深層強化学習 CartPole-v0 を動かしてみる(PyTorch のサンプルプログラムを使用)
次のWebページに記載のソースコード(単純な CNN を用いた画像分類)を実行してみる
【関連する外部ページ】 https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/reinforcement_q_learning.html
先人に感謝
PyTorch の Web ページ: http://pytorch.org
GitHub の PyTorch の Webページ: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch
前準備
PyTorch 2.3 (NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット11.8 用)のインストール(Windows 上)
次のコマンドを実行することにより, PyTorch 2.3 (NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8 用)がインストールされる.
- 以下の手順を管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー →
cmdと入力 → 右クリック → 「管理者として実行」)。 - PyTorch の公式ページを確認
- 次のようなコマンドを実行(実行するコマンドは,PyTorch のページの表示されるコマンドを使う).
次のコマンドを実行することにより, PyTorch 2.3 (NVIDIA CUDA 11.8 用)がインストールされる. 但し,Anaconda3を使いたい場合には別手順になる.
事前に NVIDIA CUDA のバージョンを確認しておくこと(ここでは,NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8 が前もってインストール済みであるとする).
PyTorch で,GPU が動作している場合には,「torch.cuda.is_available()」により,True が表示される.
python -m pip install -U --ignore-installed pip python -m pip uninstall -y torch torchvision torchaudio torchtext xformers python -m pip install -U torch torchvision torchaudio numpy --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118 python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__, torch.cuda.is_available())"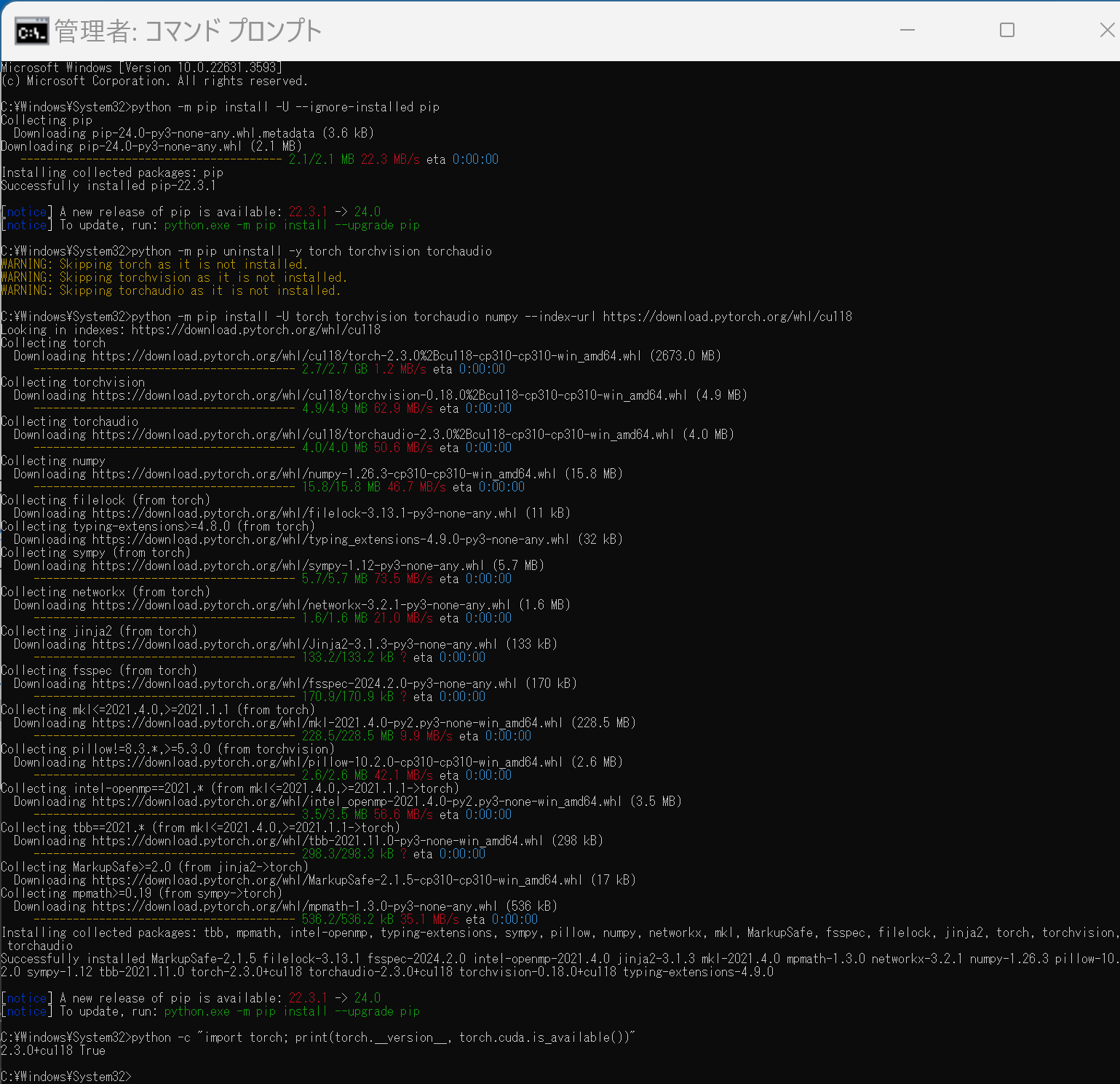
【関連する外部ページ】
【サイト内の関連ページ】
- GPU対応PyTorch 2.3のセットアップと性能確認(Windows 上): 別ページ »で説明
- PyTorch の最新版を検証,開発者に貢献したいなどの場合には,ソースコードからビルドして,インストールする: 別ページ »で説明
【関連項目】 NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット, PyTorch
Open-AI gym のインストール
- Ubuntu の場合
次のコマンドを実行.
sudo pip3 install gym
深層強化学習 CartPole-v0 を動かしてみる(PyTorch のサンプルプログラムを使用)
- Python プログラムの実行
Python プログラムの実行- Windows では python (Python ランチャーは py)
- Ubuntu では python3
Python 開発環境(Jupyter Qt Console, Jupyter ノートブック (Jupyter Notebook), Jupyter Lab, Nteract, Spyder, PyCharm, PyScripterなど)も便利である.
Python のまとめ: 別ページ »にまとめ
python- インポート
import gym import math import random import numpy as np import matplotlib %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings from collections import namedtuple from itertools import count from PIL import Image import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim import torch.nn.functional as F import torchvision.transforms as T env = gym.make('CartPole-v0').unwrapped # set up matplotlib is_ipython = 'inline' in matplotlib.get_backend() if is_ipython: from IPython import display plt.ion() # if gpu is to be used device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")Ubuntu での実行結果例
