Python で GeoTIFF を使ってみる
キーワード: GeoTIFF, Python で GeoTIFF ファイルの読み込み,Python で GeoTIFF ファイルからの緯度経度の取得,osr, gdal, 基盤地図情報, 数値標高モデル, 基盤地図情報ダウンロード
前準備
Python 64 ビット版のインストール,pip と setuptools の更新(Windows 上)
Windows での Python 3.10 のインストール,pip と setuptools の更新: 別ページ »で説明
Python の公式ページ: https://www.python.org/
Python 開発環境のインストール
- Windows での Python 開発環境として,Jupyter Qt Console, Jupyter ノートブック (Jupyter Notebook), Jupyter Lab, Nteract, spyder のインストール: 別ページ »で説明
- Windows での PyCharm のインストール: 別ページ »で説明
- Windows での PyScripter のインストール: 別ページ »で説明
gdal Windows 版のインストール
OSGeo4W のインストールを行っておくこと
GeoTIFF サンプルデータファイルの準備 (1)
- GeoTIFF サンプルデータファイルのダウンロード
次の Web ページから cea.tif をダウンロード
http://download.osgeo.org/geotiff/samples/gdal_eg/
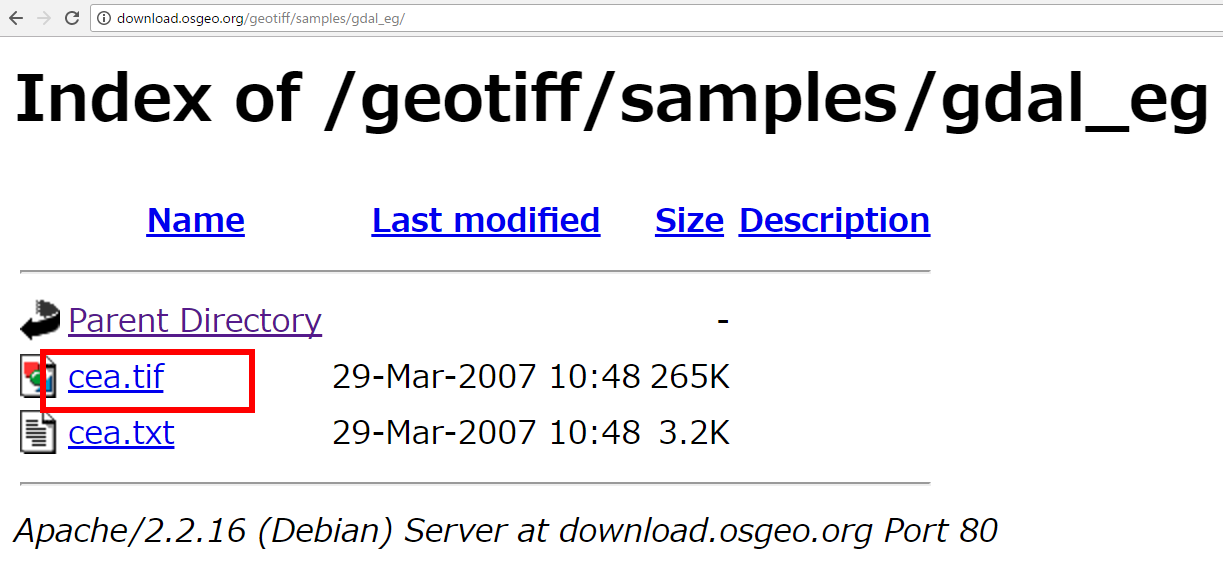
- ダウンロードした .tif ファイルを,分かりやすいディレクトリ(例えばd:\)に保存
