Ruby で SQL のテーブル定義
リレーショナルデータベースのテーブルのデータ型 (Data Types of Relational Database Table)
| MySQL の主なデータ型 (MySQL main data types) | PostgreSQL の主なデータ型 (PostgreSQL main data types) | SQLite 3 の主なデータ型 (SQLite 3 main data types) | DataMapper のプロパティ(DataMapper properties) | ActiveRecord で SQLite 3 を使う場合 (*1) | ||
| 真偽値 (boolean) | bool, boolean | boolean | Boolean | :boolean | ||
| 文字列 (character string) | 固定長 (fixed length and padded) | character(n), char(n) | character(n), char(n) | |||
| 可変長 (variable length) | tinytext, text, mediumtext, longtext, character varing(n), varchar(n) | text, character varing(n), varchar(n) | text | String, Text | :string, :text | |
| 整数 (integer) | [-32768, 32767] | smallint | smallint | integer | Integer | :integer |
| [-2147483648, 2147483648] | integer, int | integer, int | ||||
| [-9223372036854775808, 9223372036854775807] | bigint | bigint | ||||
| 可変長 (variable length) | decimal, fixed, dec, numeric | decimal, numeric | Decimal | :decimal | ||
| 浮動小数点数 (floating point number) | single precision | float | real | Float | ||
| double precision | double, double precision, real | double precision | real | :float | ||
| 年月日時分秒 (datetime) | datetime, timestamp | timestamp(n) | DateTime | :datetime, :timestamp | ||
| 年月日 (date) | date | date | Date | :date | ||
| 時分秒 (time) | time | time(n) | Time | :time | ||
| 可変長バイナリ型 (variable length binary data) | tinyblob, blob, mediumblob, longblob | bytea | blob | Binary | :binary | |
| marshalled object | Object | |||||
| a NULL value | NULL | NULL | NULL | |||
*1: Active Record が対応しているデータ型
:primary_key, :string, :text, :integer, :float, :decimal, :datetime, :timestamp, :time, :date, :binary, :boolean です.
(参考: http://guides.rails.info/migrations.html). これ以外を使うとうまく動かない(しかも、ひな形の生成時には、エラーメッセージは出ない)
ruby script/rails generate scaffold t id:primary_key a1:integer a2:string a3:text a4:integer a5:float a6:decimal a7:datetime a8:timestamp a9:time a10:date a11:binary a12:boolean
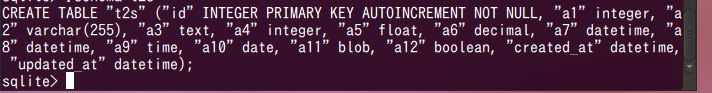
SQLite 3 での列制約とテーブル制約 (Column Constraint and Table Constraint of SQLite 3)
- SQL テーブル定義文 (create-table-statement)
create table <table-name> (<column-def> の並び, [<table-constraint> の並び]);
* 「 <table-constraint> の並び」は省略可能であることに注意
- 列定義 (column-def)
<column-name> <type-name> [<column constraint> の並び]
* 「<column constraint>」は省略可能であることに注意
- SQL 列制約 (column-constraint) の例
create-table-statement の中に含める一貫性制約やデフォルト値の指定
- PRIMARY KEY ・・・ 主キー制約
- not null ・・・ 非空制約
- UNIQUE ・・・ 一意制約
- CHECK (<expression>) ・・・ 更新時にチェックされる式 ( expression) ※ SQLite 固有の機能
- REFERENCES <foreign-table> (<column-name>, ...) ・・・ 参照整合性制約
- DEFAULT (<expression>) ・・・ デフォルト値 (default value) の指定
- autoincrement ・・・ 自動インクリメント (auto increment)
- SQL テーブル制約 (table-constraint) の例
create-table-statement の中に含める一貫性制約のうち複数の属性に関わるものは table-constraint の形で記述することになる.
- PRIMARY KEY(<indexed-column>, ...)
- UNIQUE(<indexed-column>, ...)
- CHECK(<expression>)
Active Record での列制約の記述
主なものを次に挙げます.詳しくは https://api.rubyonrails.org/classes/ActiveRecord/ConnectionAdapters/TableDefinition.html を見てください
- 「primary_key」: 主キー制約
- 「belongs_to」: 参照整合性制約
- 「:null =>l false」: 非空制約 (SQL の not null)
- 「:default => ...」: デフォルト値
- 「:limit」: 文字列の最大長
- 「:precision」: decimal の桁数
DataMapper での列制約
主なものを次に挙げます.詳しくは https://rom-rb.org
テーブル定義に反映される列制約
- 「Serial」: INTEGER not null PRIMARY KEY autoincrement
- 「has_n, belongs_to」: 参照整合性制約
- 「:required => true」: 非制約空
- 「:unique => true」: 一意制約
- 「:default => val」: デフォルト値
Ruby 側で妥当性検査 (validation) が行われるもの
- 「:max => n」: 最大値
- 「:min => n」: 最小値
- 「:length => n..m」: 文字列の長さ
- 「:format => ...」: 書式のチェック
- 「:format => :email_address」:
- 「:format => :url」:
- 「:format => /<正規表現>/l」:
DataMapper のインストール
ここで行うこと.
