MMTracking のインストールと動作確認(トラッキングビジョン)(PyTorch,Python,MMCV,MMDetection を使用)(Windows 上)
前準備
Build Tools for Visual Studio 2022 のインストール(Windows 上)
Build Tools for Visual Studio は,Visual Studio の IDE を含まない C/C++ コンパイラ,ライブラリ,ビルドツール等のコマンドライン向け開発ツールセットである。
以下のコマンドを管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー → cmd と入力 → 右クリック → 「管理者として実行」)。
REM VC++ ランタイム
winget install --scope machine --id Microsoft.VCRedist.2015+.x64 -e --silent --disable-interactivity --force --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/quiet /norestart"
REM Build Tools + Desktop development with C++(VCTools)+ 追加コンポーネント(一括)
winget install --id Microsoft.VisualStudio.2022.BuildTools --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements ^
--override "--passive --wait --norestart --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Workload.VCTools --includeRecommended --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Llvm.Clang --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.ComponentGroup.ClangCL --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.CMake.Project --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.Windows11SDK.26100"--add で追加されるコンポーネント
上記のコマンドでは,まず Build Tools 本体と Visual C++ 再頒布可能パッケージをインストールし,次に setup.exe を用いて以下のコンポーネントを追加している。
VCTools:C++ デスクトップ開発ワークロード(--includeRecommendedにより、MSVC コンパイラ、C++ AddressSanitizer、vcpkg、CMake ツール、Windows 11 SDK 等の推奨コンポーネントが含まれる)VC.Llvm.Clang:Windows 向け C++ Clang コンパイラClangCL:clang-cl ツールセットを含むコンポーネントグループ(MSBuild から Clang を使用するために必要)VC.CMake.Project:Windows 向け C++ CMake ツールWindows11SDK.26100:Windows 11 SDK(ビルド 10.0.26100)
インストール完了の確認
winget list Microsoft.VisualStudio.2022.BuildTools上記以外の追加のコンポーネントが必要になった場合は Visual Studio Installer で個別にインストールできる。
Visual Studio の機能を必要とする場合は、追加インストールできる。
Python 3.12 のインストール(Windows 上) [クリックして展開]
以下のいずれかの方法で Python 3.12 をインストールする。Python がインストール済みの場合、この手順は不要である。
方法1:winget によるインストール
管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 -e --silent --disable-interactivity --force --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/quiet InstallAllUsers=1 PrependPath=1 Include_pip=1 Include_test=0 Include_launcher=1 InstallLauncherAllUsers=1"--scope machine を指定することで、システム全体(全ユーザー向け)にインストールされる。このオプションの実行には管理者権限が必要である。インストール完了後、コマンドプロンプトを再起動すると PATH が自動的に設定される。
方法2:インストーラーによるインストール
- Python 公式サイト(https://www.python.org/downloads/)にアクセスし、「Download Python 3.x.x」ボタンから Windows 用インストーラーをダウンロードする。
- ダウンロードしたインストーラーを実行する。
- 初期画面の下部に表示される「Add python.exe to PATH」に必ずチェックを入れてから「Customize installation」を選択する。このチェックを入れ忘れると、コマンドプロンプトから
pythonコマンドを実行できない。 - 「Install Python 3.xx for all users」にチェックを入れ、「Install」をクリックする。
インストールの確認
コマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。
python --versionバージョン番号(例:Python 3.12.x)が表示されればインストール成功である。「'python' は、内部コマンドまたは外部コマンドとして認識されていません。」と表示される場合は、インストールが正常に完了していない。
Git のインストール
管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
REM Git をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Git.Git -e --silent --disable-interactivity --force --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/VERYSILENT /NORESTART /NOCANCEL /SP- /CLOSEAPPLICATIONS /RESTARTAPPLICATIONS /COMPONENTS=""icons,ext\reg\shellhere,assoc,assoc_sh"" /o:PathOption=Cmd /o:CRLFOption=CRLFCommitAsIs /o:BashTerminalOption=MinTTY /o:DefaultBranchOption=main /o:EditorOption=VIM /o:SSHOption=OpenSSH /o:UseCredentialManager=Enabled /o:PerformanceTweaksFSCache=Enabled /o:EnableSymlinks=Disabled /o:EnableFSMonitor=Disabled"
【関連する外部ページ】
- Git の公式ページ: https://git-scm.com/
Build Tools for Visual Studio 2022,NVIDIA ドライバ,NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8,NVIDIA cuDNN 8.9.7 のインストール(Windows 上)
【サイト内の関連ページ】 NVIDIA グラフィックスボードを搭載しているパソコンの場合には, NVIDIA ドライバ, NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット, NVIDIA cuDNN のインストールを行う.