GeoTIFF サンプルデータファイルの準備 (基盤地図情報の数値標高モデル)
【関連する外部ページ】 http://sanvarie.hatenablog.com/entry/2016/01/10/163027
ありがとうございます.
基盤地図情報・数値標高モデルのダウンロード
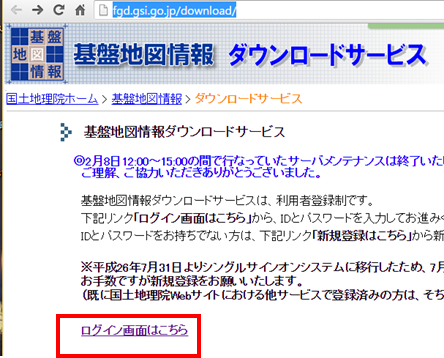
- 国土地理院の「基盤地図情報ダウンロード」の Web ページを開く
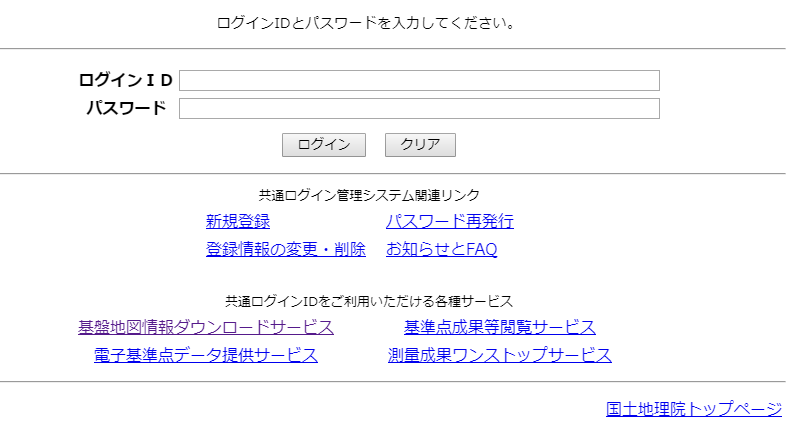
- 「ログイン画面はこちら」をクリック
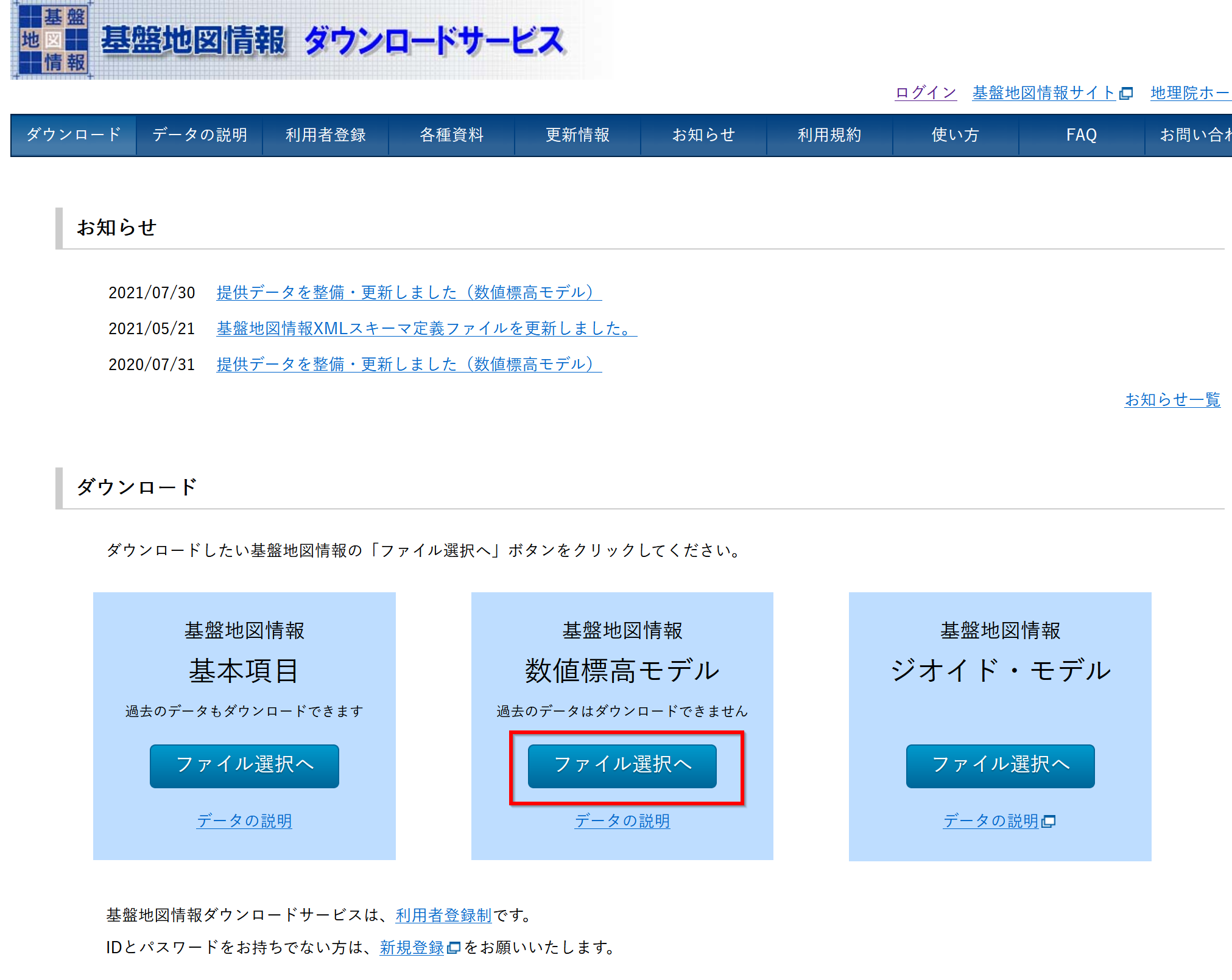
- 「基盤地図情報・数値標高モデル」の下の
「ファイル選択へ」をクリック
- ダウンロードしたい数値標高モデルの範囲を選ぶ
