows 上,Google Colaboratroy の両方を記載)
ニューラルネットワークの作成,学習,データの2クラス分類を行う. IMDb データセットを使用する.
【目次】
- Google Colaboratory での実行
- Windows での実行
- IMDb データセットのロード
- IMDb データセットの確認
- Keras を用いたニューラルネットワークの作成
- ニューラルネットワークの学習と検証
【関連する外部ページ】
- 「https://keras.io/ja/」の「30 秒で Keras に入門しましょう」
- TensorFlow のチュートリアルの Web ページ: https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/quickstart
1. Google Colaboratory での実行
Google Colaboratory のページ:
次のリンクをクリックすると,Google Colaboratory のノートブックが開く. そして,Google アカウントでログインすると,Google Colaboratory のノートブック内のコード等を編集したり再実行したりができる.編集した場合でも,他の人に影響が出たりということはない.そして,編集後のものを,各自の Google ドライブ内に保存することもできる.
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1hBMPOyUaDCTNYqOcHoQRiilznK728r_T?usp=sharing
2. Windows での実行
Python 3.12,Git のインストール(Windows 上)
Pythonは,プログラミング言語の1つ. Gitは,分散型のバージョン管理システム.
【手順】
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。次のコマンドを実行
次のコマンドは,Python ランチャーとPython 3.12とGitをインストールし,Gitにパスを通すものである.
次のコマンドでインストールされるGitは 「git for Windows」と呼ばれるものであり, Git,MinGW などから構成されている.
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem" /v LongPathsEnabled /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f REM Python, Git をシステム領域にインストール winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 --id Python.Launcher --id Git.Git -e --silent REM Python のパス set "INSTALL_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312" echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%INSTALL_PATH%" >nul if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%INSTALL_PATH%" /M >nul echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%INSTALL_PATH%\Scripts" >nul if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%INSTALL_PATH%\Scripts" /M >nul REM Git のパス set "NEW_PATH=C:\Program Files\Git\cmd" if exist "%NEW_PATH%" echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%NEW_PATH%" >nul if exist "%NEW_PATH%" if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%NEW_PATH%" /M >nul
【関連する外部ページ】
- Python の公式ページ: https://www.python.org/
- Git の公式ページ: https://git-scm.com/
【サイト内の関連ページ】
【関連項目】 Python, Git バージョン管理システム, Git の利用
TensorFlow 2.10.1 のインストール(Windows 上)
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - TensorFlow 2.10.1 のインストール(Windows 上)
次のコマンドを実行することにより,TensorFlow 2.10.1 および関連パッケージ(tf_slim,tensorflow_datasets,tensorflow-hub,Keras,keras-tuner,keras-visualizer)がインストール(インストール済みのときは最新版に更新)される. そして,Pythonパッケージ(Pillow, pydot, matplotlib, seaborn, pandas, scipy, scikit-learn, scikit-learn-intelex, opencv-python, opencv-contrib-python)がインストール(インストール済みのときは最新版に更新)される.
python -m pip uninstall -y protobuf tensorflow tensorflow-cpu tensorflow-gpu tensorflow-intel tensorflow-text tensorflow-estimator tf-models-official tf_slim tensorflow_datasets tensorflow-hub keras keras-tuner keras-visualizer python -m pip install -U protobuf tensorflow==2.10.1 tf_slim tensorflow_datasets==4.8.3 tensorflow-hub tf-keras keras keras_cv keras-tuner keras-visualizer python -m pip install git+https://github.com/tensorflow/docs python -m pip install git+https://github.com/tensorflow/examples.git python -m pip install git+https://www.github.com/keras-team/keras-contrib.git python -m pip install -U pillow pydot matplotlib seaborn pandas scipy scikit-learn scikit-learn-intelex opencv-python opencv-contrib-python
Graphviz のインストール
Windows での Graphviz のインストール: 別ページ »で説明
numpy,matplotlib, seaborn, scikit-learn, pandas, pydot のインストール
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。次のコマンドを実行する.
python -m pip install -U numpy matplotlib seaborn scikit-learn pandas pydot
IMDb データセットのロード
【Python の利用】
Python は,次のコマンドで起動できる.
Python 開発環境(Jupyter Qt Console, Jupyter ノートブック (Jupyter Notebook), Jupyter Lab, Nteract, Spyder, PyCharm, PyScripterなど)も便利である.
