Dlib を用いて,顔検出,顔のランドマーク検知(68 ランドマーク法),表情判定を行う(Windows 上)
前準備
Visual Studio 2022 Build Toolsとランタイムのインストール
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要である。
REM Visual Studio 2022 Build Toolsとランタイムをシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --wait --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements Microsoft.VisualStudio.2022.BuildTools Microsoft.VCRedist.2015+.x64
REM インストーラーとインストールパスの設定
set "VS_INSTALLER=C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\Installer\vs_installer.exe"
set VS_PATH="C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\BuildTools"
REM C++開発ワークロードのインストール
"%VS_INSTALLER%" modify --installPath "%VS_PATH%" --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Workload.VCTools --includeRecommended --quiet --norestart
"%VS_INSTALLER%" modify --installPath "%VS_PATH%" --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Tools.x86.x64 --includeRecommended --quiet --norestart
Python 3.12 のインストール
インストール済みの場合は実行不要。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要である。
REM Python 3.12 をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements
REM Python のパス設定
set "PYTHON_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312"
set "PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312\Scripts"
if exist "%PYTHON_PATH%" setx PYTHON_PATH "%PYTHON_PATH%" /M >nul
if exist "%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" setx PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH "%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%" /M >nul
for /f "skip=2 tokens=2*" %a in ('reg query "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" /v Path') do set "SYSTEM_PATH=%b"
echo "%SYSTEM_PATH%" | find /i "%PYTHON_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PYTHON_PATH%;%PYTHON_SCRIPTS_PATH%;%SYSTEM_PATH%" /M >nul【関連する外部ページ】
Python の公式ページ: https://www.python.org/
AI エディタ Windsurf のインストール
Pythonプログラムの編集・実行には、AI エディタの利用を推奨する。ここでは,Windsurfのインストールを説明する。
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行して、Windsurfをシステム全体にインストールする。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
winget install --scope machine --id Codeium.Windsurf -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements【関連する外部ページ】
Windsurf の公式ページ: https://windsurf.com/
Gitのインストール
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
REM Git をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Git.Git -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements
REM Git のパス設定
set "GIT_PATH=C:\Program Files\Git\cmd"
for /f "skip=2 tokens=2*" %a in ('reg query "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" /v Path') do set "SYSTEM_PATH=%b"
if exist "%GIT_PATH%" (
echo "%SYSTEM_PATH%" | find /i "%GIT_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%GIT_PATH%;%SYSTEM_PATH%" /M >nul
)
7-Zip のインストール
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
REM 7-Zip をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id 7zip.7zip -e --silent
REM 7-Zip のパス設定
set "SEVENZIP_PATH=C:\Program Files\7-Zip"
for /f "skip=2 tokens=2*" %a in ('reg query "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" /v Path') do set "SYSTEM_PATH=%b"
if exist "%SEVENZIP_PATH%" (
echo "%SYSTEM_PATH%" | find /i "%SEVENZIP_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%SEVENZIP_PATH%;%SYSTEM_PATH%" /M >nul
)
Visual Studio 2022 Build Toolsとランタイムのインストール
管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー > cmd と入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)し、以下を実行する。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要である。
REM Visual Studio 2022 Build Toolsとランタイムをシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --wait --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements Microsoft.VisualStudio.2022.BuildTools Microsoft.VCRedist.2015+.x64
REM インストーラーとインストールパスの設定
set "VS_INSTALLER=C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\Installer\vs_installer.exe"
set VS_PATH="C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\BuildTools"
REM C++開発ワークロードのインストール
"%VS_INSTALLER%" modify --installPath "%VS_PATH%" --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Workload.VCTools --includeRecommended --quiet --norestart
"%VS_INSTALLER%" modify --installPath "%VS_PATH%" --add Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Tools.x86.x64 --includeRecommended --quiet --norestart
NVIDIA ドライバのインストール(Windows 上)
NVIDIA ドライバ
NVIDIA ドライバは,NVIDIA製GPUを動作させるための重要なソフトウェアである.このドライバをインストールすることにより,GPUの性能を引き出すことができ,グラフィックス関連のアプリ,AI関連のアプリの高速化が期待できる.
ドライバはNVIDIA公式サイトである https://www.nvidia.co.jp/Download/index.aspx?lang=jp からダウンロードできる.このサイトからダウンロードするときには,グラフィックスカードとオペレーティングシステムを選択する. なお,NVIDIA GeForce Experiance を用いてインストールすることも可能である.
【サイト内の関連ページ】
- NVIDIA グラフィックス・ボードの確認
Windows で,NVIDIA グラフィックス・ボードの種類を調べたいときは, 次のコマンドを実行することにより調べることができる.
wmic path win32_VideoController get name - NVIDIA ドライバのダウンロード
NVIDIA ドライバは,以下の NVIDIA 公式サイトからダウンロードできる.
- ダウンロードの際には,使用しているグラフィックス・ボードの型番とオペレーティングシステムを選択する.
NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8 のインストール(Windows 上)
NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストール時の注意点
NVIDIAのGPUを使用して並列計算を行うためのツールセット
主な機能: GPU を利用した並列処理,GPU のメモリ管理,C++をベースとした拡張言語とAPIとライブラリ
【NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットの動作に必要なもの】
- CUDA対応のNVIDIA GPUが必要.
そのために,NVIDIA グラフィックス・ボードを確認する. Windows で,NVIDIA グラフィックス・ボードの種類を調べたいときは, 次のコマンドを実行することにより調べることができる.
wmic path win32_VideoController get name - NVIDIA ドライバのダウンロードとインストール
NVIDIA ドライバは,以下の NVIDIA 公式サイトからダウンロードできる. ダウンロードの際には,使用しているグラフィックス・ボードの型番とオペレーティングシステムを選択する.