Ruby のプログラムから DataMapper を使って sqlite3 のデータベースを扱えるように、いくつかのソフトウェアをインストールする.
- dm-sqlite-adapter のインストール
- ruby のインストール (rvm を使用.rvm は前もってインストールしておくこと)
- rails のインストール
- rails の空のアプリケーションの生成
- DataMapper のインストール
DataMapper のインストールを Rails のツール (bundle install) を使って行うことにする.
- dm-sqlite-adapter のインストール
- Ubuntu
sudo apt -y update sudo apt -y install libsqlite3-dev
- RedHat / Fedora
sudo yum install sqlite-devel
- MacPorts
sudo port install sqlite3
- Ubuntu
- rvm を用いて Ruby 1.9.2 のインストール
rvm install ruby-1.9.2-head rvm list rvm use ruby-1.9.2-head - rails のインストール
gem install rails - Rails アプリケーションの生成と,DataMapper 等のインストール
rails new hogeapp -d sqlite3 -m http://datamapper.org/templates/rails.rb cd hogeapp bundle install - gem を用いて data_mapper のインストール
あとで使いたい
sudo gem install data_mapper
DataMapper を使ってみる
ここで行うこと
- 使用する sqlite3 データベースファイル名: /home/windowslike/hoge.db
- 次のテーブル定義と一貫性制約の記述を行う
(Table defintion and integrity constraint specification using SQL)
リレーショナル・スキーマ (relational schema): order_records(id, year, month, day, customer_name, product_name, unit_price, qty)
SQL プログラム:
create table order_records ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY autoincrement not null, year INTEGER not null, month INTEGER not null, day INTEGER not null, customer_name TEXT not null, product_name TEXT not null, unit_price REAL not null, qty INTEGER not null DEFAULT 1, created_at DATETIME not null, updated_at DATETIME, - テーブルの生成
- SQL 問い合わせの発行と評価結果の確認も行う.(Issue SQL queries and inspect the results)
SELECT * FROM order_records WHERE id = 1; SELECT * FROM order_records; SELECT * FROM order_records WHERE day = 25; SELECT * FROM order_records WHERE customer_name = 'kaneko'; SELECT * FROM order_records WHERE unit_price > 200;
- テーブル定義
次の手順で、irb を使って、プログラムを実行する ここでは、OrderRecord クラスを定義し, 「DataMapper.auto_migrate!」でマイグレーションを行なって、テーブル order_records を作る(この時点では、テーブルは空)。
irb require 'rubygems' # require 'data_mapper' require 'dm-core' # # An in-memory Sqlite3 connection: # DataMapper.setup(:default, 'sqlite::memory:') # A Sqlite3 connection to a persistent database DataMapper.setup(:default, 'sqlite:///home/windowslike/hoge.db') class OrderRecord include DataMapper::Resource property :id, Serial # INTEGER not null PRIMARY KEY autoincrement property :year, Integer, :required => true, :min => 2011 property :month, Integer, :required => true, :min => 1, :max => 12 property :day, Integer, :required => true, :min => 1, :max => 31 