Python のまとめ: 別ページ »にまとめ
- Windows で,コマンドプロンプトを実行.
- jupyter qtconsole の起動
これ以降の操作は,jupyter qtconsole で行う.
jupyter qtconsole
Python 開発環境として,Jupyter Qt Console, Jupyter ノートブック (Jupyter Notebook), Jupyter Lab, Nteract, spyder のインストール
Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。し,次のコマンドを実行する.次のコマンドを実行することにより,pipとsetuptoolsを更新する,Jupyter Notebook,PyQt5、Spyderなどの主要なPython環境がインストールされる.
python -m pip install -U pip setuptools requests notebook==6.5.7 jupyterlab jupyter jupyter-console jupytext PyQt5 nteract_on_jupyter spyder
- パッケージのインポート,TensorFlow のバージョン確認など
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras import layers from tensorflow.keras import backend as K K.clear_session() import numpy as np import tensorflow_datasets as tfds from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings # TensorFlow のバージョン print(tf.__version__) # GPU を利用しているか gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices(device_type = 'GPU') if len(gpus)>0: print(f">> GPU detected. {gpus[0].name}") tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpus[0], True)
- IMDb データセットのロード
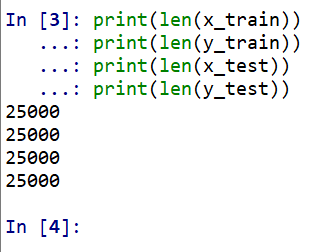
x_train: 25000件のデータ,批評文
y_train: 25000件のデータ,ラベル(ラベルの値は 0 または 1)
x_test: 25000件のデータ,批評文
y_test: 25000件のデータ,ラベル(ラベルの値は 0 または 1)
IMDb での映画の批評は,批評文とスコア(10点満点)である.
IMDb の URL: https://www.imdb.com/
IMDb データセットでは,7点以上の批評は positive,4点以下の批評は negative としている.つまり,2種類ある. そして,IMDb データセットには,positive か negative の批評のみが含まれている(中間の点数である 5点,6点のものは含まれていない).そして, positive,negative の批評が同数である. 学習用として,positive,negative がそれぞれ 25000. テスト用として,positive,negative がそれぞれ 25000.
IMDb データセットのURL: https://ai.stanford.edu/%7Eamaas/data/sentiment/
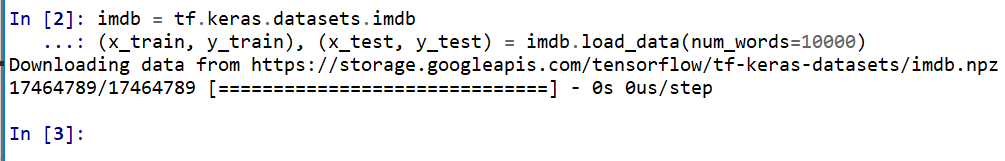
imdb = tf.keras.datasets.imdb (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = imdb.load_data(num_words=10000)
IMDb データセットの確認
- IMDb データセット要素数の確認
print(len(x_train)) print(len(y_train)) print(len(x_test)) print(len(y_test))
- IMDb データセットの確認
まず,単語を整数にマッピングするなどを行う.
# 単語を整数にマッピングする辞書 word_index = imdb.get_word_index() # インデックスの最初の方は予約済み word_index = {k:(v+3) for k,v in word_index.items()} word_index["<PAD>"] = 0 word_index["<START>"] = 1 word_index["<UNK>"] = 2 # unknown word_index["<UNUSED>"] = 3 reverse_word_index = dict([(value, key) for (key, value) in word_index.items()]) def decode_review(text): return ' '.join([reverse_word_index.get(i, '?') for i in text])
批評文の確認
0番目の批評文とその単語数を表示.
x_train は費用文のデータセットである. x_train[0] は 0 番目の批評文である. 批評文は整数のリストになっている. それぞれの整数は,単語をコード化したものである. それぞれの整数を decode_review を使って単語に変換.
print(decode_review(x_train[0])) print(len(x_train[0]))

1番目の批評文とその単語数を表示.
print(decode_review(x_train[1])) print(len(x_train[1]))

ラベルの確認
print(y_train[0])

print(y_train[1])
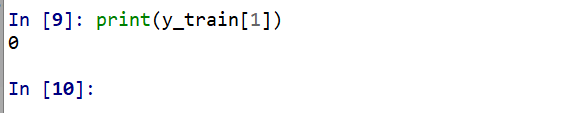
Keras を用いたニューラルネットワークの作成
- ニューラルネットワークを使うために,データの前処理
パッデングを行う. 批評文のそれぞれは長さが異なるのを,同じ長さ 256 にそろえる.