- CIFAR 10 のダウンロード
transform = transforms.Compose( [transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]) trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform) trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=4, shuffle=True, num_workers=2) testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform) testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=4, shuffle=False, num_workers=2) classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')Ubuntu の PyCharm での実行結果例

- Replay Memory の作成
Transition = namedtuple('Transition', ('state', 'action', 'next_state', 'reward')) class ReplayMemory(object): def __init__(self, capacity): self.capacity = capacity self.memory = [] self.position = 0 def push(self, *args): """Saves a transition.""" if len(self.memory) < self.capacity: self.memory.append(None) self.memory[self.position] = Transition(*args) self.position = (self.position + 1) % self.capacity def sample(self, batch_size): return random.sample(self.memory, batch_size) def __len__(self): return len(self.memory)
- Q-network の作成
class DQN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, h, w, outputs): super(DQN, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=5, stride=2) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=5, stride=2) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32) self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=5, stride=2) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32) # Number of Linear input connections depends on output of conv2d layers # and therefore the input image size, so compute it. def conv2d_size_out(size, kernel_size = 5, stride = 2): return (size - (kernel_size - 1) - 1) // stride + 1 convw = conv2d_size_out(conv2d_size_out(conv2d_size_out(w))) convh = conv2d_size_out(conv2d_size_out(conv2d_size_out(h))) linear_input_size = convw * convh * 32 self.head = nn.Linear(linear_input_size, outputs) # Called with either one element to determine next action, or a batch # during optimization. Returns tensor([[left0exp,right0exp]...]). def forward(self, x): x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(x))) return self.head(x.view(x.size(0), -1))