property :customer_name, String, :required => true property :product, String, :required => true property :unit_price, Float, :required => true, :min => 0 property :qty, Integer, :required => true, :default => 1, :min => 1 property :created_at, DateTime, :required => true property :updated_at, DateTime end DataMapper.finalize require 'dm-migrations' DataMapper.auto_migrate! exit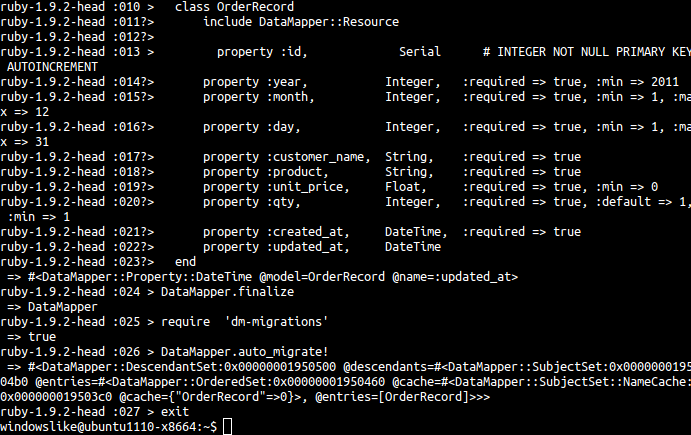
- テーブル定義の確認
テーブル order_records が定義されていることを確認
sqlite3 /home/windowslike/hoge.db select * from sqlite_master; .exit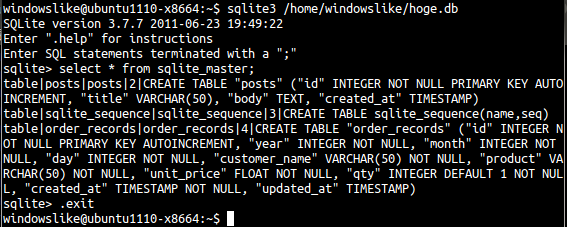
- テーブルの作成
次の手順で、irb を使って、プログラムを実行する
OrderRecord クラスのクラス定義の部分は、先のものと同じ (本格的に使うなら、クラス定義を別ファイルに分けてインクルードする)
new メソッドでオブジェクトを生成し、save メソッドを発行すると、データベースに保存される(テーブルが1行増える)
irb require 'rubygems' # require 'data_mapper' require 'dm-core' # # An in-memory Sqlite3 connection: # DataMapper.setup(:default, 'sqlite::memory:') # A Sqlite3 connection to a persistent database DataMapper.setup(:default, 'sqlite:///home/windowslike/hoge.db') class OrderRecord include DataMapper::Resource property :id, Serial # INTEGER not null PRIMARY KEY autoincrement property :year, Integer, :required => true, :min => 2011 property :month, Integer, :required => true, :min => 1, :max => 12 property :day, Integer, :required => true, :min => 1, :max => 31 property :customer_name, String, :required => true property :product, String, :required => true property :unit_price, Float, :required => true, :min => 0 property :qty, Integer, :required => true, :default => 1, :min => 1 property :created_at, DateTime, :required => true property :updated_at, DateTime end obj = OrderRecord.new obj.year = 2011 obj.month = 11 obj.day = 25 obj.customer_name = "kaneko" obj.product = "orange" obj.unit_price = 120 obj.qty = 3 obj.created_at = "2011/11/25 11:24:11" obj.save obj = OrderRecord.new obj.year = 2011 obj.month = 11 obj.day = 25 obj.customer_name = "kaneko" obj.product = "apple" obj.unit_price = 220 obj.qty = 10 obj.created_at = "2011/11/25 11:26:30" obj.save DataMapper.finalize exit
- テーブルの確認
念のためテーブル order_records を確認する
sqlite3 /home/windowslike/hoge.db select * from order_records; .exit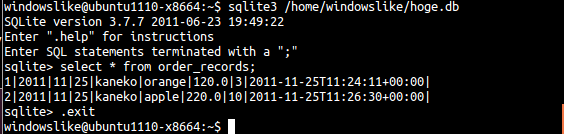
- 問い合わせの発行と評価結果の確認.(Issue SQL queries and inspect the results)
次の手順で、irb を使って、プログラムを実行
テーブルの1行がオブジェクトにマッピングされ、テーブルがクラスにマッピングされている. 問い合わせは、get メソッド、all メソッドなどを使って行う.