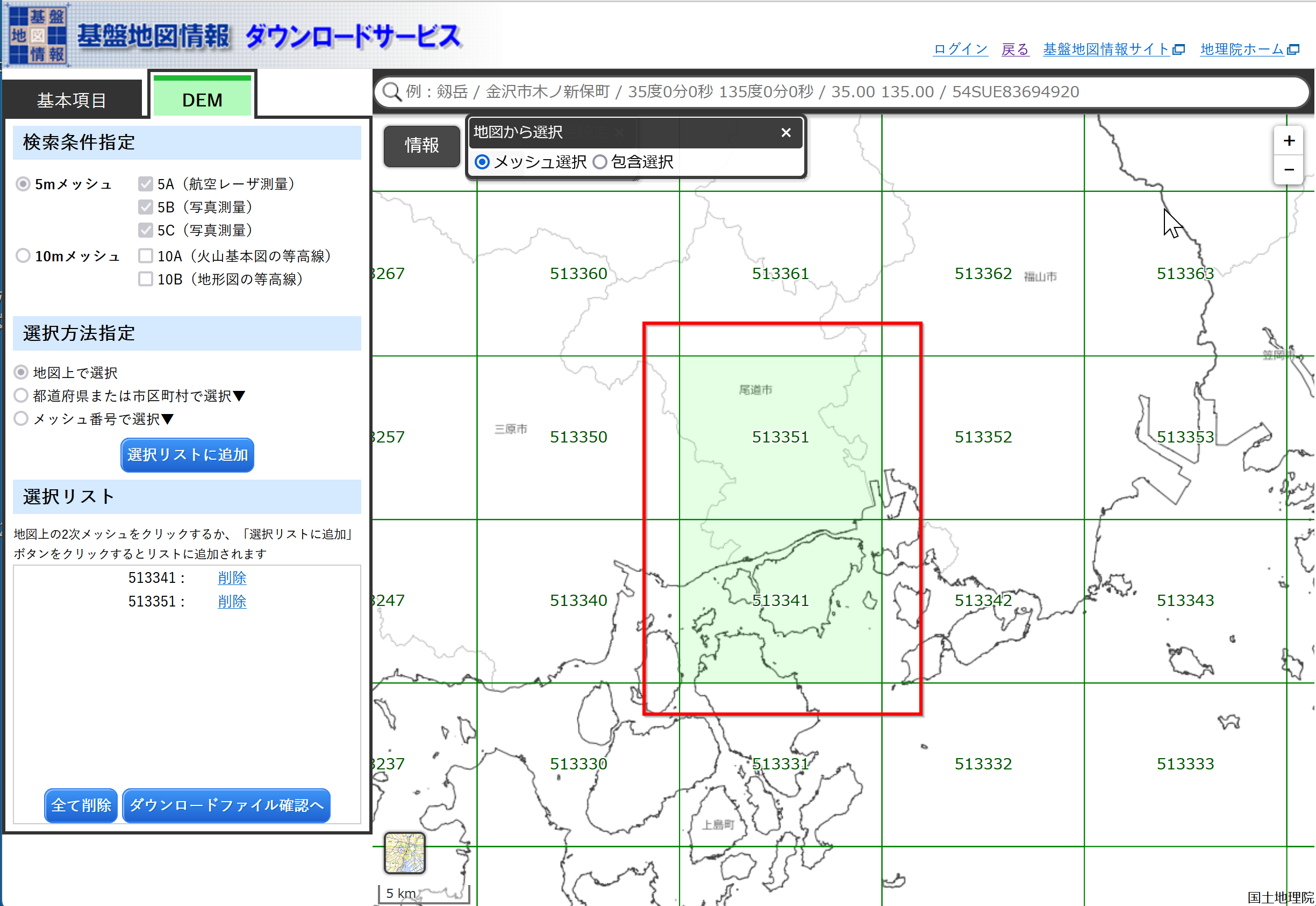
- 選び終わったら,「ダウンロードファイル確認へ」をクリック
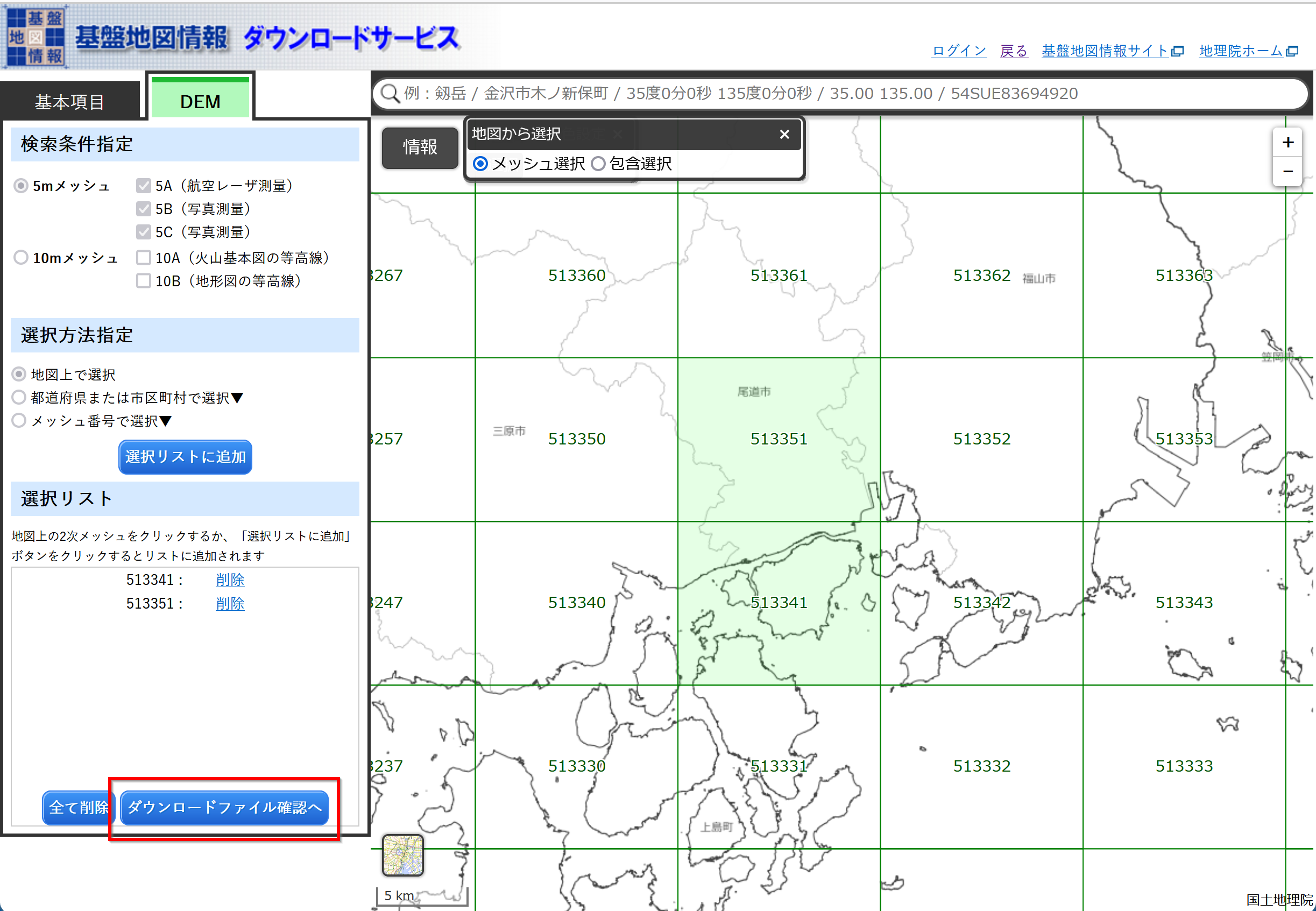
- 「すべてチェック」をクリック
* 「5A」は航空レーザー測量,「5B」は写真測量.
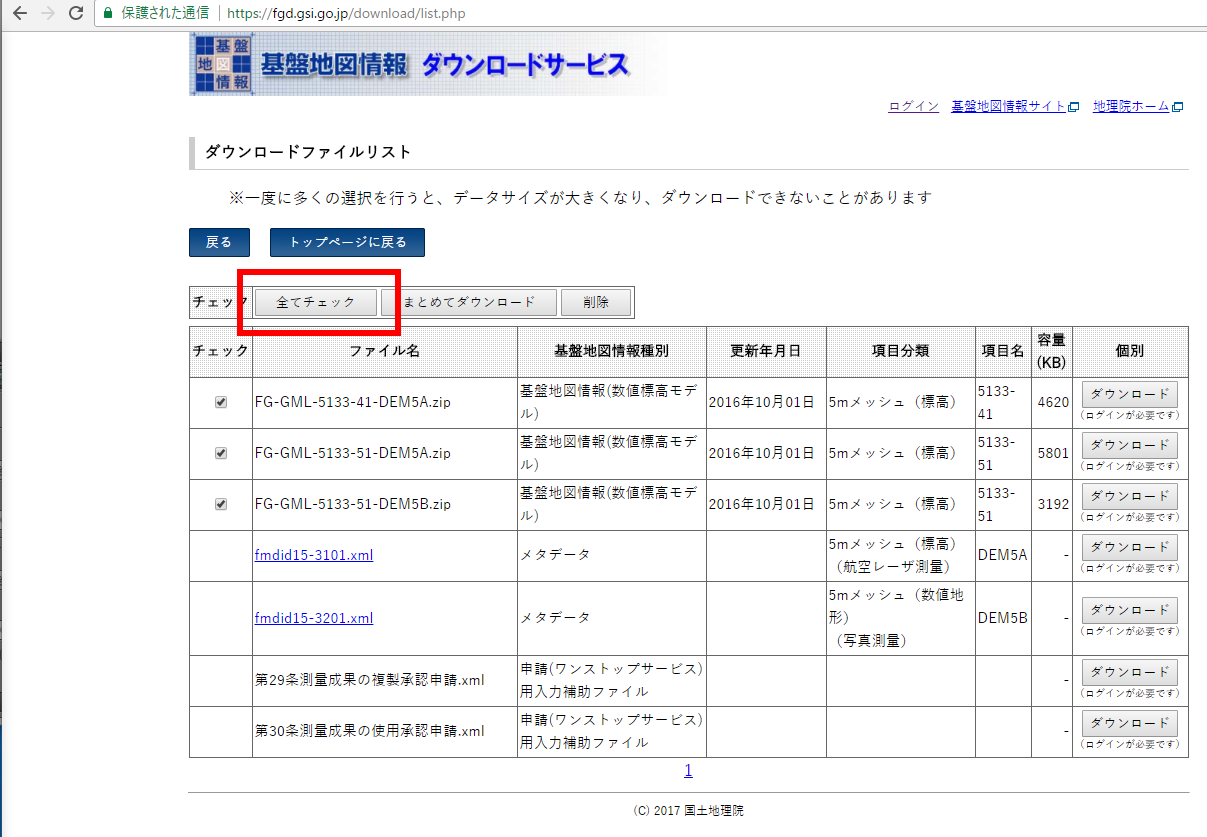
- 「まとめてダウンロード」をクリック
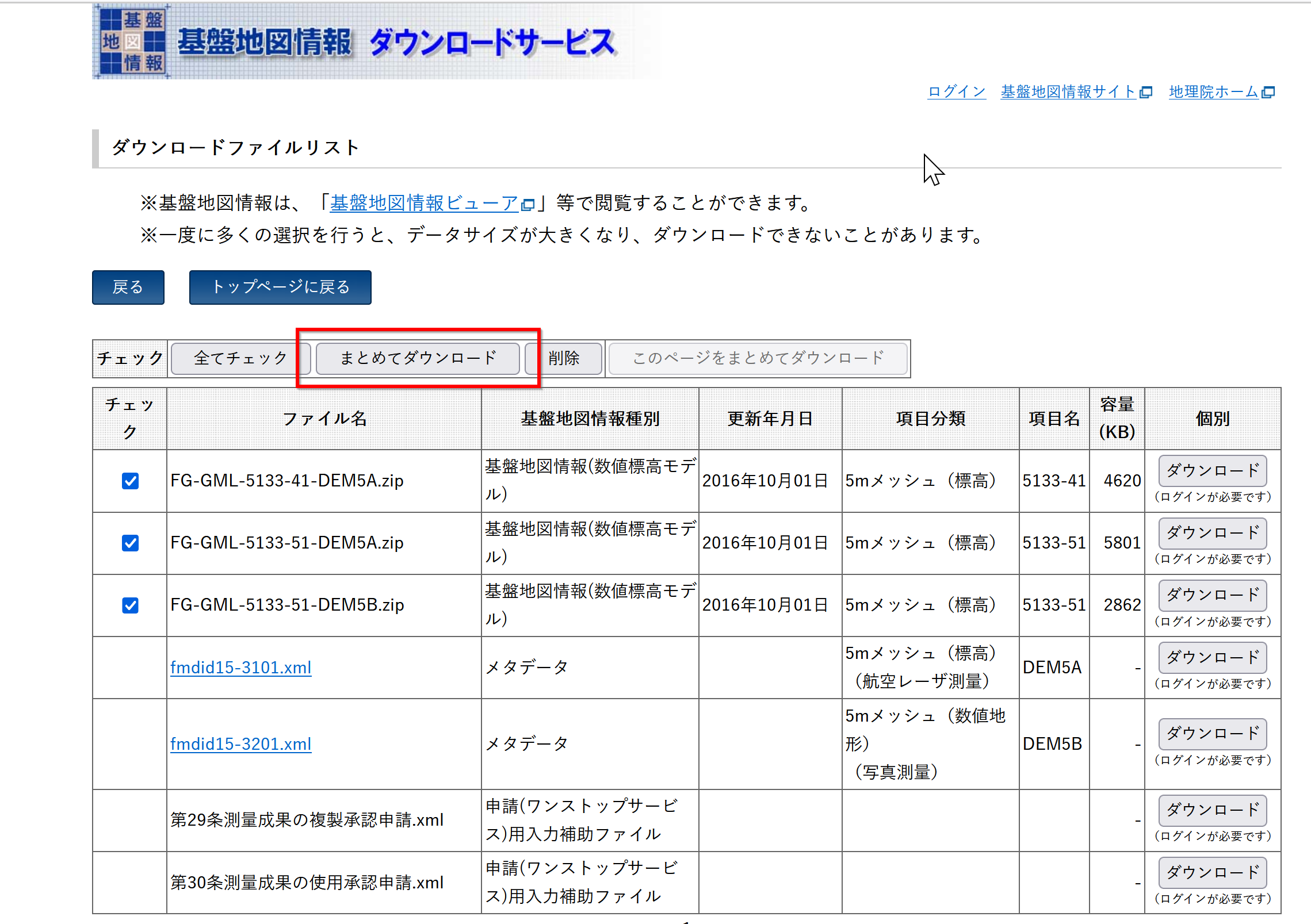
- ログインする
- アンケートに協力する(正しく回答する)
- .zip ファイルのダウンロードが始まるので確認する

- ダウンロードした .zip ファイルを展開(解凍)する.分かりやすいディレクトリに置く.
※ 展開(解凍)すると .zip ファイルができるので確認する.