- Windows での Build Tools for Visual Studio 2022 のインストール: 別ページ »で説明
- Windows での NVIDIA ドライバ,NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8,NVIDIA cuDNN v8.9.7 のインストール手順: 別ページ »で説明
【関連する外部ページ】
- Build Tools for Visual Studio 2022 (ビルドツール for Visual Studio 2022)の公式ダウンロードページ: https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/ja/visual-cpp-build-tools/
- NVIDIA ドライバのダウンロードの公式ページ: https://www.nvidia.co.jp/Download/index.aspx?lang=jp
- NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのアーカイブの公式ページ: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive
- NVIDIA cuDNN のダウンロードの公式ページ: https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn
PyTorch のインストール(Windows 上)
- 以下の手順を管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー →
cmdと入力 → 右クリック → 「管理者として実行」)。 - PyTorch のページを確認
- 次のようなコマンドを実行(実行するコマンドは,PyTorch のページの表示されるコマンドを使う).
次のコマンドを実行することにより, PyTorch 2.3 (NVIDIA CUDA 11.8 用)がインストールされる. 但し,Anaconda3を使いたい場合には別手順になる.
事前に NVIDIA CUDA のバージョンを確認しておくこと(ここでは,NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8 が前もってインストール済みであるとする).
PyTorch で,GPU が動作している場合には,「torch.cuda.is_available()」により,True が表示される.
python -m pip install -U --ignore-installed pip python -m pip uninstall -y torch torchvision torchaudio torchtext xformers python -m pip install -U torch torchvision torchaudio numpy --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118 python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__, torch.cuda.is_available())"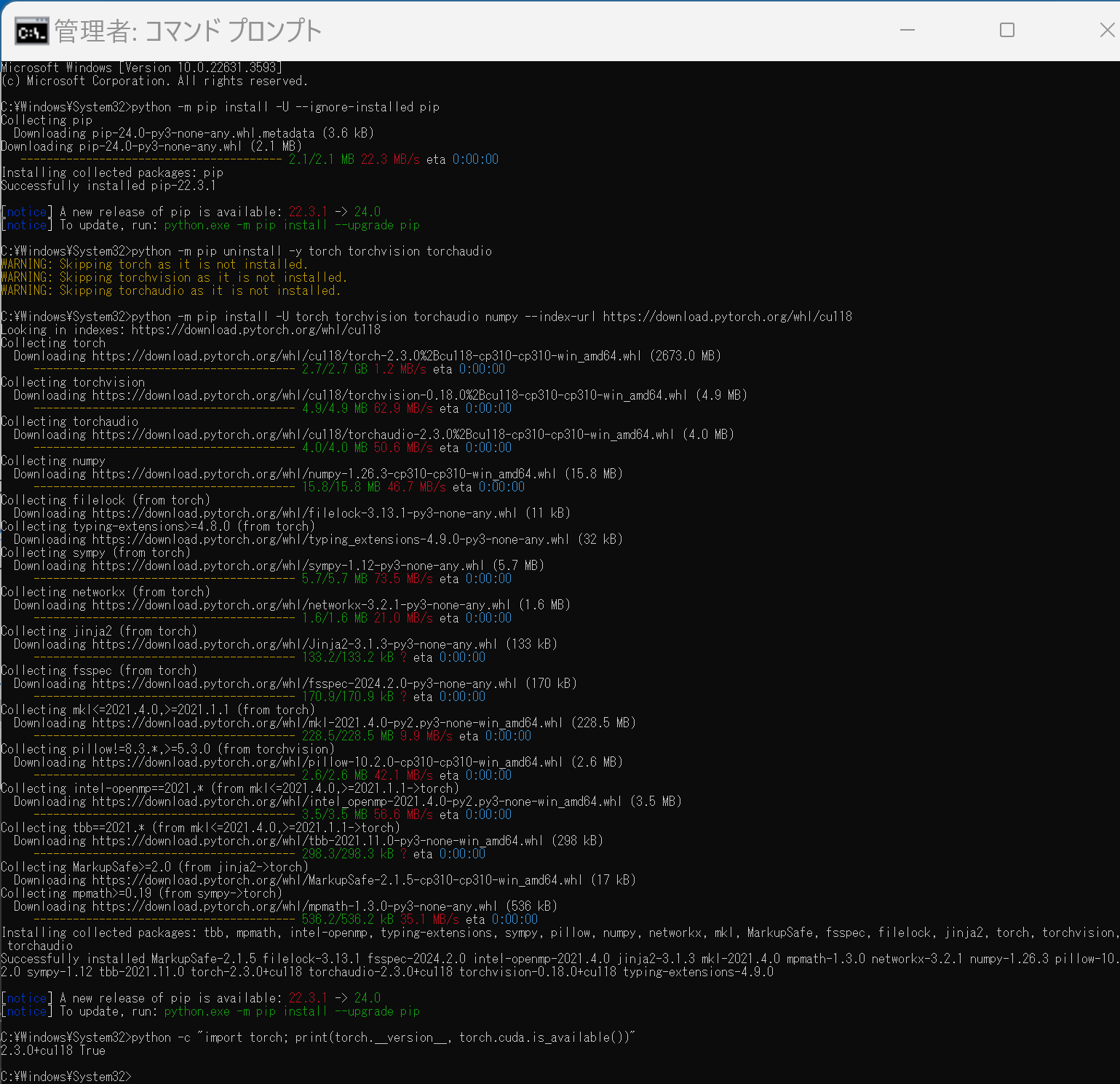 Anaconda3を使いたい場合には, Anaconda プロンプト (Anaconda Prompt) を管理者として実行し, 次のコマンドを実行する. (PyTorch と NVIDIA CUDA との連携がうまくいかない可能性があるため,Anaconda3を使わないことも検討して欲しい).
Anaconda3を使いたい場合には, Anaconda プロンプト (Anaconda Prompt) を管理者として実行し, 次のコマンドを実行する. (PyTorch と NVIDIA CUDA との連携がうまくいかない可能性があるため,Anaconda3を使わないことも検討して欲しい).conda install -y pytorch torchvision torchaudio pytorch-cuda=11.8 cudnn -c pytorch -c nvidia py -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__, torch.cuda.is_available())"【サイト内の関連ページ】
【関連する外部ページ】
MMTracking のインストール(Windows 上)