irb require 'rubygems' # require 'data_mapper' require 'dm-core' # # An in-memory Sqlite3 connection: # DataMapper.setup(:default, 'sqlite::memory:') # A Sqlite3 connection to a persistent database DataMapper.setup(:default, 'sqlite:///home/windowslike/hoge.db') class OrderRecord include DataMapper::Resource property :id, Serial # INTEGER not null PRIMARY KEY autoincrement property :year, Integer, :required => true, :min => 2011 property :month, Integer, :required => true, :min => 1, :max => 12 property :day, Integer, :required => true, :min => 1, :max => 31 property :customer_name, String, :required => true property :product, String, :required => true property :unit_price, Float, :required => true, :min => 0 property :qty, Integer, :required => true, :default => 1, :min => 1 property :created_at, DateTime, :required => true property :updated_at, DateTime end # SELECT * FROM order_records WHERE id = 1; p OrderRecord.get(1) # SELECT * FROM order_records; p OrderRecord.all # SELECT * FROM order_records WHERE day = 25; p OrderRecord.all( :conditions => ["day = ?", 100] ) # SELECT * FROM order_records WHERE customer_name = 'kaneko'; p OrderRecord.all( :conditions => ["customer_name = ?", 'kaneko'] ) # SELECT * FROM order_records WHERE unit_price > 200; p OrderRecord.all( :conditions => ["unit_price > ?", 200] ) DataMapper.finalize exit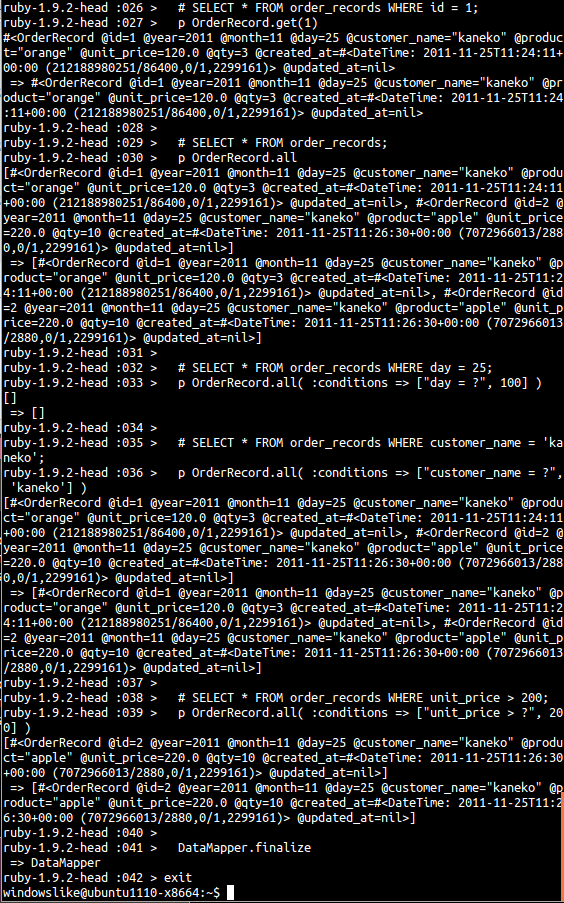
テーブルの定義(データ型と制約)、テーブルの生成、問い合わせを行った。 テーブルはRuby のクラスにマッピングされていて、SQLを使うことは(確認を除き)ありませんでした。
* ActiveRecord と比べて、機能的には遜色はないように見えます.使用感は違う. DataMapperではクラスを定義してマイグレーションを行うこと、SQL で定められている列制約を簡単な形で記述できることが特徴に見えます.
Rails でも DataMapper を使ってみる
scaffold を動かしてみる.scaffold を動かす程度ならば、ActiveRecord と DataMapper での使用感 には差がみえません。
- Rails で,データベースの生成とテーブル定義
cd hogeapp rails g scaffold order_record year:integer month:integer day:integer customer_name:string product:string unit_price:float qty:integer created_at:datetime updated_at:datetime rake db:create rake db:automigrate - 引き続き、テーブル定義の確認
sqlite3 db/hogeapp_development.db select * from sqlite_master; .exit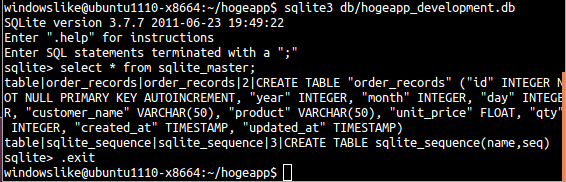
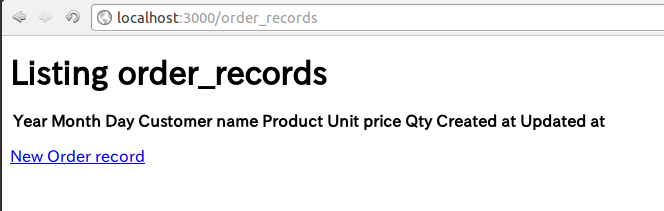
- Rails のサーバを立ち上げて、
rails sWeb ブラウザで http://localhost:3000/order_records
- 試しに、さきほど作ったデータベースファイルをコピーしてみる
cp ../hoge.db db/hogeapp_development.dbもう1度、Web ブラウザで http://localhost:3000/order_records
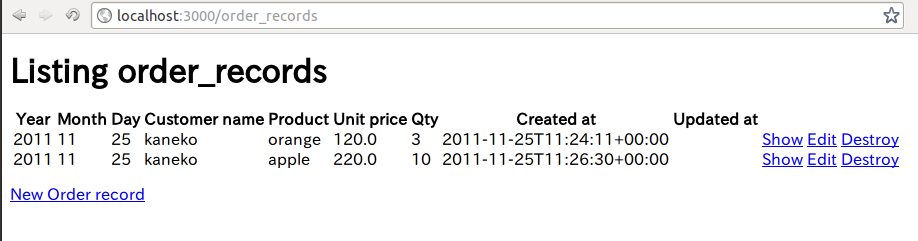
DataMapper と Rails を使いたい人 (テーブル定義の操作感が AcriveRecord 風なんだけど、実際には DataMapper), DataMapper と Rails 以外を使いたい人が同じデータベースを使うこともできそうです.
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)