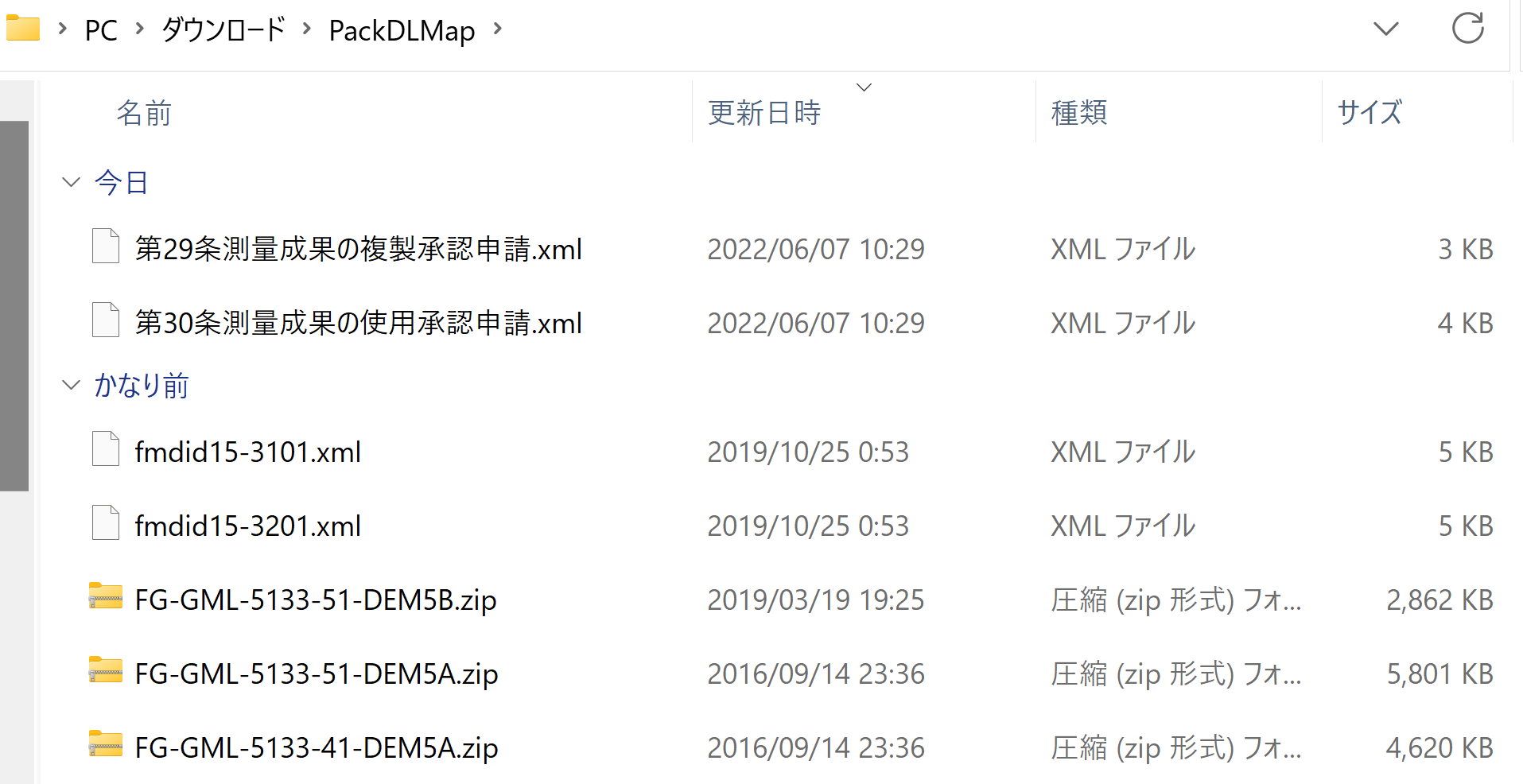
- さらに展開(解凍)すると .xml ファイルができるので確認する.
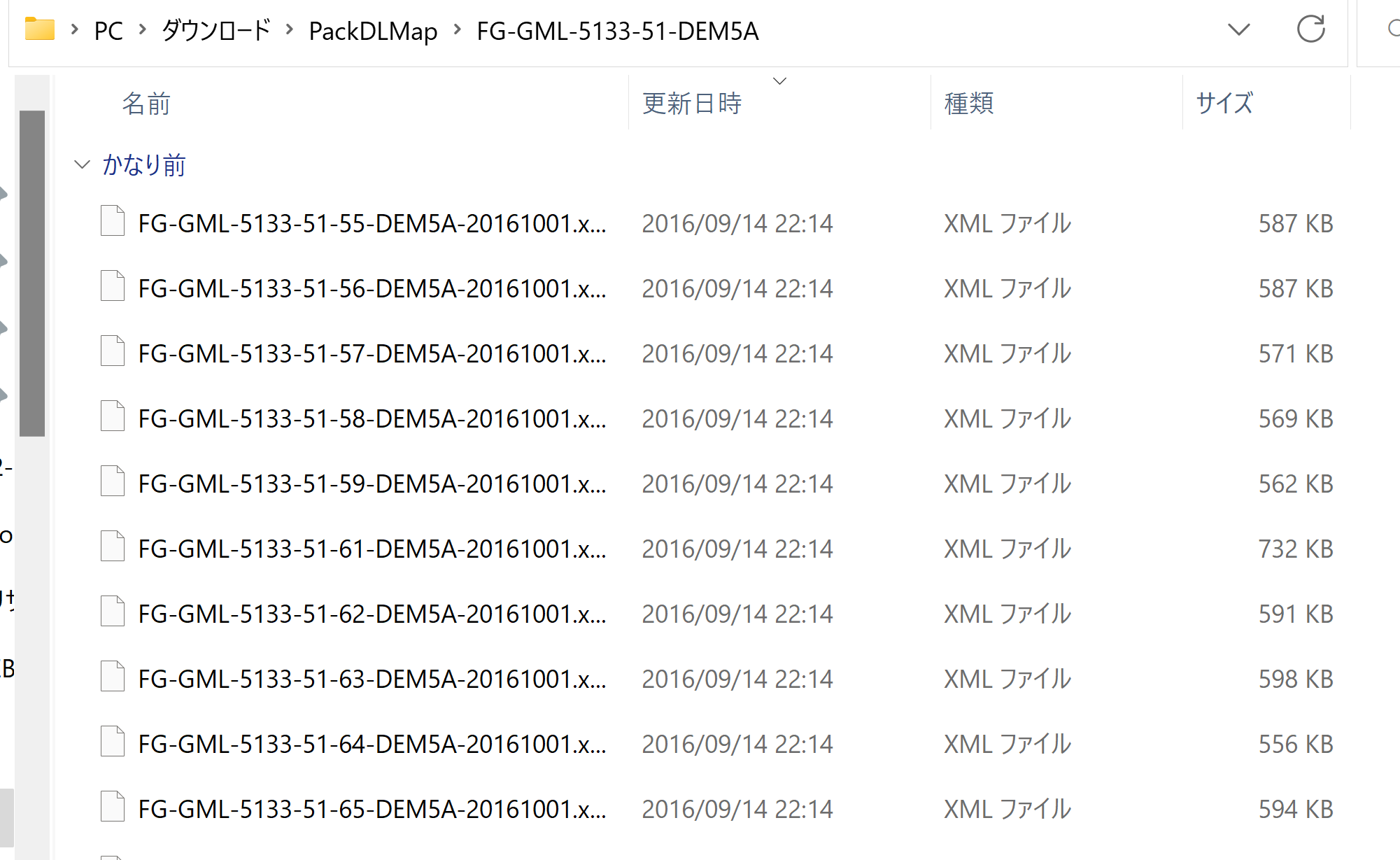
ファイル名: FG_GML-5133-41-00-DEM5A-201601001.xml
- 5133: 1次メッシュ番号
- 41: 2次メッシュ番号
- 00: 3次メッシュ番号
- 5A: 「5A」は航空レーザー測量,「5B」は写真測量.
- 20161001: 年月日
基盤地図情報の数値標高モデルを GeoTIFF に変換
- 「GeoTIFFを格納するフォルダ」を1つ作り,そこに,すべての .xml ファイル を集める.
