くずし字 MNIST データセット(Kuzushiji-MNIST データセット)のダウンロード,画像分類の学習,画像分類の実行
【目次】
* くずし字 MNIST データセット(Kuzushiji-MNIST データセット)
くずし字 MNIST データセットは,公開されているデータセット(オープンデータ)である.
【文献】 CODH:Center for Open Data in the Humanities), KMNISTデータセット(機械学習用くずし字データセット), arXiv:1812.01718 [cs.CV], 2018.
【サイト内の関連ページ】
【関連する外部ページ】
- くずし字 MNIST データセットの公式ページ:
https://github.com/rois-codh/kmnist
Kuzushiji-MNIST, Kuzushiji-49, Kuzushiji-Kanji の 3種類が公開されている(オープンデータ).
前準備
Git のインストール
Git の URL: https://git-scm.com/
Python 3.12 のインストール(Windows 上) [クリックして展開]
以下のいずれかの方法で Python 3.12 をインストールする。Python がインストール済みの場合、この手順は不要である。
方法1:winget によるインストール
管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
winget install -e --id Python.Python.3.12 --scope machine --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/quiet InstallAllUsers=1 PrependPath=1 AssociateFiles=1 InstallLauncherAllUsers=1"--scope machine を指定することで、システム全体(全ユーザー向け)にインストールされる。このオプションの実行には管理者権限が必要である。インストール完了後、コマンドプロンプトを再起動すると PATH が自動的に設定される。
方法2:インストーラーによるインストール
- Python 公式サイト(https://www.python.org/downloads/)にアクセスし、「Download Python 3.x.x」ボタンから Windows 用インストーラーをダウンロードする。
- ダウンロードしたインストーラーを実行する。
- 初期画面の下部に表示される「Add python.exe to PATH」に必ずチェックを入れてから「Customize installation」を選択する。このチェックを入れ忘れると、コマンドプロンプトから
pythonコマンドを実行できない。 - 「Install Python 3.xx for all users」にチェックを入れ、「Install」をクリックする。
インストールの確認
コマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。
python --versionバージョン番号(例:Python 3.12.x)が表示されればインストール成功である。「'python' は、内部コマンドまたは外部コマンドとして認識されていません。」と表示される場合は、インストールが正常に完了していない。
AIエディタ Windsurf のインストール(Windows 上) [クリックして展開]
Pythonプログラムの編集・実行には、AIエディタの利用を推奨する。ここでは、Windsurfのインストールを説明する。Windsurf がインストール済みの場合、この手順は不要である。
管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
winget install -e --id Codeium.Windsurf --scope machine --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/VERYSILENT /NORESTART /MERGETASKS=!runcode,addtopath,associatewithfiles,!desktopicon"
powershell -Command "$env:Path=[System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','Machine')+';'+[System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','User'); windsurf --install-extension MS-CEINTL.vscode-language-pack-ja --force; windsurf --install-extension ms-python.python --force"--scope machine を指定することで、システム全体(全ユーザー向け)にインストールされる。このオプションの実行には管理者権限が必要である。インストール完了後、コマンドプロンプトを再起動すると PATH が自動的に設定される。
【関連する外部ページ】
Windsurf の公式ページ: https://windsurf.com/
Python 用 numpy,pandas,seaborn,matplotlib のインストール
- 管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「
cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
python -m pip install -U numpy pandas seaborn matplotlib
端末で,次のコマンドを実行
# パッケージリストの情報を更新
sudo apt update
sudo apt -y install python3-numpy python3-pandas python3-seaborn python3-matplotlib
kmnist のダウンロード
Windows での手順を示す.Ubuntu でも同様の手順である.
- 以下の手順を管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー →
cmdと入力 → 右クリック → 「管理者として実行」)。
.
- ダウンロード用ディレクトリの準備
cd /d c:\ rmdir /s /q kmnist
- Kuzushiji-49 のダウンロード
Kuzushiji-MNIST, Kuzushiji-49, Kuzushiji-Kanji の 3種類をダウンロードできる.
下の実行例では,「2」,「1」を選び,Kuzushiji-49 をダウンロードしている.