詳細は https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/keras/text_classification?hl=ja に説明がある.
x_train = tf.keras.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(x_train, value=word_index["<PAD>"], padding='post', maxlen=256) x_test = tf.keras.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(x_test, value=word_index["<PAD>"], padding='post', maxlen=256)

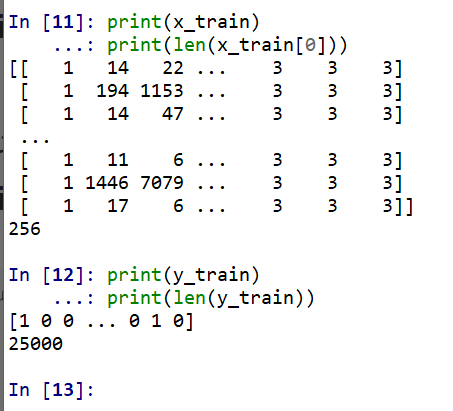
- x_train, y_train の確認
print(x_train) print(len(x_train[0]))
print(y_train) print(len(y_train))
- ニューラルネットワークの作成と確認とコンパイル
- ニューラルネットワークの種類: 層構造 (Sequential Model)
- 1番目の層: embedding
- 2番めの層: 平均プーリング
- 3番目の層: sigmoid, 値は確率を表す 0 から 1 の間の浮動小数点数
# 入力の形式は映画レビューで使われている語彙数(10,000語) VOCAB_SIZE = 10000 m = tf.keras.Sequential( [ layers.Embedding(VOCAB_SIZE, 16), layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D(), layers.Dense(16, activation='relu'), layers.Dense(1, activation=tf.nn.sigmoid) ] ) m.summary()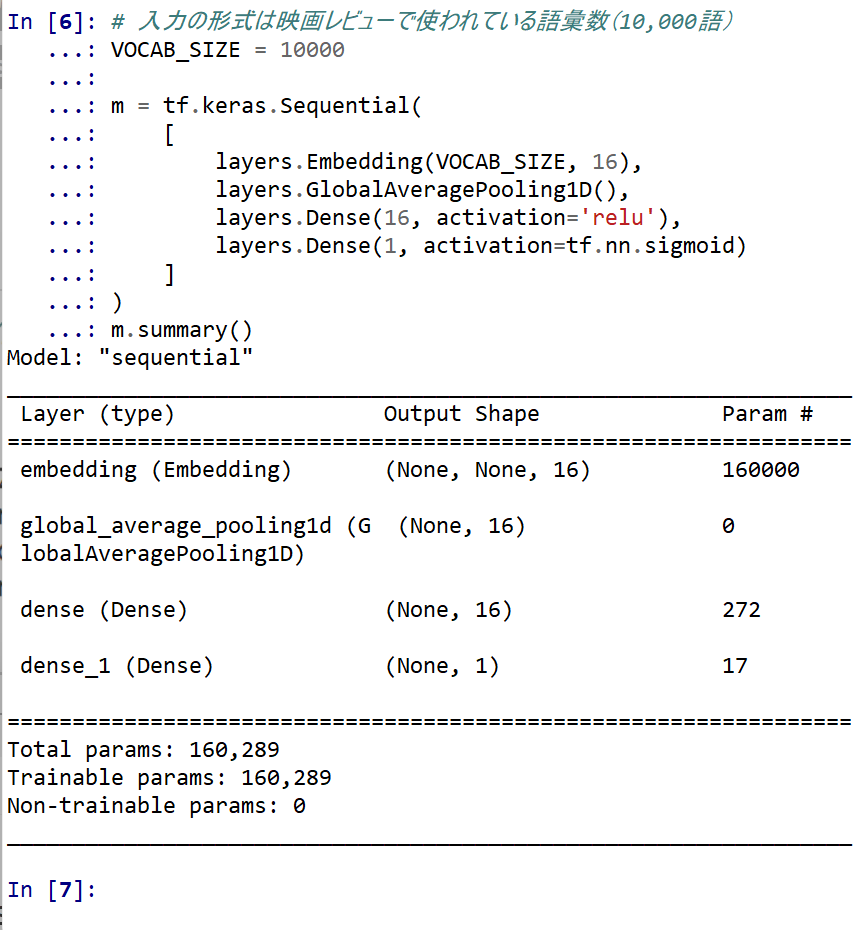
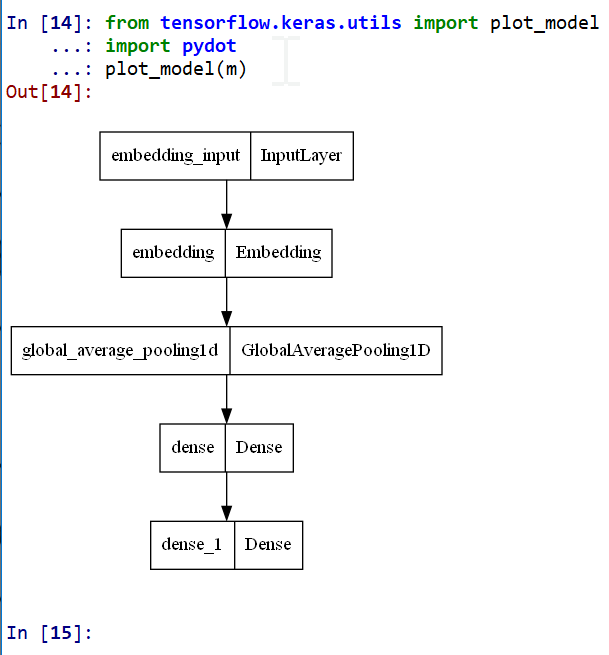
- モデルのビジュアライズ
Keras のモデルのビジュアライズについては: https://keras.io/ja/visualization/
ここでの表示で,エラーメッセージが出る場合でも,モデル自体は問題なくできていると考えられる.続行する.
from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model import pydot plot_model(m)