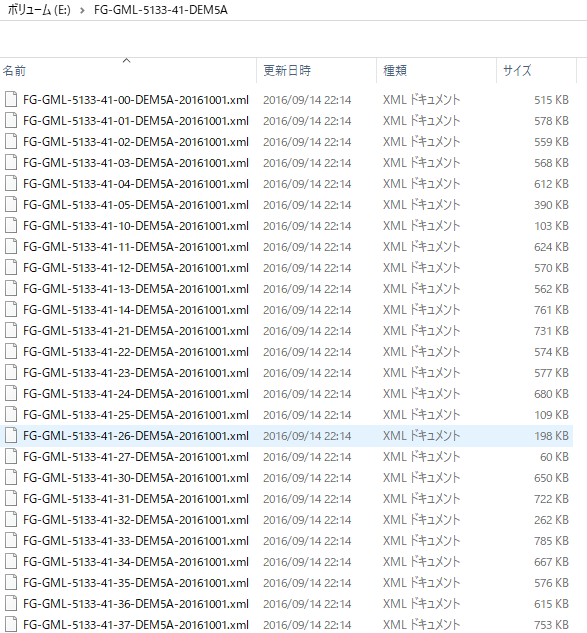
- http://sanvarie.hatenablog.com/entry/2016/01/10/163027 に記載のプログラムを実行してみる
優れたソフトウェアの公開に感謝を表明します.
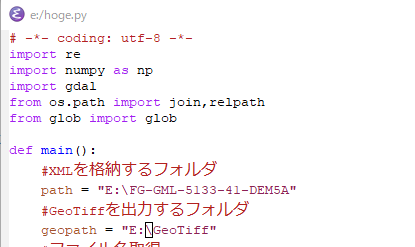
まず,プログラム内のXMLを格納するフォルダ,GeoTIFFを格納するフォルダは適切に設定する必要がある(下図のように).
実行は簡単でした.
 * Windows で実行するとき,次のようなエラーが出ることがある.
* Windows で実行するとき,次のようなエラーが出ることがある.UnicodeDecodeError: 'cp932' codec can't decode byte 0x85 in position 395: illegal multibype sequence.

* 次のように,プログラムファイルを書き換えて回避しました(書き換え箇所2か所)
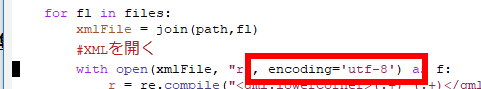
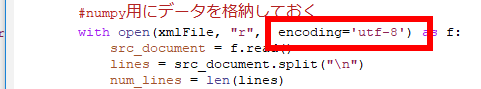
- Windows でファイルを見てみると、つぎのようになります
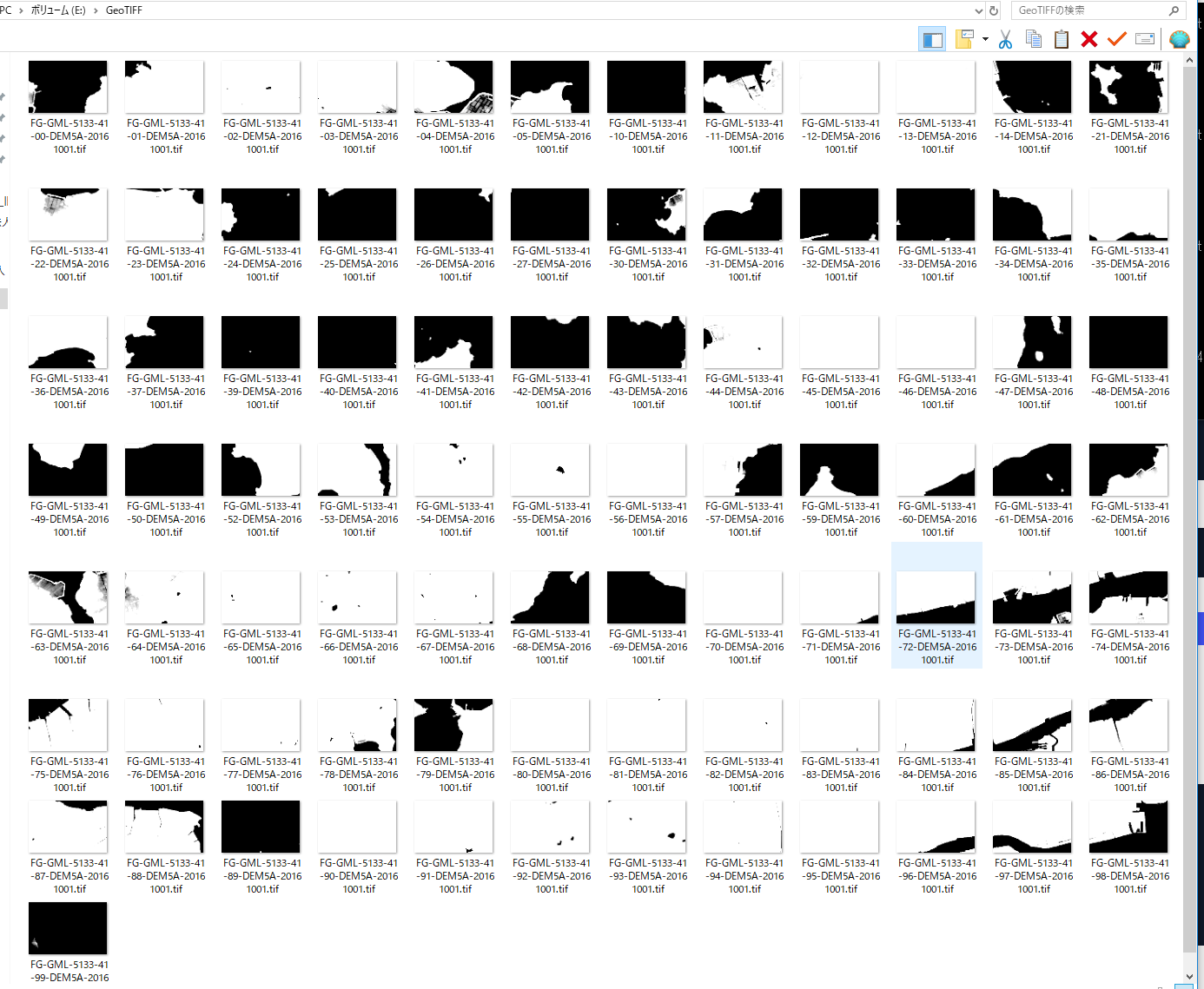
- Windows でファイルを見てみると、つぎのようになります
GeoTIFF ファイルの読み込み
Python で GeoTIFF のデータを読み込む
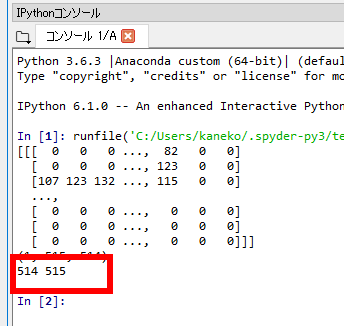
ここでは,GeoTIFF のファイル d:/cea.tif を numpy 形式のオブジェクト a に読み込む.確認のため print コマンドで,a の中身, a の要素数, GeoTIFF の縦横, 画素値の最大値と最小値を表示している
- Python プログラムの実行
import gdal import numpy as np ds = gdal.Open('d:/cea.tif', gdal.GA_ReadOnly) a = np.array([ds.GetRasterBand(i + 1).ReadAsArray() for i in range(ds.RasterCount)]) print(a) print(a.shape) print(ds.RasterXSize, ds.RasterYSize)Python プログラムの編集と実行
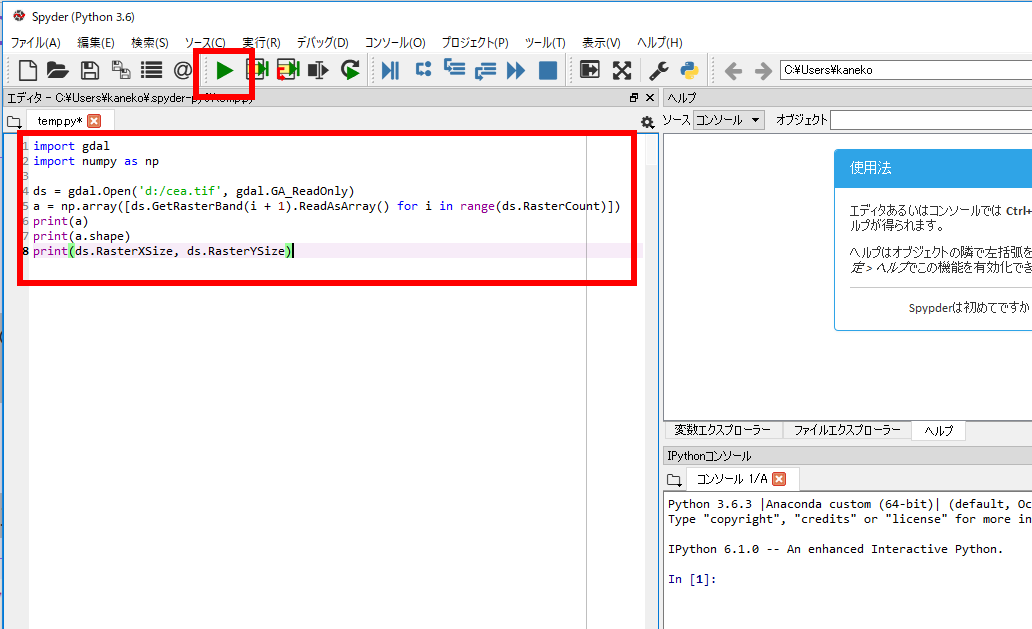
- 実行結果を確認する.
「514 415」は、GeoTIFF の縦横を表示している
- 続いて次のプログラムを実行してみる
「255」や「0」は、画素値の最大値と最小値である.
np.max(a) np.min(a)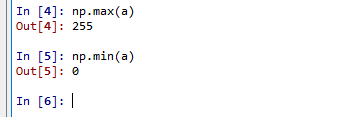
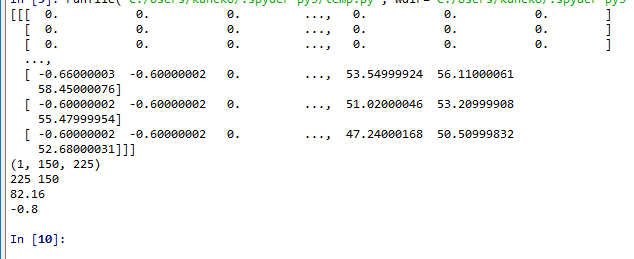
- 念のため別の GeoTIFF ファイル E:/FG-GML-5133-41-DEM5A/51334100.tifで,同じことを繰り返してみる