- 以下の手順を管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー →
cmdと入力 → 右クリック → 「管理者として実行」)。 - MIM,MMTracking のインストール
インストール手順は, https://mmcv.readthedocs.io/en/latest/get_started/installation.html に記載の手順による
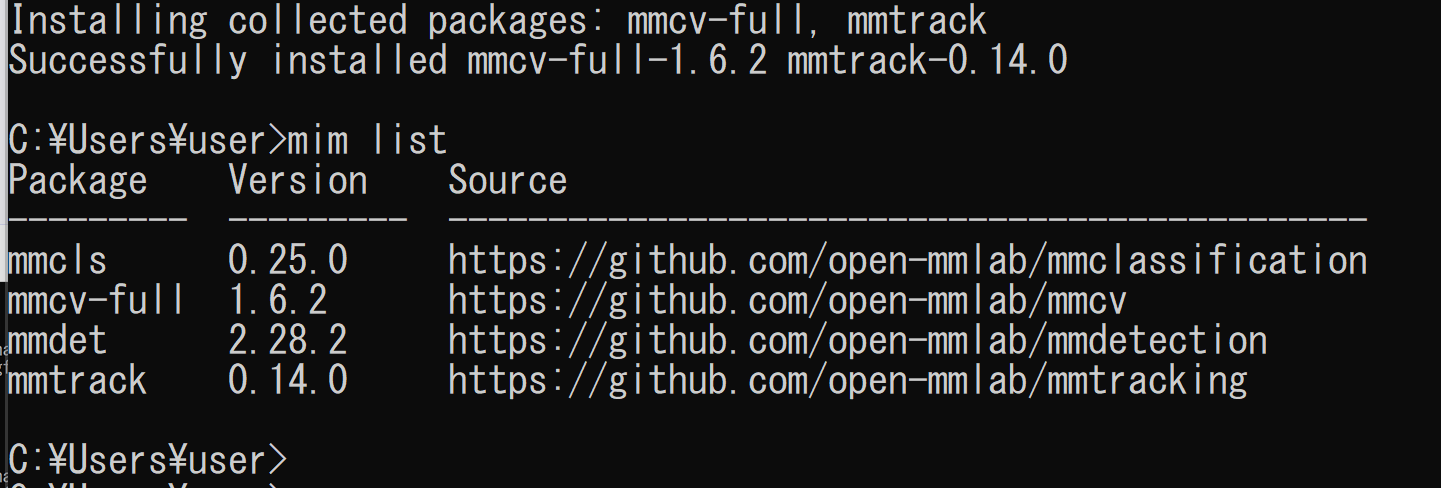
python -m pip install -U --ignore-installed pip python -m pip uninstall -y openmim mmcv mmcv-full opencv-python opencv-python-headless python -m pip install -U openmim opencv-python python -m pip install -U --ignore-installed --no-cache-dir numpy cd /d c:%HOMEPATH% rmdir /s /q mmtracking git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmtracking.git cd mmtracking mim uninstall -y mmtrack pip install -r requirements.txt mim install -e . mim list(途中省略)
- MOT evaluation のインストール
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/JonathonLuiten/TrackEval.git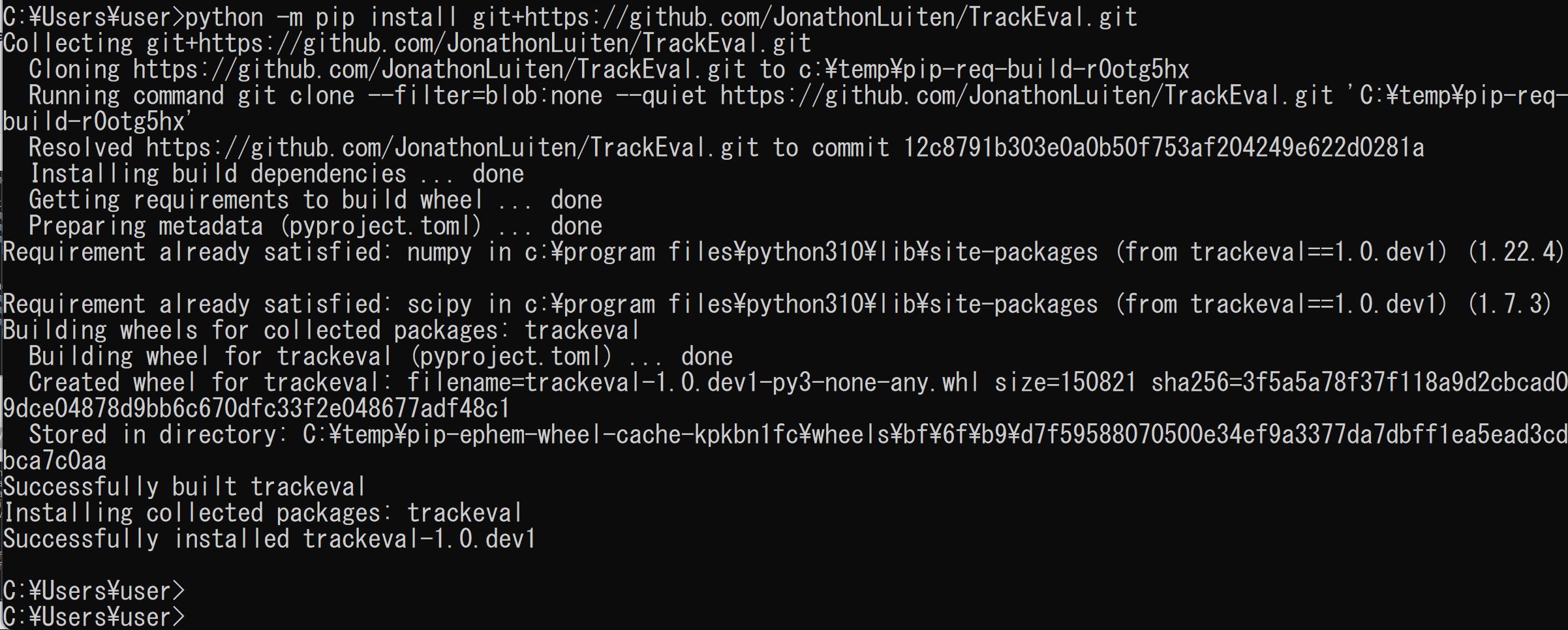
MMTracking の動作確認(Windows 上)
- 以下の手順を管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー →
cmdと入力 → 右クリック → 「管理者として実行」)。 - 事前学習済みモデルのダウンロード
次のコマンドを実行する.