ニューラルネットワークの学習と検証
- 学習(訓練)
EPOCHS = 40 m.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001), loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) history = m.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=EPOCHS, batch_size=512, validation_data=(x_test, y_test), verbose=1)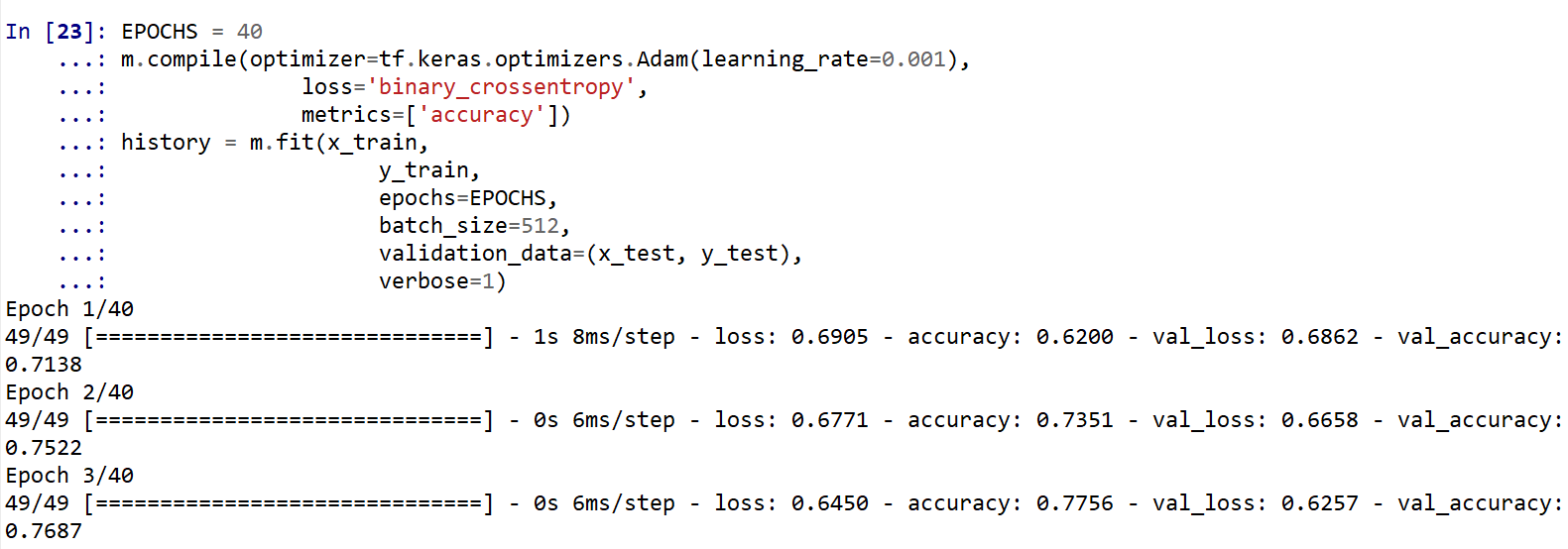
- ニューラルネットワークによるデータの2クラス分類
print(m.predict(x_test))
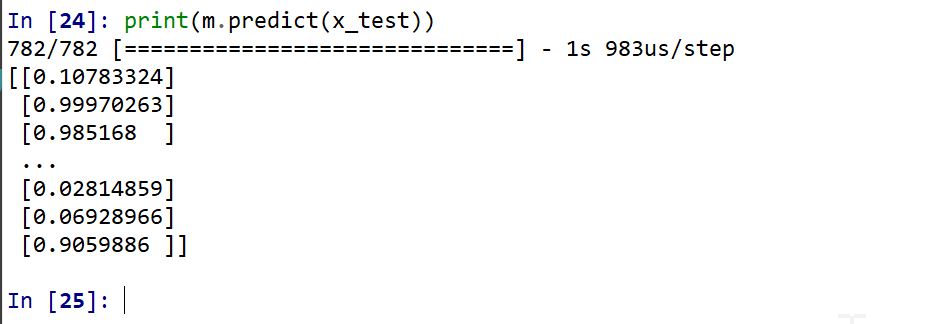
(以下省略)y_test 内にある正解のラベル(クラス名)を表示する(上の結果と比べるため)
print(y_test)

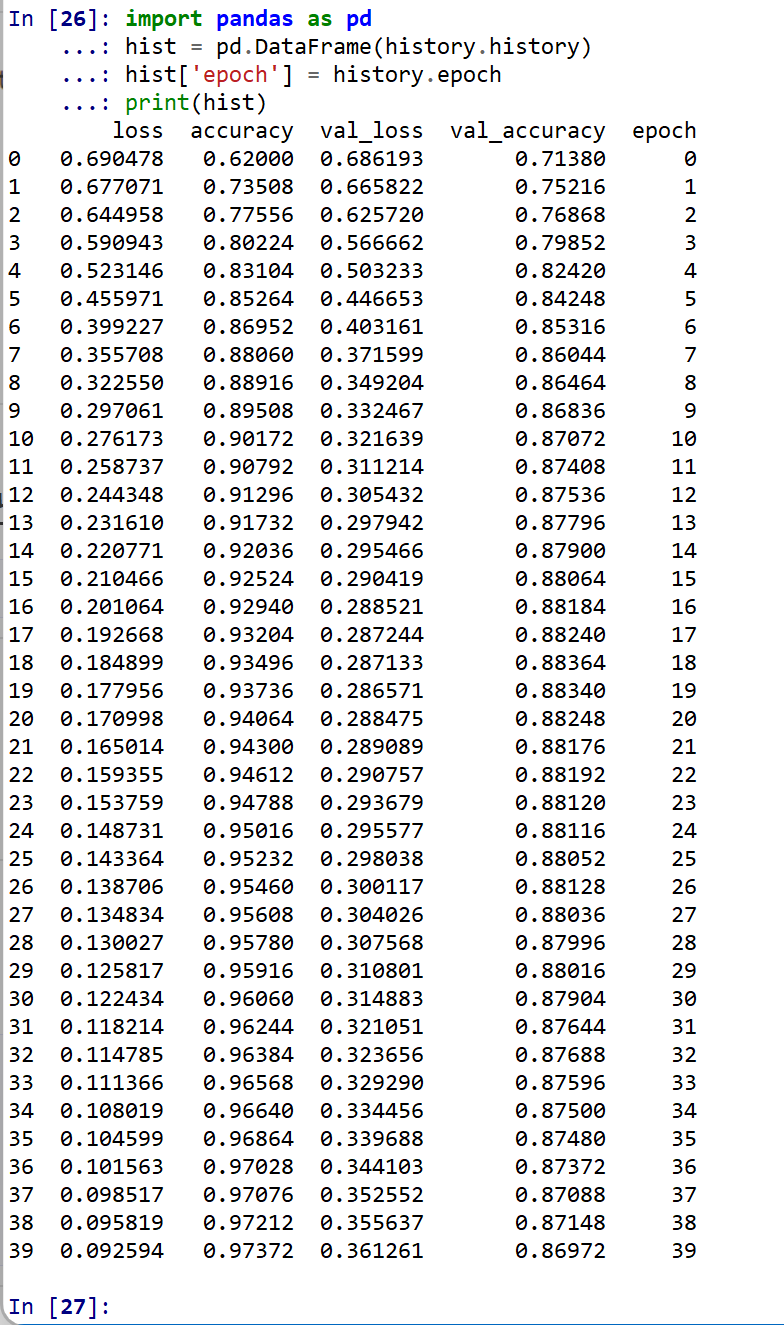
- 学習曲線の確認
過学習や学習不足について確認.