import gdal import numpy as np ds = gdal.Open('E:/FG-GML-5133-41-DEM5A/51334100.tif', gdal.GA_ReadOnly) a = np.array([ds.GetRasterBand(i + 1).ReadAsArray() for i in range(ds.RasterCount)]) print(a) print(a.shape) print(ds.RasterXSize, ds.RasterYSize) print( np.max(a) ) print( np.min(a) )そして、実行結果を確認する
GeoTIFF ファイルからの緯度経度の取得
- Python で GeoTIFF の緯度経度を取得
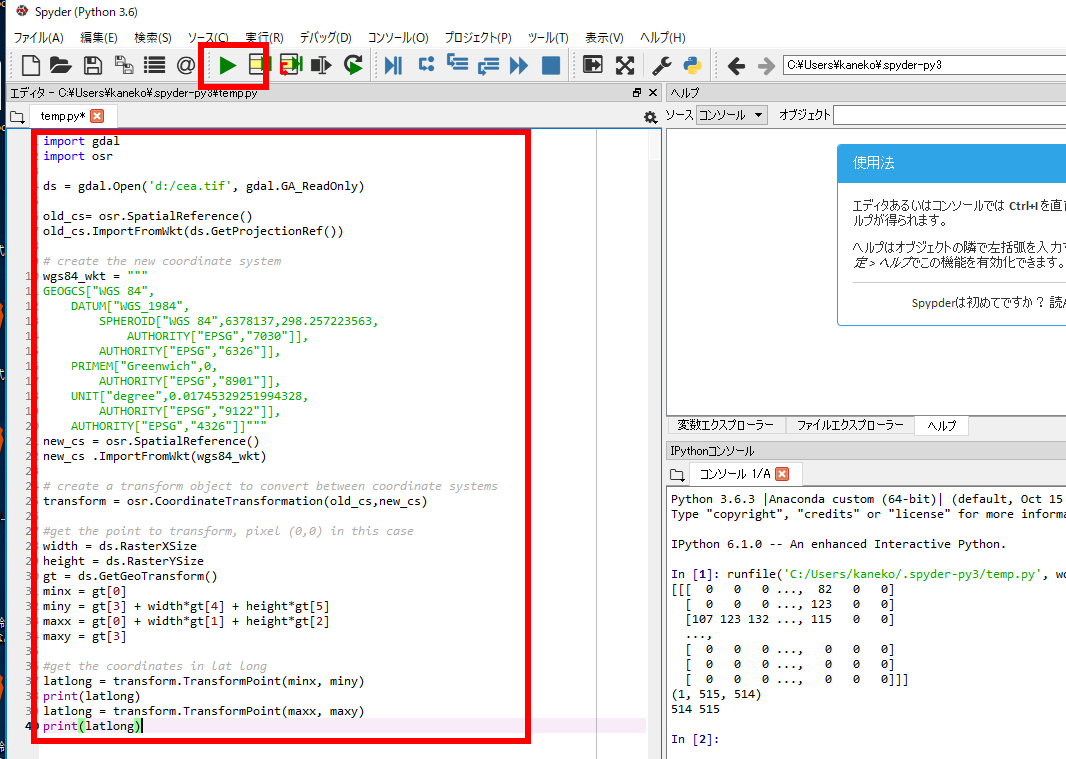
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2922532/obtain-latitude-and-longitude-from-a-geotiff-file に記載のプログラムを次のように書き換えて使用.(書き換えた部分は太字で示す)。
import gdal import osr ds = gdal.Open('d:/cea.tif', gdal.GA_ReadOnly) old_cs= osr.SpatialReference() old_cs.ImportFromWkt(ds.GetProjectionRef()) # create the new coordinate system wgs84_wkt = """ GEOGCS["WGS 84", DATUM["WGS_1984", SPHEROID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563, AUTHORITY["EPSG","7030"]], AUTHORITY["EPSG","6326"]], PRIMEM["Greenwich",0, AUTHORITY["EPSG","8901"]], UNIT["degree",0.01745329251994328, AUTHORITY["EPSG","9122"]], AUTHORITY["EPSG","4326"]]""" new_cs = osr.SpatialReference() new_cs .ImportFromWkt(wgs84_wkt) # create a transform object to convert between coordinate systems transform = osr.CoordinateTransformation(old_cs,new_cs) #get the point to transform, pixel (0,0) in this case width = ds.RasterXSize height = ds.RasterYSize gt = ds.GetGeoTransform() minx = gt[0] miny = gt[3] + width*gt[4] + height*gt[5] maxx = gt[0] + width*gt[1] + height*gt[2] maxy = gt[3] #get the coordinates in lat long latlong = transform.TransformPoint(minx, miny) print(latlong) latlong = transform.TransformPoint(maxx, maxy) print(latlong)Python プログラムの編集と実行
実行結果の例