cd C:\ git clone https://github.com/rois-codh/kmnist cd kmnist python download_data.py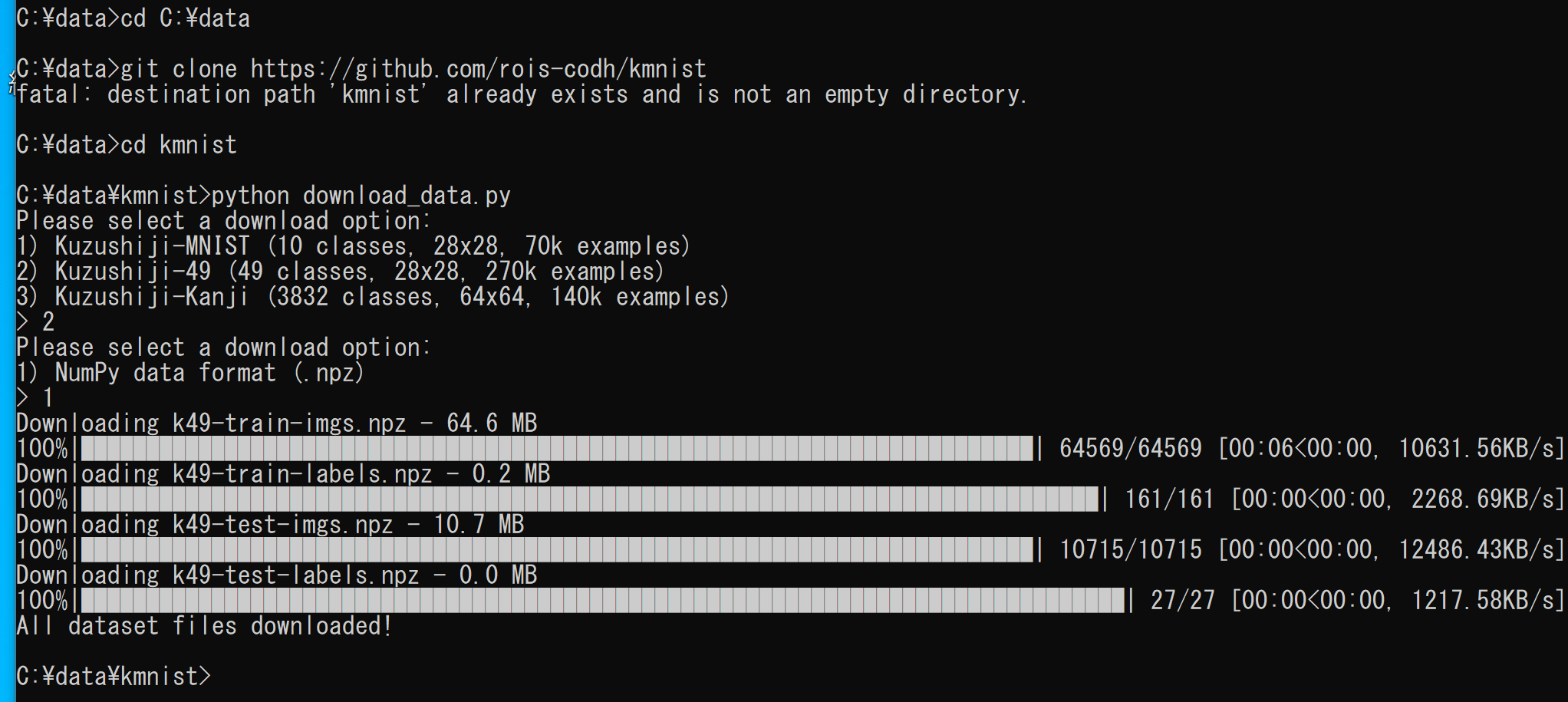
- Kuzushiji-MNIST のダウンロード
Kuzushiji-MNIST, Kuzushiji-49, Kuzushiji-Kanji の 3種類をダウンロードできる.
下の実行例では,「1」,「2」を選び,Kuzushiji-49 をダウンロードしている.
cd C:\kmnist python download_data.py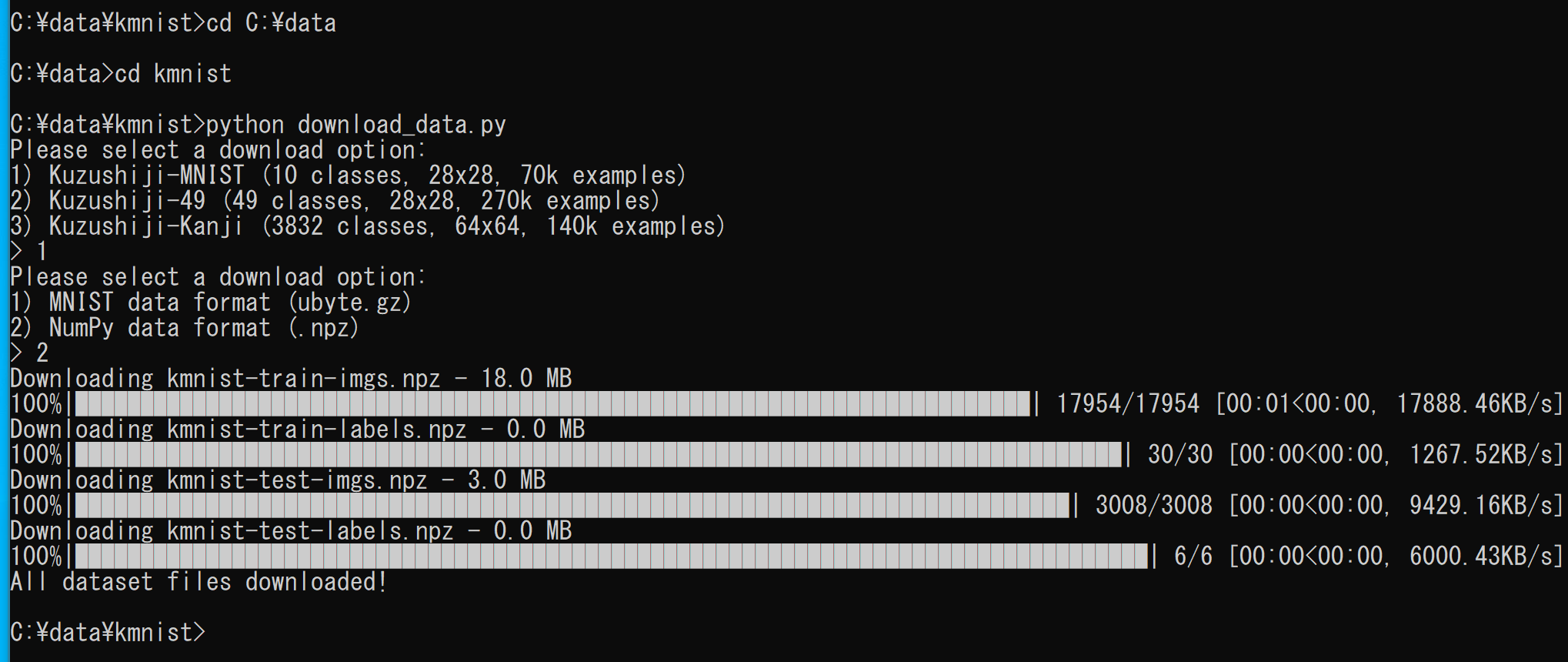
くずし字 MNIST データセット(Kuzushiji-MNIST データセット)のダウンロード,画像分類の学習,画像分類の実行
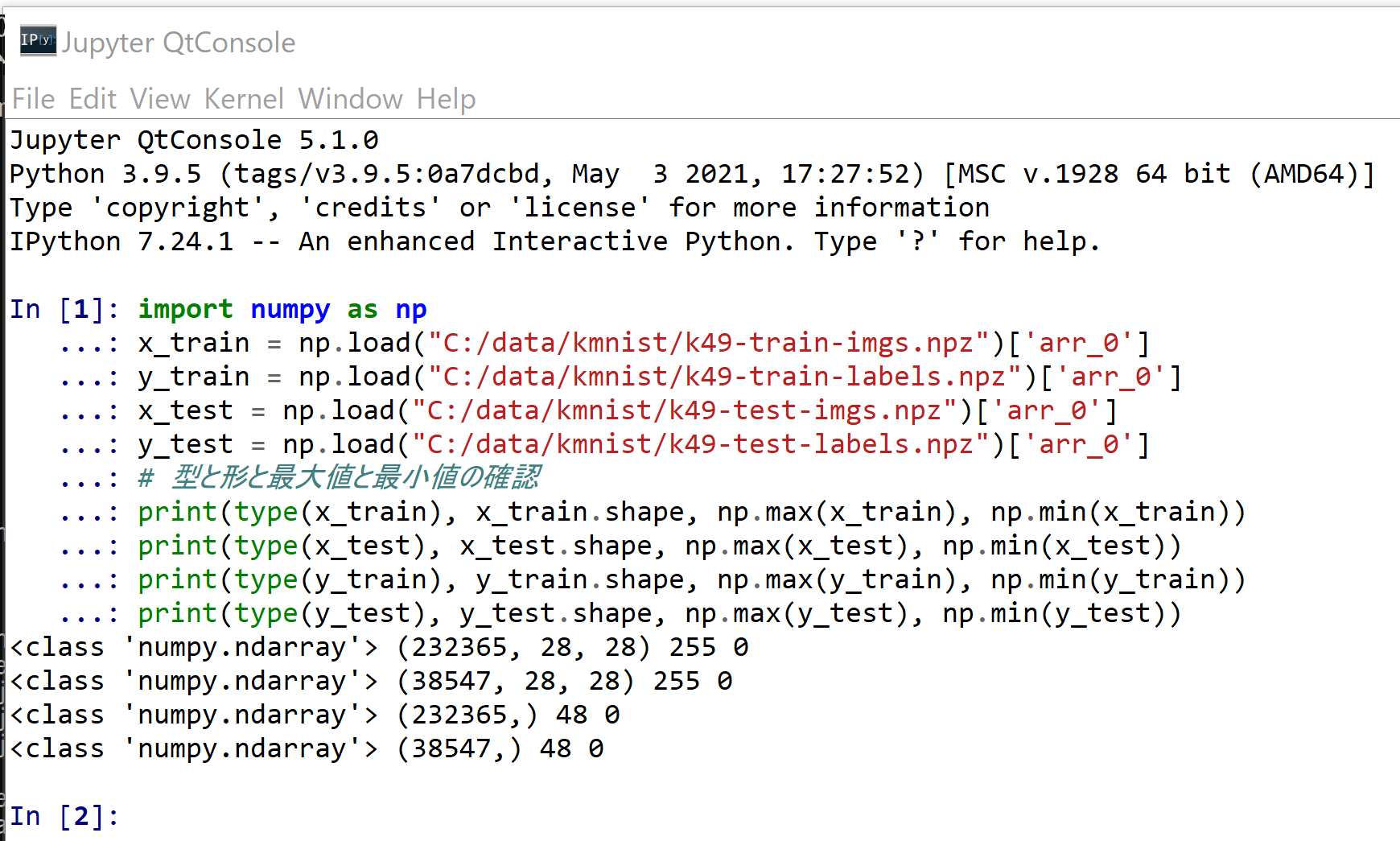
Kuzushiji-49 の読み込み
import numpy as np
x_train = np.load("C:/data/kmnist/k49-train-imgs.npz")['arr_0']
y_train = np.load("C:/data/kmnist/k49-train-labels.npz")['arr_0']
x_test = np.load("C:/data/kmnist/k49-test-imgs.npz")['arr_0']
y_test = np.load("C:/data/kmnist/k49-test-labels.npz")['arr_0']