import pandas as pd hist = pd.DataFrame(history.history) hist['epoch'] = history.epoch print(hist)
- 学習曲線のプロット
学習時と検証時で,大きく損失や精度が違っており,過学習が起きていることが確認できる
- 学習時と検証時の,損失の違い
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings accuracy = history.history['accuracy'] val_accuracy = history.history['val_accuracy'] loss = history.history['loss'] val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] epochs = range(1, len(accuracy) + 1) # "bo" は青いドット plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss') # ”b" は青い実線 plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss') plt.title('Training and validation loss') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Loss') plt.legend() plt.show()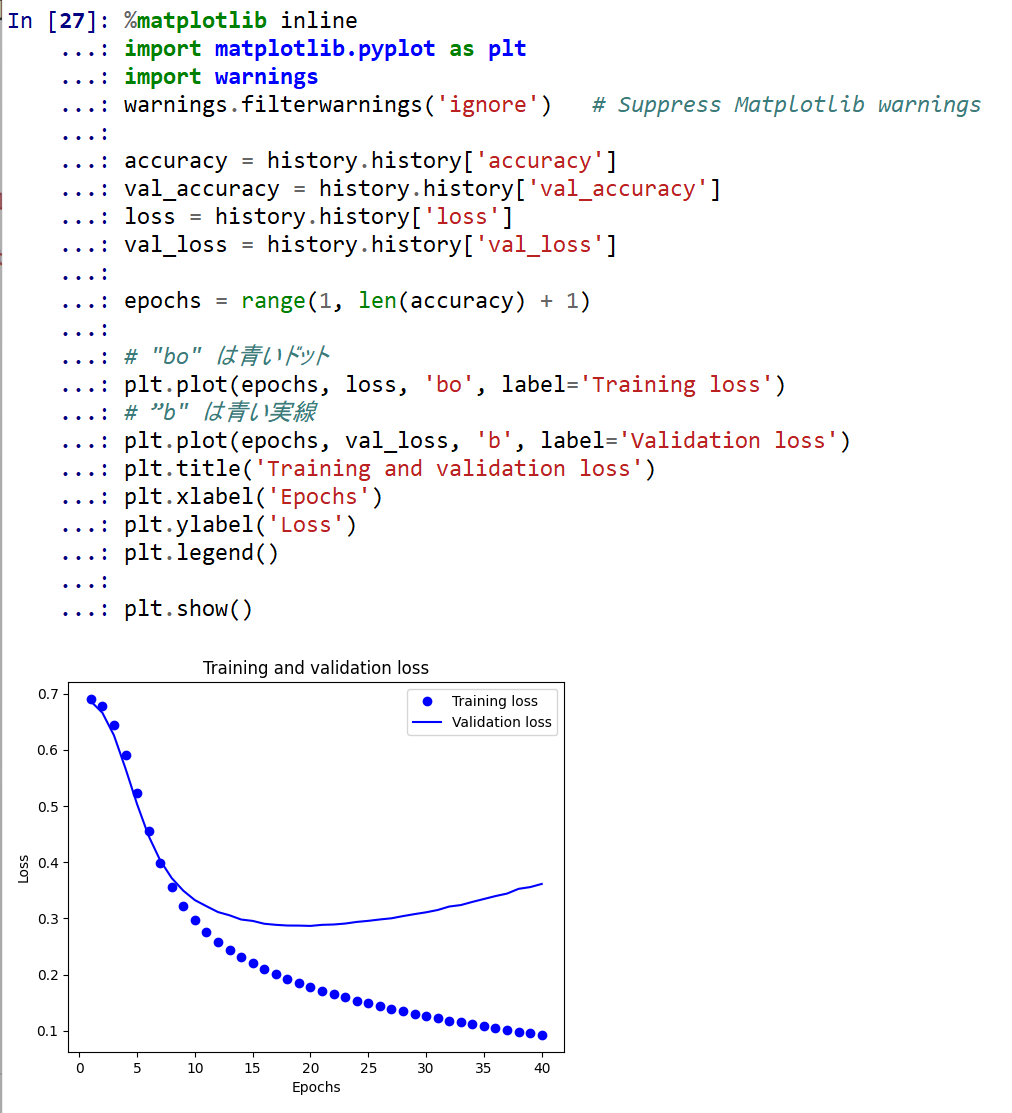
- 学習曲線
# plt.clf() # 図のクリア accuracy = history.history['accuracy'] val_accuracy = history.history['val_accuracy'] plt.plot(epochs, accuracy, 'bo', label='Training acc') plt.plot(epochs, val_accuracy, 'b', label='Validation acc') plt.title('Training and validation accuracy') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.legend() plt.show()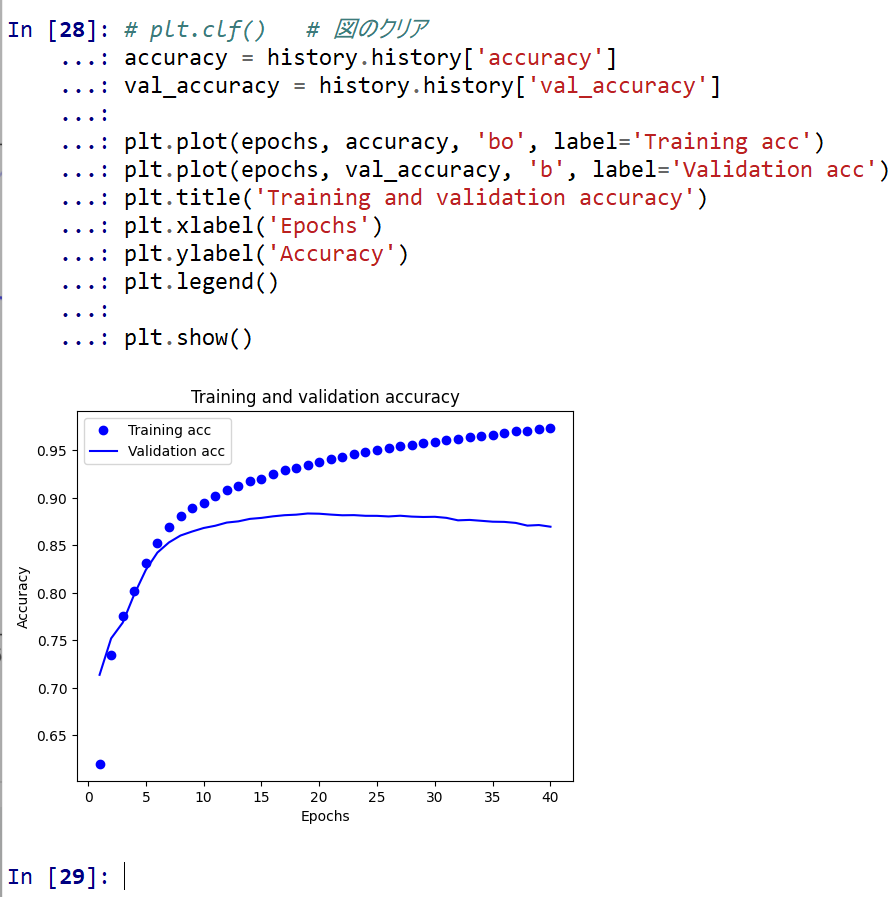
- 学習曲線
- ニューラルネットワークによるデータの2クラス分類
- x_train, y_train の確認
- IMDb データセットの確認
- パッケージのインポート,TensorFlow のバージョン確認など
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)