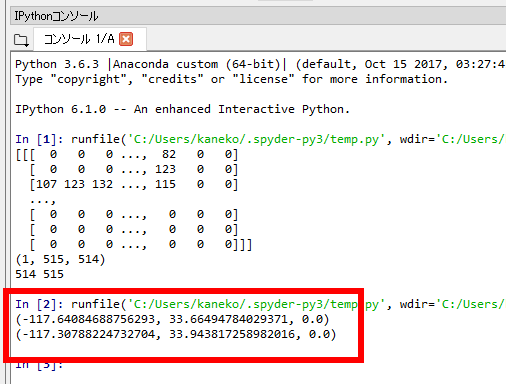
- 正しい値なのか確認のため,gdal に付属の gdalinfo コマンドで, .tif ファイルの情報を取得. 先ほどの結果が正しいか確認できる.
太字のところは、実際のディレクトリを調べて読み替えてください
C:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\pkgs\libgdal-2.2.1-vc14_2\Library\bin\gdalinfo.exe d:\cea.tif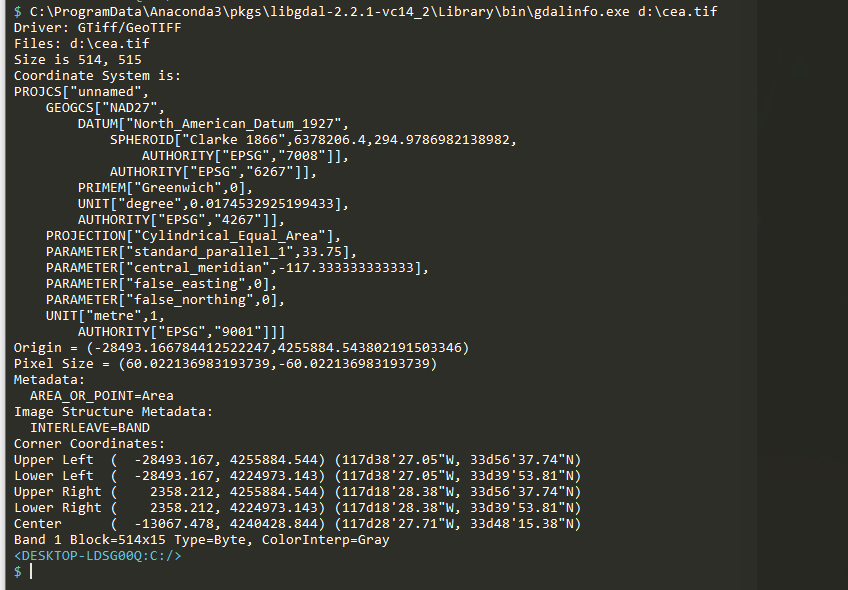
- 念のため別の GeoTIFF ファイル E:/FG-GML-5133-41-DEM5A/51334100.tifで,同じことを繰り返してみる
import gdal import osr ds = gdal.Open('E:/FG-GML-5133-41-DEM5A/51334100.tif', gdal.GA_ReadOnly) old_cs= osr.SpatialReference() old_cs.ImportFromWkt(ds.GetProjectionRef()) # create the new coordinate system wgs84_wkt = """ GEOGCS["WGS 84", DATUM["WGS_1984", SPHEROID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563, AUTHORITY["EPSG","7030"]], AUTHORITY["EPSG","6326"]], PRIMEM["Greenwich",0, AUTHORITY["EPSG","8901"]], UNIT["degree",0.01745329251994328, AUTHORITY["EPSG","9122"]], AUTHORITY["EPSG","4326"]]""" new_cs = osr.SpatialReference() new_cs .ImportFromWkt(wgs84_wkt) # create a transform object to convert between coordinate systems transform = osr.CoordinateTransformation(old_cs,new_cs) #get the point to transform, pixel (0,0) in this case width = ds.RasterXSize height = ds.RasterYSize gt = ds.GetGeoTransform() minx = gt[0] miny = gt[3] + width*gt[4] + height*gt[5] maxx = gt[0] + width*gt[1] + height*gt[2] maxy = gt[3] #get the coordinates in lat long latlong = transform.TransformPoint(minx, miny) print(latlong) latlong = transform.TransformPoint(maxx, maxy) print(latlong)
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)