# 【x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test の numpy ndarray への変換と,値の範囲の調整(値の範囲が 0 ~ 255 であるのを,0 ~ 1 に調整)する】
print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train))
print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test))
print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train))
print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test))
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings
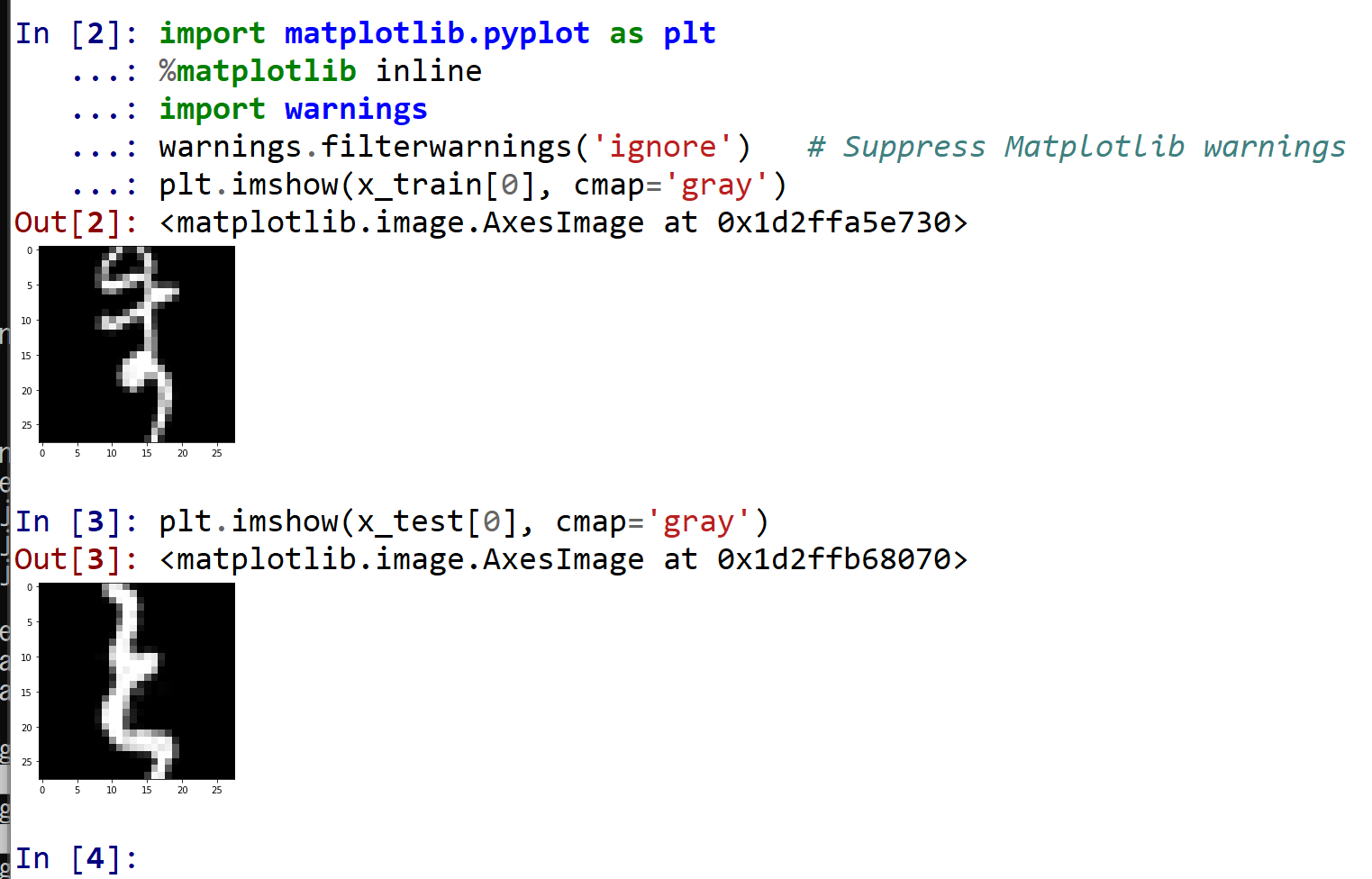
plt.imshow(x_train[0], cmap='gray')
plt.imshow(x_test[0], cmap='gray')
Kuzushiji-MNIST の読み込み
- 読み込み