- Input Extraction (入力の抽出)
resize = T.Compose([T.ToPILImage(), T.Resize(40, interpolation=Image.CUBIC), T.ToTensor()]) def get_cart_location(screen_width): world_width = env.x_threshold * 2 scale = screen_width / world_width return int(env.state[0] * scale + screen_width / 2.0) # MIDDLE OF CART def get_screen(): # Returned screen requested by gym is 400x600x3, but is sometimes larger # such as 800x1200x3. Transpose it into torch order (CHW). screen = env.render(mode='rgb_array').transpose((2, 0, 1)) # Cart is in the lower half, so strip off the top and bottom of the screen _, screen_height, screen_width = screen.shape screen = screen[:, int(screen_height*0.4):int(screen_height * 0.8)] view_width = int(screen_width * 0.6) cart_location = get_cart_location(screen_width) if cart_location < view_width // 2: slice_range = slice(view_width) elif cart_location > (screen_width - view_width // 2): slice_range = slice(-view_width, None) else: slice_range = slice(cart_location - view_width // 2, cart_location + view_width // 2) # Strip off the edges, so that we have a square image centered on a cart screen = screen[:, :, slice_range] # Convert to float, rescale, convert to torch tensor # (this doesn't require a copy) screen = np.ascontiguousarray(screen, dtype=np.float32) / 255 screen = torch.from_numpy(screen) # Resize, and add a batch dimension (BCHW) return resize(screen).unsqueeze(0).to(device) env.reset() plt.figure() plt.imshow(get_screen().cpu().squeeze(0).permute(1, 2, 0).numpy(), interpolation='none') plt.title('Example extracted screen') plt.show()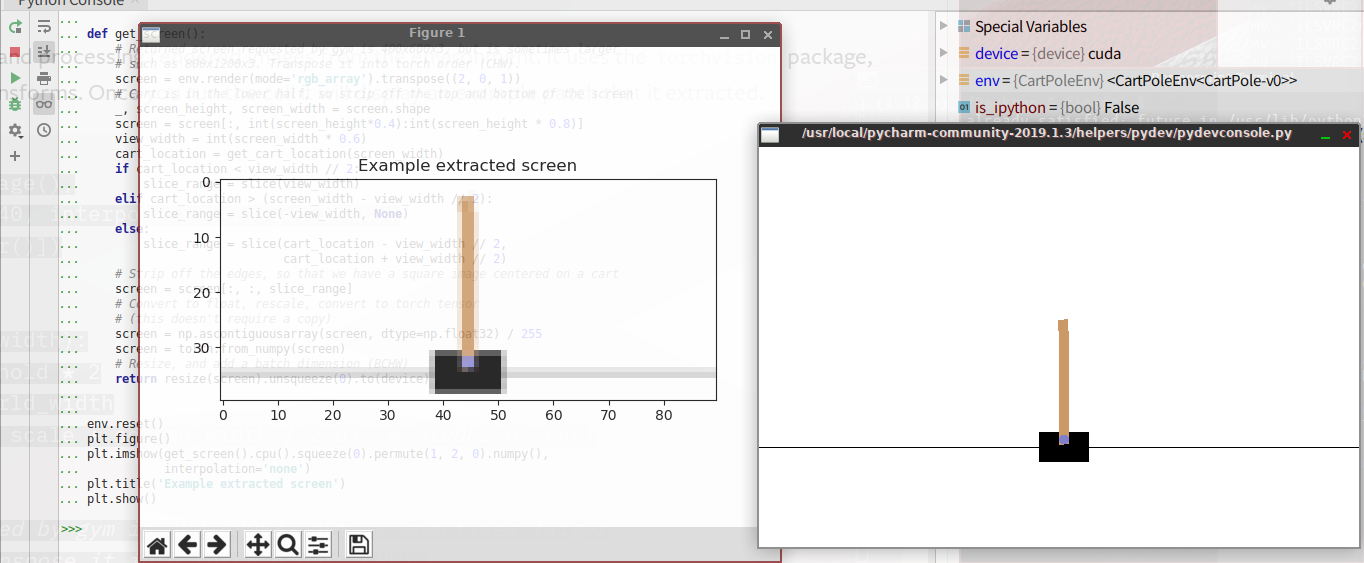
- ハイパーパラメータなど
BATCH_SIZE = 128 GAMMA = 0.999 EPS_START = 0.9 EPS_END = 0.05 EPS_DECAY = 200 TARGET_UPDATE = 10 # Get screen size so that we can initialize layers correctly based on shape # returned from AI gym. Typical dimensions at this point are close to 3x40x90 # which is the result of a clamped and down-scaled render buffer in get_screen() init_screen = get_screen() _, _, screen_height, screen_width = init_screen.shape # Get number of actions