cd /d c:%HOMEPATH%\mmtracking mkdir checkpoints cd checkpoints curl -O https://download.openmmlab.com/mmtracking/vid/selsa/selsa_faster_rcnn_r50_dc5_1x_imagenetvid/selsa_faster_rcnn_r50_dc5_1x_imagenetvid_20201227_204835-2f5a4952.pth curl -O https://download.openmmlab.com/mmtracking/sot/siamese_rpn/siamese_rpn_r50_1x_lasot/siamese_rpn_r50_1x_lasot_20211203_151612-da4b3c66.pth curl -O https://download.openmmlab.com/mmtracking/vis/masktrack_rcnn/masktrack_rcnn_r50_fpn_12e_youtubevis2019/masktrack_rcnn_r50_fpn_12e_youtubevis2019_20211022_194830-6ca6b91e.pth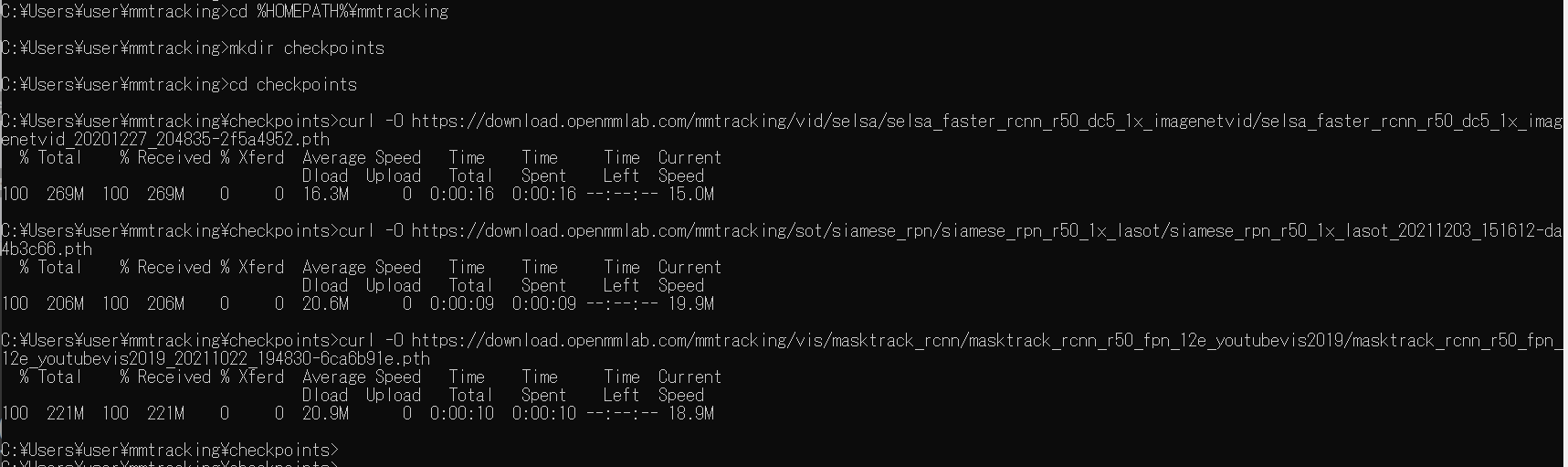
- MOT (Multiple Object Tracling) を行う Python プログラム
次の Python プログラムを実行する.mmcv を用いた表示を行うので,Jupyter QtConsole や Jupyter ノートブック (Jupyter Notebook) の利用が便利である.
Python プログラムは,公式ページhttps://github.com/open-mmlab/mmtracking/blob/master/demo/MMTracking_Tutorial.ipynb のものを書き換えて使用.
下図では,Python プログラムの実行のため,jupyter qtconsole を使用している.
import os import mmcv import tempfile from mmtrack.apis import inference_mot, init_model os.chdir((os.getenv('HOMEPATH') + '\\' + 'mmtracking')) mot_config = './configs/mot/deepsort/deepsort_faster-rcnn_fpn_4e_mot17-private-half.py' input_video = './demo/demo.mp4' imgs = mmcv.VideoReader(input_video) # build the model from a config file mot_model = init_model(mot_config, device='cuda:0') prog_bar = mmcv.ProgressBar(len(imgs)) out_dir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() out_path = out_dir.name # test and show/save the images for i, img in enumerate(imgs): result = inference_mot(mot_model, img, frame_id=i) mot_model.show_result( img, result, show=False, wait_time=int(1000. / imgs.fps), out_file=f'{out_path}/{i:06d}.jpg') prog_bar.update() output = './demo/mot.mp4' print(f'\n making the output video at {output} with a FPS of {imgs.fps}') mmcv.frames2video(out_path, output, fps=imgs.fps, fourcc='mp4v') out_dir.cleanup()
./demo/mot.mp4 を表示.