import numpy as np x_train = np.load("C:/data/kmnist/kmnist-train-imgs.npz")['arr_0'] y_train = np.load("C:/data/kmnist/kmnist-train-labels.npz")['arr_0'] x_test = np.load("C:/data/kmnist/kmnist-test-imgs.npz")['arr_0'] y_test = np.load("C:/data/kmnist/kmnist-test-labels.npz")['arr_0'] # 【x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test の numpy ndarray への変換と,値の範囲の調整(値の範囲が 0 ~ 255 であるのを,0 ~ 1 に調整)する】 print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test))
- 確認表示
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings plt.imshow(x_train[0], cmap='gray') plt.imshow(x_test[0], cmap='gray')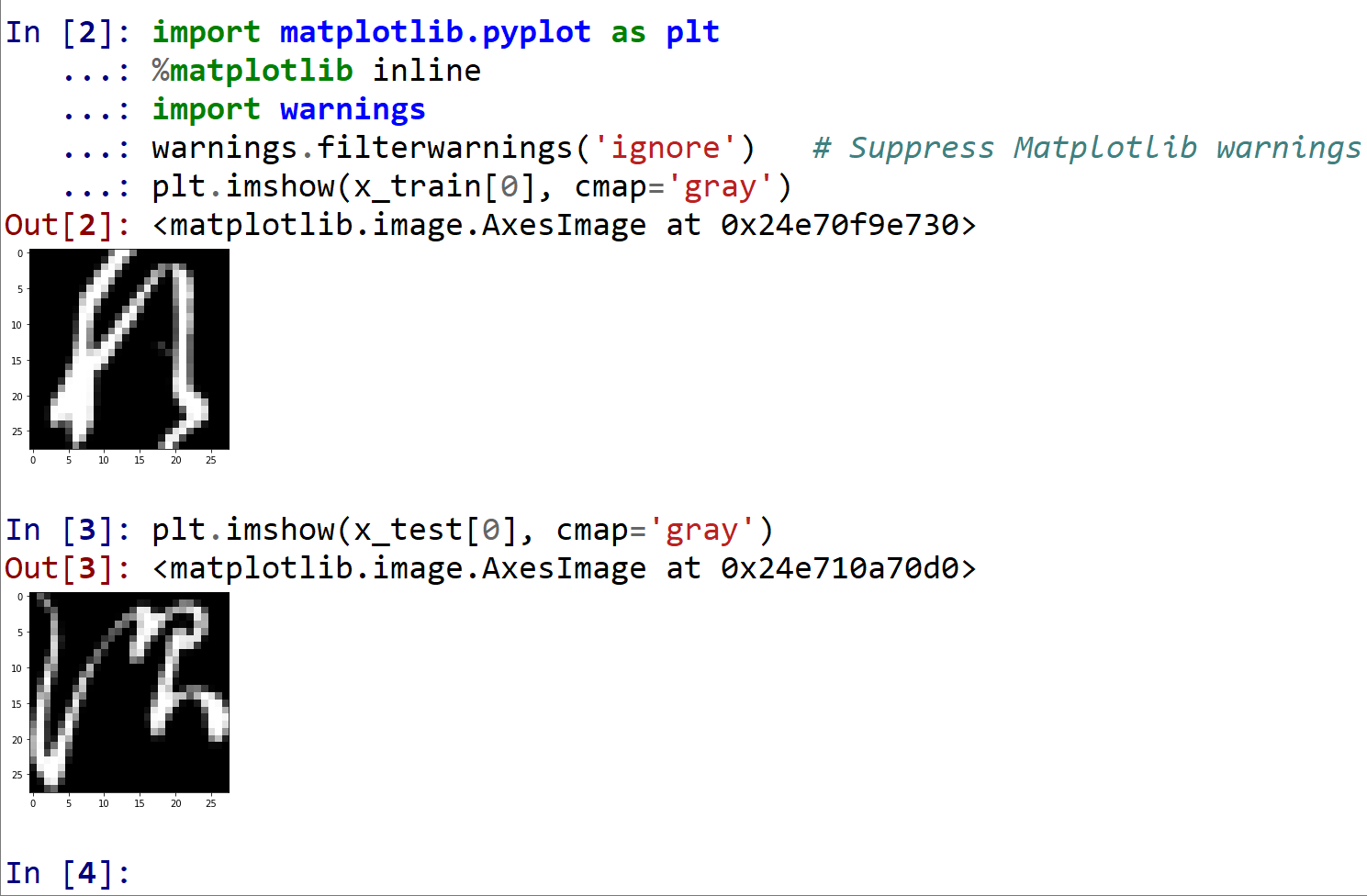
ディープラーニングの実行
Kuzushiji-MNIST を用いる.
- パッケージのインポート,TensorFlow のバージョン確認など