from gym action space n_actions = env.action_space.n policy_net = DQN(screen_height, screen_width, n_actions).to(device) target_net = DQN(screen_height, screen_width, n_actions).to(device) target_net.load_state_dict(policy_net.state_dict()) target_net.eval() optimizer = optim.RMSprop(policy_net.parameters()) memory = ReplayMemory(10000) steps_done = 0 def select_action(state): global steps_done sample = random.random() eps_threshold = EPS_END + (EPS_START - EPS_END) * \ math.exp(-1. * steps_done / EPS_DECAY) steps_done += 1 if sample > eps_threshold: with torch.no_grad(): # t.max(1) will return largest column value of each row. # second column on max result is index of where max element was # found, so we pick action with the larger expected reward. return policy_net(state).max(1)[1].view(1, 1) else: return torch.tensor([[random.randrange(n_actions)]], device=device, dtype=torch.long) episode_durations = [] def plot_durations(): plt.figure(2) plt.clf() durations_t = torch.tensor(episode_durations, dtype=torch.float) plt.title('Training...') plt.xlabel('Episode') plt.ylabel('Duration') plt.plot(durations_t.numpy()) # Take 100 episode averages and plot them too if len(durations_t) >= 100: means = durations_t.unfold(0, 100, 1).mean(1).view(-1) means = torch.cat((torch.zeros(99), means)) plt.plot(means.numpy()) plt.pause(0.001) # pause a bit so that plots are updated if is_ipython: display.clear_output(wait=True) display.display(plt.gcf())
- 最適化の1ステップを実行する関数
def optimize_model(): if len(memory) < BATCH_SIZE: return transitions = memory.sample(BATCH_SIZE) # Transpose the batch (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/19343/3343043 for # detailed explanation). This converts batch-array of Transitions # to Transition of batch-arrays. batch = Transition(*zip(*transitions)) # Compute a mask of non-final states and concatenate the batch elements # (a final state would've been the one after which simulation ended) non_final_mask = torch.tensor(tuple(map(lambda s: s is not None, batch.next_state)), device=device, dtype=torch.uint8) non_final_next_states = torch.cat([s for s in batch.next_state if s is not None]) state_batch = torch.cat(batch.state) action_batch = torch.cat(batch.action) reward_batch = torch.cat(batch.reward) # Compute