- VIS (Video Instance Segmentation) を行う Python プログラム
次の Python プログラムを実行する.mmcv を用いた表示を行うので,Jupyter QtConsole や Jupyter ノートブック (Jupyter Notebook) の利用が便利である.
Python プログラムは,公式ページhttps://github.com/open-mmlab/mmtracking/blob/master/demo/MMTracking_Tutorial.ipynb のものを書き換えて使用.
下図では,Python プログラムの実行のため,jupyter qtconsole を使用している.
import os import mmcv import tempfile from mmtrack.apis import inference_mot, init_model os.chdir((os.getenv('HOMEPATH') + '\\' + 'mmtracking')) vis_config = './configs/vis/masktrack_rcnn/masktrack_rcnn_r50_fpn_12e_youtubevis2019.py' vis_checkpoint = './checkpoints/masktrack_rcnn_r50_fpn_12e_youtubevis2019_20211022_194830-6ca6b91e.pth' # build the model from a config file and a checkpoint file vis_model = init_model(vis_config, vis_checkpoint, device='cuda:0') input_video = './demo/demo.mp4' imgs = mmcv.VideoReader(input_video) prog_bar = mmcv.ProgressBar(len(imgs)) out_dir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() out_path = out_dir.name for i, img in enumerate(imgs): result = inference_mot(vis_model, img, frame_id=i) vis_model.show_result( img, result, wait_time=int(1000. / imgs.fps), out_file=f'{out_path}/{i:06d}.jpg') prog_bar.update() output = './demo/vis.mp4' print(f'\n making the output video at {output} with a FPS of {imgs.fps}') mmcv.frames2video(out_path, output, fps=imgs.fps, fourcc='mp4v') out_dir.cleanup()
./demo/vis.mp4 を表示.

- VID (Video Object Detection) を行う Python プログラム
次の Python プログラムを実行する.mmcv を用いた表示を行うので,Jupyter QtConsole や Jupyter ノートブック (Jupyter Notebook) の利用が便利である.
Python プログラムは,公式ページhttps://github.com/open-mmlab/mmtracking/blob/master/demo/MMTracking_Tutorial.ipynb のものを書き換えて使用.
下図では,Python プログラムの実行のため,jupyter qtconsole を使用している.
import os import mmcv import tempfile from mmtrack.apis import inference_vid, init_model os.chdir((os.getenv('HOMEPATH') + '\\' + 'mmtracking')) vid_config = './configs/vid/selsa/selsa_faster_rcnn_r50_dc5_1x_imagenetvid.py' vid_checkpoint = './checkpoints/selsa_faster_rcnn_r50_dc5_1x_imagenetvid_20201227_204835-2f5a4952.pth' # build the model from a config file and a checkpoint file vid_model = init_model(vid_config, vid_checkpoint, device='cuda:0') input_video = './demo/demo.mp4' imgs = mmcv.VideoReader(input_video) prog_bar = mmcv.ProgressBar(len(imgs)) out_dir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() out_path = out_dir.name for i, img in enumerate(imgs): result = inference_vid(vid_model, img, frame_id=i) vid_model.show_result( img, result, wait_time=int(1000. / imgs.fps), out_file=f'{out_path}/{i:06d}.jpg') prog_bar.update() output = './demo/vid.mp4' print(f'\n making the output video at {output} with a FPS of {imgs.fps}') mmcv.frames2video(out_path, output, fps=imgs.fps, fourcc='mp4v') out_dir.cleanup()
./demo/vid.mp4 を表示.