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras import backend as K K.clear_session() import numpy as np import tensorflow_datasets as tfds from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings
- x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test の numpy ndarray への変換と,値の範囲の調整(値の範囲が 0 〜 255 であるのを,0 〜 1 に調整)
x_train = x_train.astype("float32") / 255.0 x_test = x_test.astype("float32") / 255.0 print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test))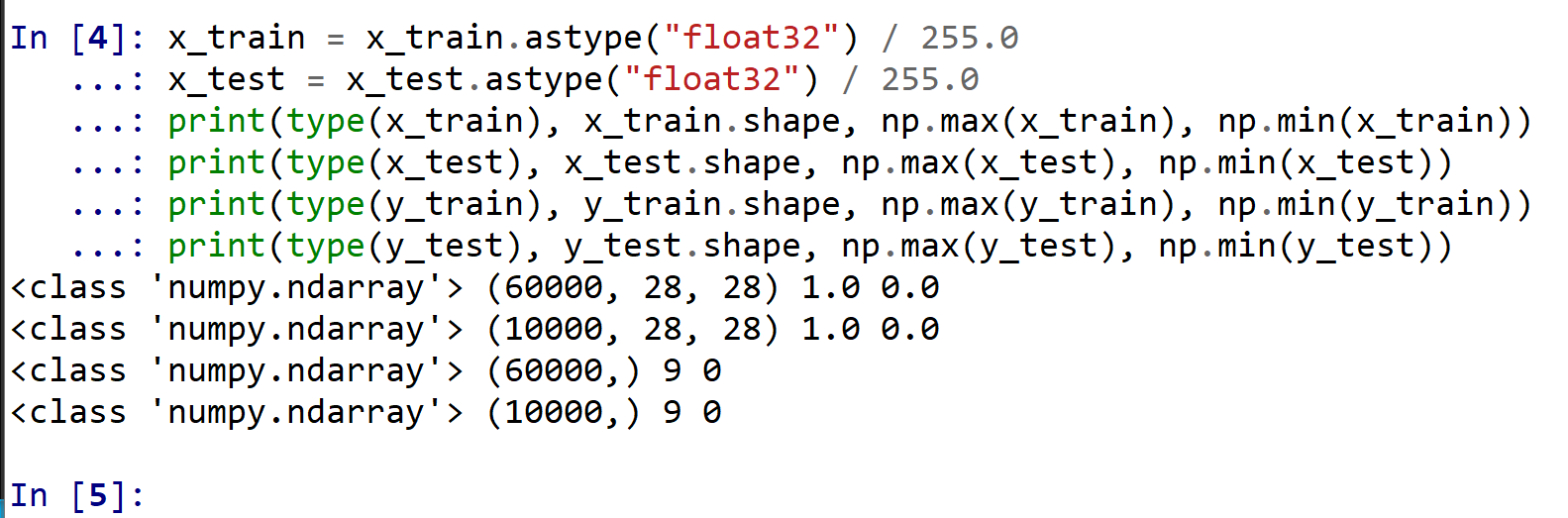
- データの確認表示
class_names = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'] plt.style.use('default') plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) for i in