Q(s_t, a) - the model computes Q(s_t), then we select the # columns of actions taken. These are the actions which would've been taken # for each batch state according to policy_net state_action_values = policy_net(state_batch).gather(1, action_batch) # Compute V(s_{t+1}) for all next states. # Expected values of actions for non_final_next_states are computed based # on the "older" target_net; selecting their best reward with max(1)[0]. # This is merged based on the mask, such that we'll have either the expected # state value or 0 in case the state was final. next_state_values = torch.zeros(BATCH_SIZE, device=device) next_state_values[non_final_mask] = target_net(non_final_next_states).max(1)[0].detach() # Compute the expected Q values expected_state_action_values = (next_state_values * GAMMA) + reward_batch # Compute Huber loss loss = F.smooth_l1_loss(state_action_values, expected_state_action_values.unsqueeze(1)) # Optimize the model optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() for param in policy_net.parameters(): param.grad.data.clamp_(-1, 1) optimizer.step()
- 学習
num_episodes = 50 for i_episode in range(num_episodes): # Initialize the environment and state env.reset() last_screen = get_screen() current_screen = get_screen() state = current_screen - last_screen for t in count(): # Select and perform an action action = select_action(state) _, reward, done, _ = env.step(action.item()) reward = torch.tensor([reward], device=device) # Observe new state last_screen = current_screen current_screen = get_screen() if not done: next_state = current_screen - last_screen else: next_state = None # Store the transition in memory memory.push(state, action, next_state, reward) # Move to the next state state = next_state # Perform one step of the optimization (on the target network) optimize_model() if done: episode_durations.append(t + 1) plot_durations() break # Update the target network, copying all weights and biases in DQN if i_episode % TARGET_UPDATE == 0: target_net.load_state_dict(policy_net.state_dict()) print('Complete') env.render() env.close() plt.ioff() plt.show()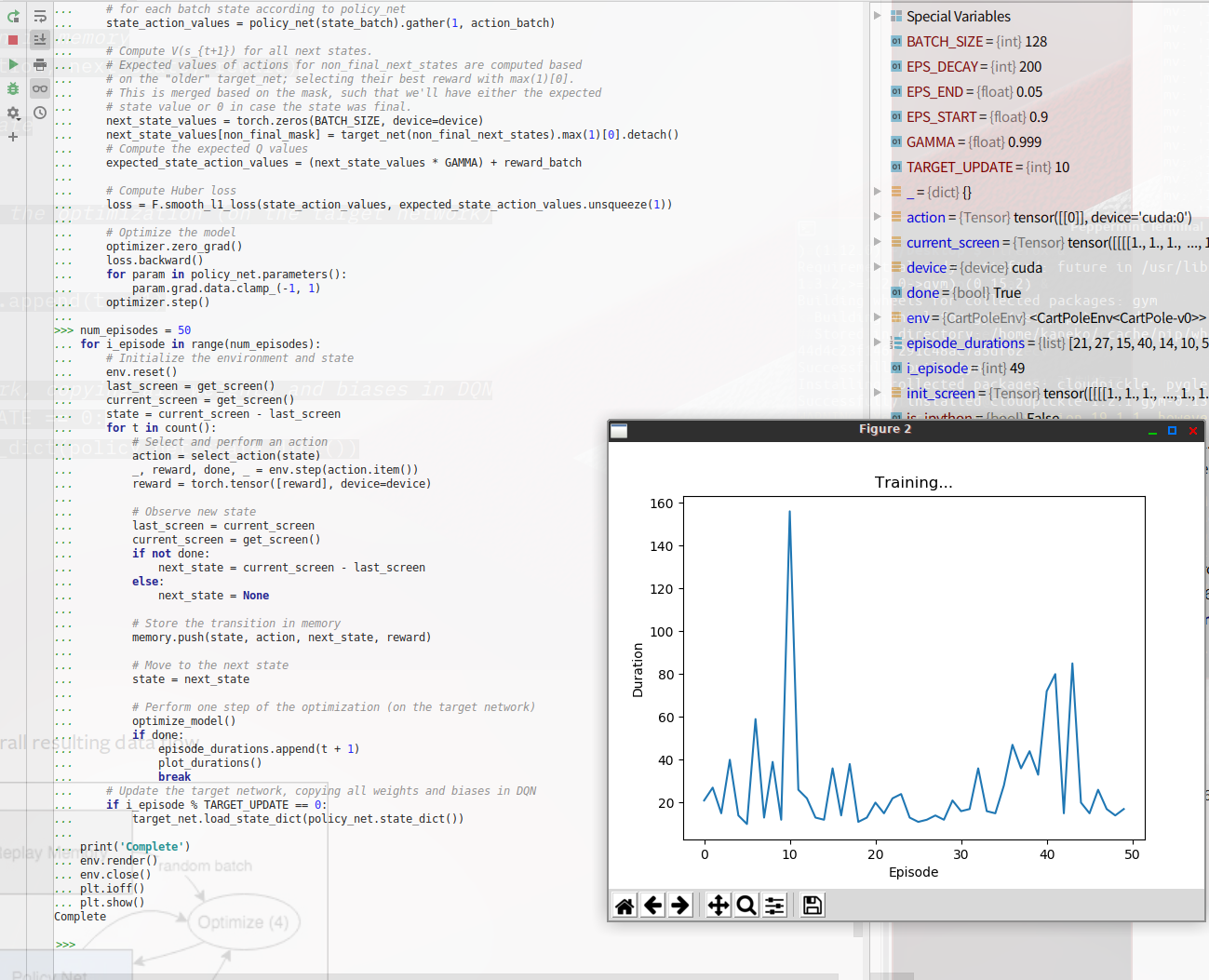
- CIFAR 10 のダウンロード
- Python プログラムの実行
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)