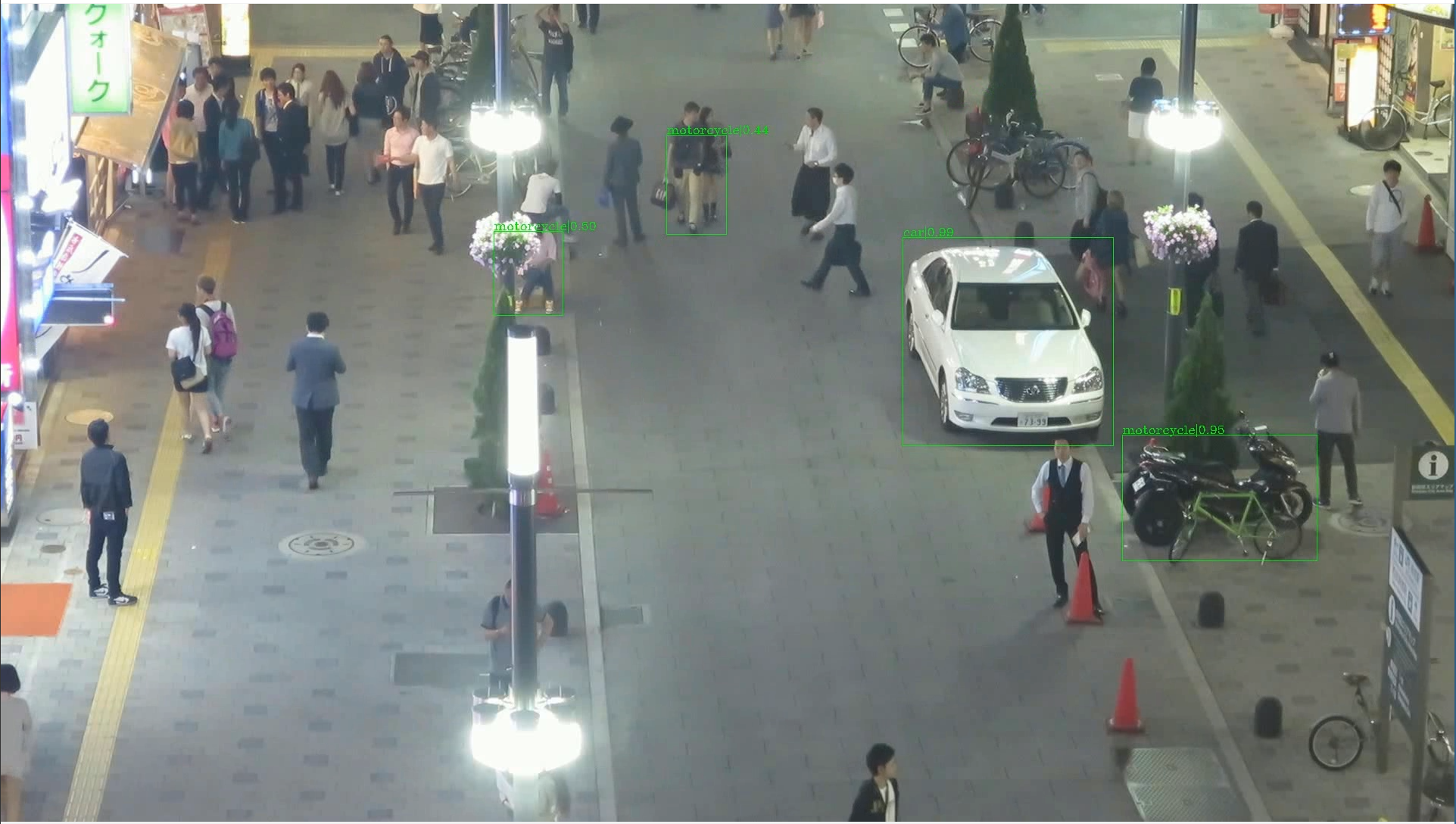

- SOT (Single Object Tracking) を行う Python プログラム
次の Python プログラムを実行する.mmcv を用いた表示を行うので,Jupyter QtConsole や Jupyter ノートブック (Jupyter Notebook) の利用が便利である.
Python プログラムは,公式ページhttps://github.com/open-mmlab/mmtracking/blob/master/demo/MMTracking_Tutorial.ipynb のものを書き換えて使用.
下図では,Python プログラムの実行のため,jupyter qtconsole を使用している.
import os import mmcv import tempfile from mmtrack.apis import inference_sot, init_model os.chdir((os.getenv('HOMEPATH') + '\\' + 'mmtracking')) sot_config = './configs/sot/siamese_rpn/siamese_rpn_r50_20e_lasot.py' sot_checkpoint = './checkpoints/siamese_rpn_r50_1x_lasot_20211203_151612-da4b3c66.pth' # build the model from a config file and a checkpoint file sot_model = init_model(sot_config, sot_checkpoint, device='cuda:0') init_bbox = [371, 411, 450, 646] input_video = './demo/demo.mp4' imgs = mmcv.VideoReader(input_video) prog_bar = mmcv.ProgressBar(len(imgs)) out_dir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() out_path = out_dir.name for i, img in enumerate(imgs): result = inference_sot(sot_model, img, init_bbox, frame_id=i) sot_model.show_result( img, result, wait_time=int(1000. / imgs.fps), out_file=f'{out_path}/{i:06d}.jpg') prog_bar.update() output = './demo/sot.mp4' print(f'\n making the output video at {output} with a FPS of {imgs.fps}') mmcv.frames2video(out_path, output, fps=imgs.fps, fourcc='mp4v') out_dir.cleanup()
./demo/sot.mp4 を表示.