range(25): plt.subplot(5,5,i+1) plt.xticks([]) plt.yticks([]) plt.grid(False) plt.imshow(x_train[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary) plt.xlabel(class_names[y_train[i]]) plt.show()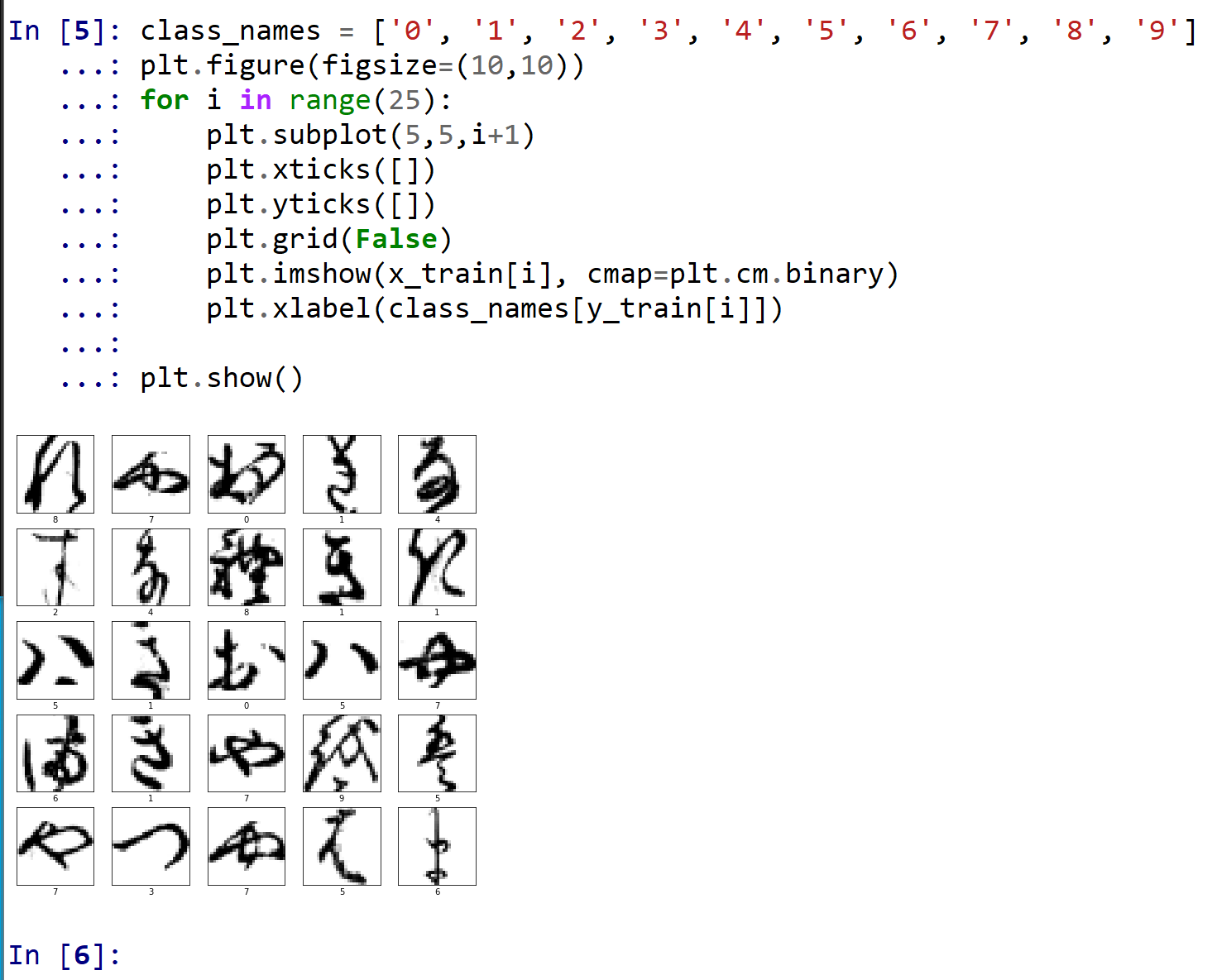
- ニューラルネットワークの作成と確認とコンパイル
2層のニューラルネットワークを作成
1層目:ユニット数は 128
2層目:ユニット数は 10
ADAM を使う場合のプログラム例
NUM_CLASSES = 10 m = tf.keras.Sequential() m.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28))) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=128, activation='relu')) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate=0.5)) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=NUM_CLASSES, activation='softmax')) m.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001), loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
SGD を使う場合のプログラム例
m = tf.keras.Sequential() m.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28))) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=128, activation='relu')) m.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate=0.5)) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=10, activation='softmax')) m.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True), loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) - ニューラルネットワークの確認表示
print(m.summary())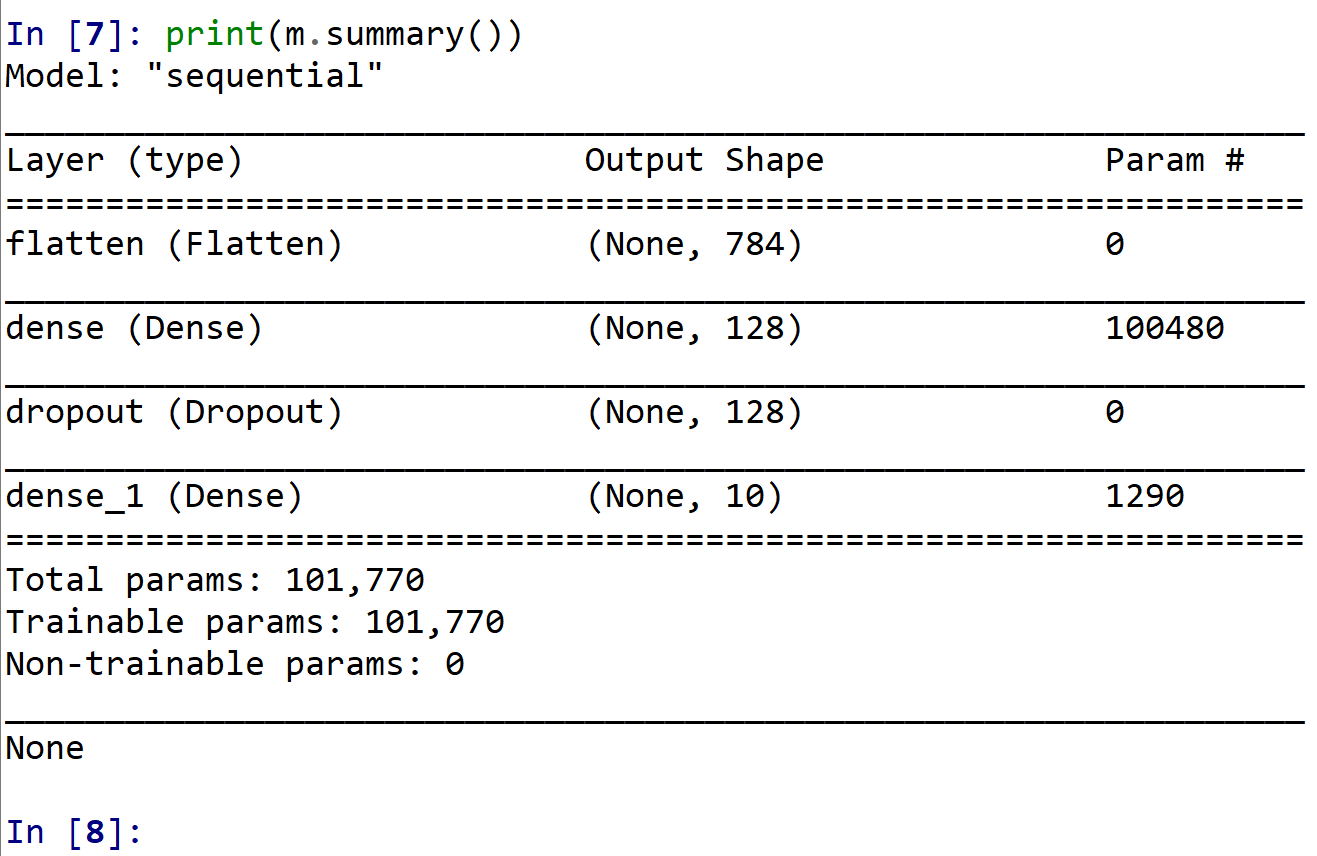
- ニューラルネットワークの学習を行う
EPOCHS = 50 history = m.fit(x_train, y_train, validation_data=(x_test, y_test), verbose=2, epochs=EPOCHS)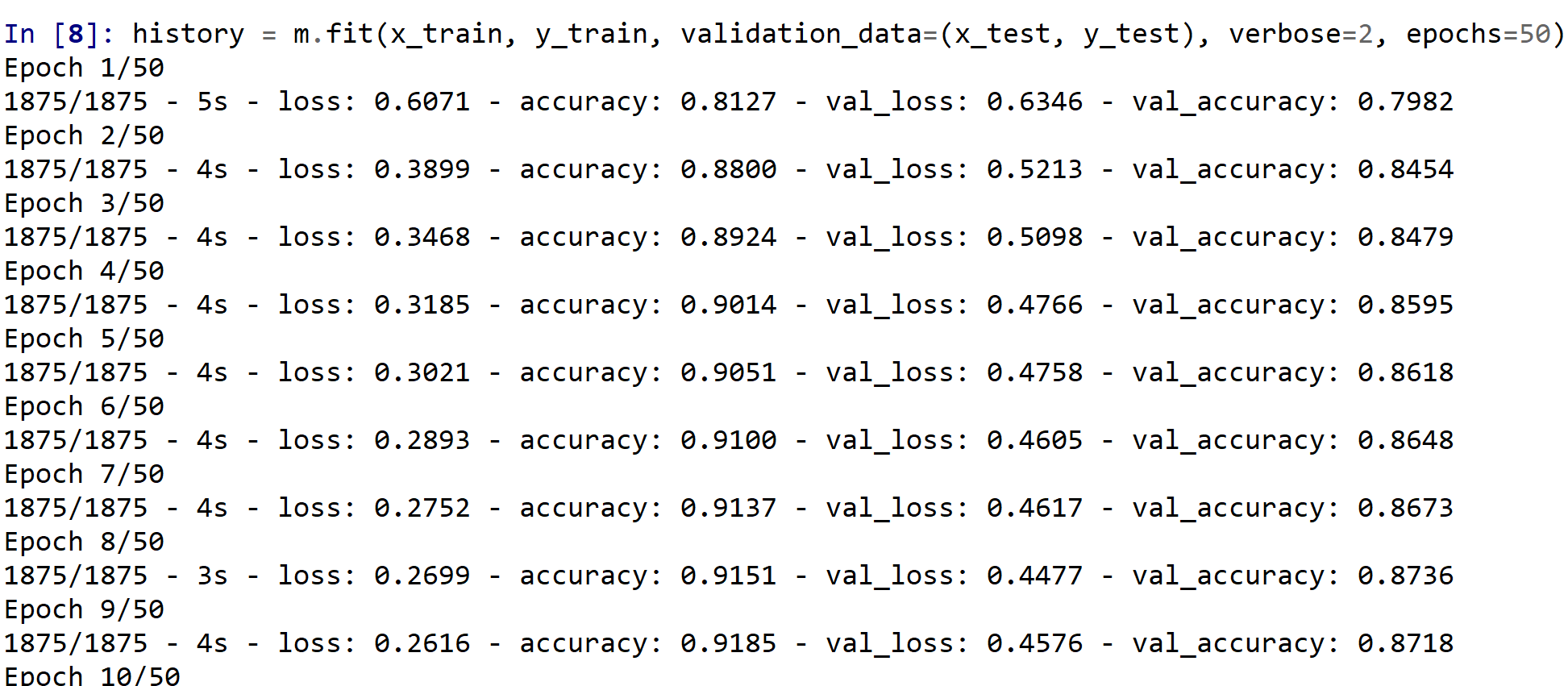
- ニューラルネットワークを使い,分類を行う.