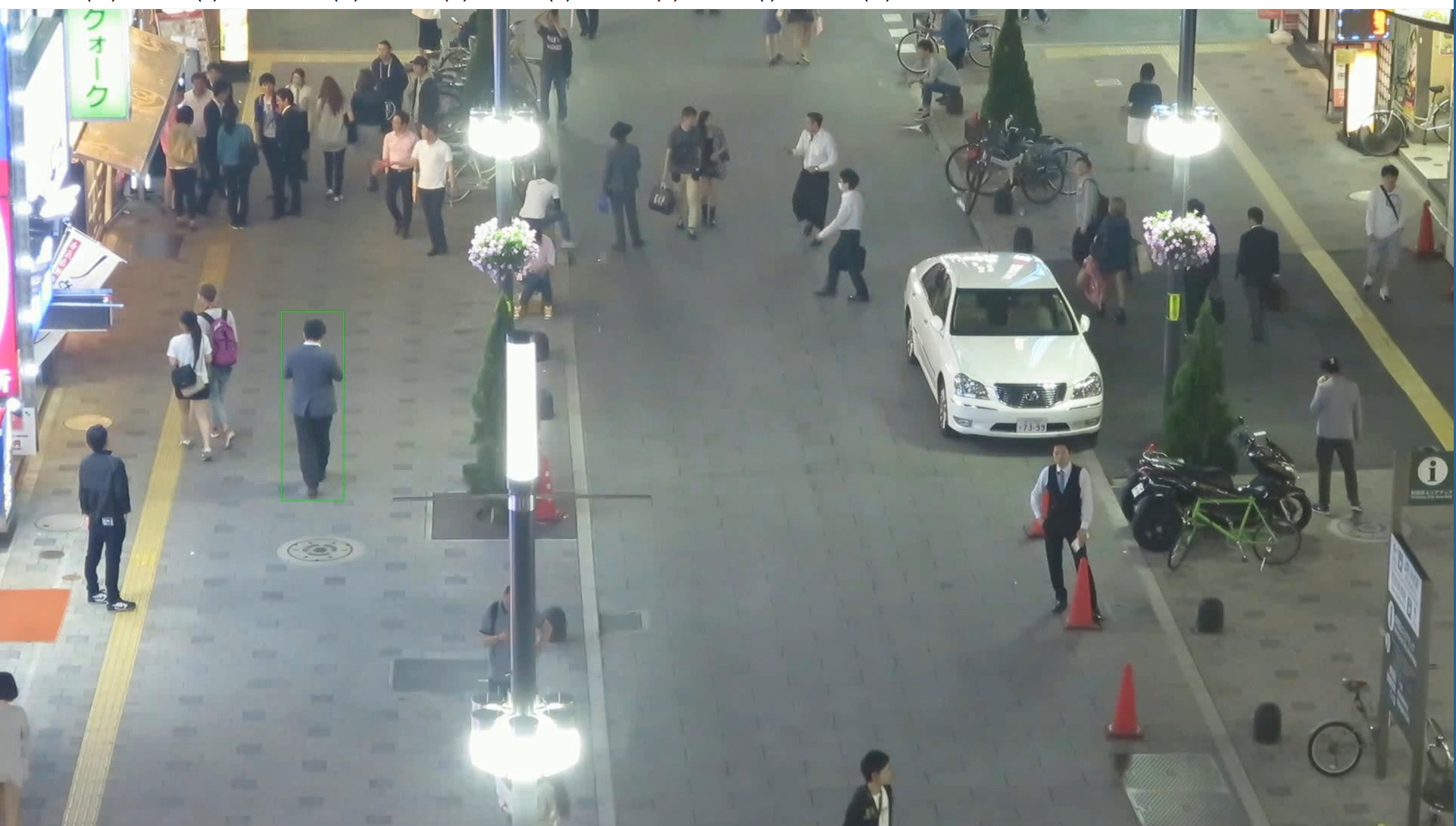

- 以下の手順を管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー →
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)