* 訓練(学習)などで乱数が使われるので,下図と違う値になる.
predictions = m.predict(x_test) print(predictions[0])
- 正解表示
テスト画像 0 番の正解を表示
print(y_test[0])
- 訓練の履歴の可視化
【関連する外部ページ】 訓練の履歴の可視化については,https://keras.io/ja/visualization/
- 学習時と検証時の,損失の違い
acc = history.history['accuracy'] val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy'] loss = history.history['loss'] val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1) # "bo" は青いドット plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss') # ”b" は青い実線 plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss') plt.title('Training and validation loss') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Loss') plt.legend() plt.show()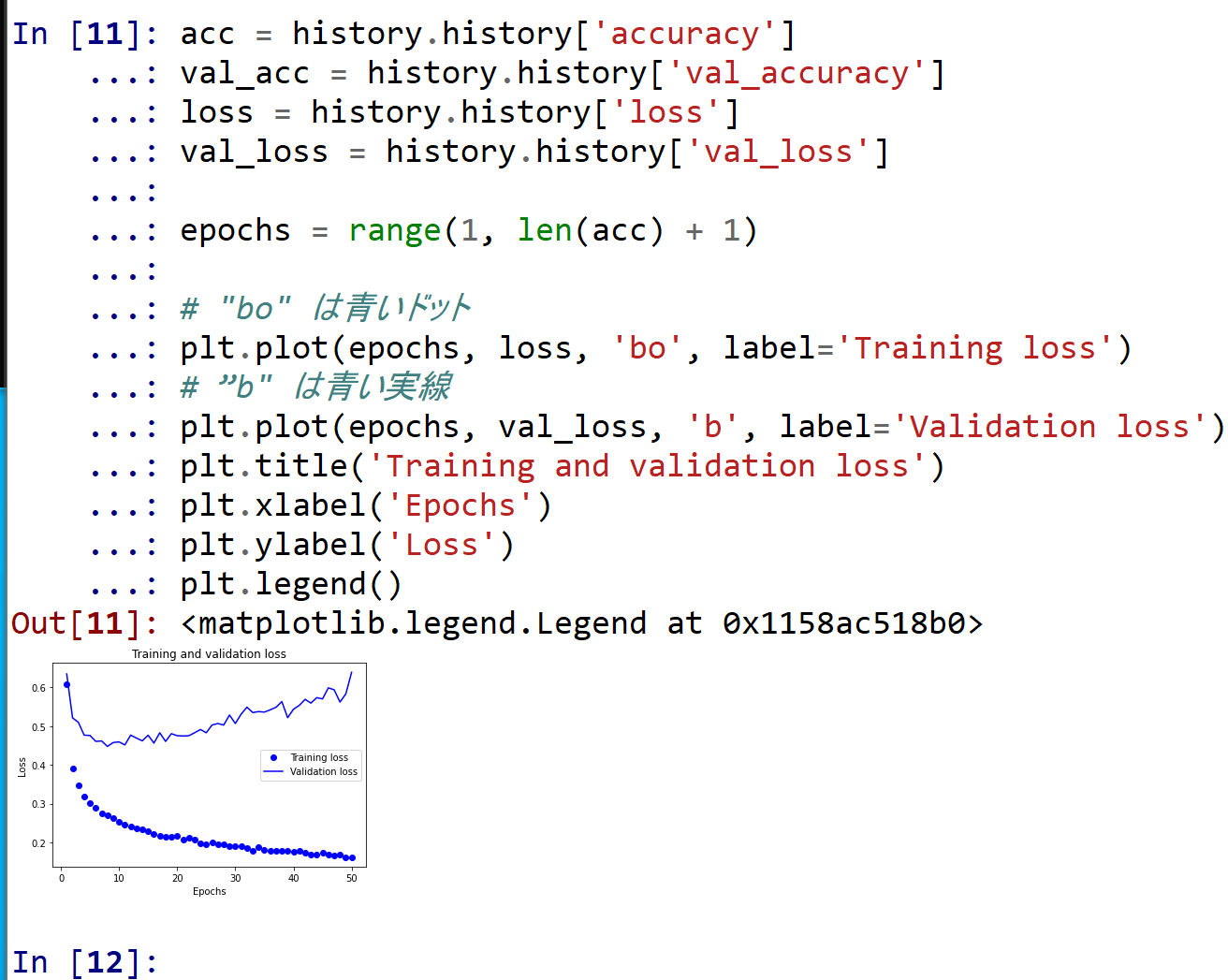
- 学習時と検証時の,精度の違い
acc = history.history['accuracy'] val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy'] loss = history.history['loss'] val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] plt.clf() # 図のクリア plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc') plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc') plt.title('Training and validation accuracy') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.legend() plt.show()
- 学習時と検証時の,損失の違い
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)