- Windows では,インストール前に,Build Tools for Visual Studio もしくは Visual Studio をインストールしておくことが必要である.
【Windows でインストールするときの注意点】
- Windows では, NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストール中は,なるべく他のウインドウはすべて閉じておくこと.
- NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストールが終わったら,ユーザ環境変数 TEMP の設定を行う.
Windows のユーザ名が日本語のとき,nvcc がうまく動作しないエラーを回避するためである.
ユーザ環境変数 TEMP に「C:\TEMP」を設定するために, コマンドプロンプトで,次のコマンドを実行する.
mkdir C:\TEMP powershell -command "[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(\"TEMP\", \"C:\TEMP\", \"User\")"
【関連する外部ページ】
- NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのアーカイブの公式ページ: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive
- NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット の公式のドキュメント: https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-installation-guide-linux/index.html
- NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストールに関する,NVIDIA CUDA クイックスタートガイドの公式ページ: https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-quick-start-guide/index.html
【関連項目】 NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット, NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 12.6 のインストール(Windows 上), NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8 のインストール(Windows 上)
- Windows では,NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストール中は,なるべく他のウインドウはすべて閉じておくこと.
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - 次のコマンドを実行
次のコマンドは,NVIDIA GeForce Experience,NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット 11.8 をインストールするものである.
wmic path win32_VideoController get name winget install --scope machine Nvidia.CUDA --version 11.8 powershell -command "[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(\"CUDA_HOME\", \"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.8\", \"Machine\")" - NVIDIA CUDA ツールキットのインストールが終わったら,ユーザ環境変数 TEMP の設定を行う.
Windows のユーザ名が日本語のとき,nvcc がうまく動作しないエラーを回避するためである.
ユーザ環境変数 TEMP に「C:\TEMP」を設定するために, コマンドプロンプトで,次のコマンドを実行する.
mkdir C:\TEMP powershell -command "[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(\"TEMP\", \"C:\TEMP\", \"User\")"
Dlib のインストールと関連ファイルのダウンロード
Dlib および関連ソフトウェアのインストール
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - 次のコマンドを実行する.
python -m pip install --ignore-installed -U dlib imutils numpy==1.23.4
Dlib 関連ファイルのダウンロード
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - Dlib のソースコード等のダウンロード
次のコマンドを実行.
cd C:\ rmdir /s /q dlib git clone https://github.com/davisking/dlib - Dlib の学習済みモデルのダウンロード
次のコマンドを実行.
cd C:\dlib cd python_examples curl -O http://dlib.net/files/mmod_human_face_detector.dat.bz2 curl -O http://dlib.net/files/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat.bz2 curl -O http://dlib.net/files/shape_predictor_5_face_landmarks.dat.bz2 curl -O http://dlib.net/files/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2 "c:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe" x mmod_human_face_detector.dat.bz2 "c:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe" x dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat.bz2 "c:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe" x shape_predictor_5_face_landmarks.dat.bz2 "c:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe" x shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2 del mmod_human_face_detector.dat.bz2 del dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat.bz2 del shape_predictor_5_face_landmarks.dat.bz2 del shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2
ezgiakcora/Facial-Expression-Keras のインストール
GitHub の ezgiakcora/Facial-Expression-Keras で公開されているプログラムを試してみる. これは Dlibを使う表情認識のプログラムである
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - インストール
cd /d c:%HOMEPATH% rmdir /s /q Facial-Expression-Keras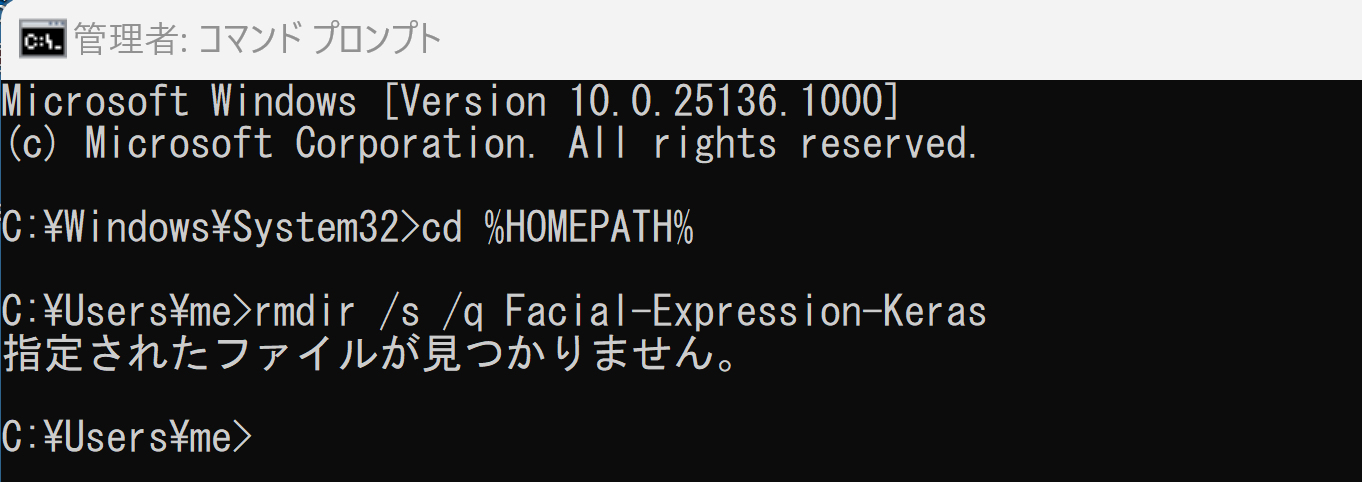
cd /d c:%HOMEPATH% git clone https://github.com/ezgiakcora/Facial-Expression-Keras cd Facial-Expression-Keras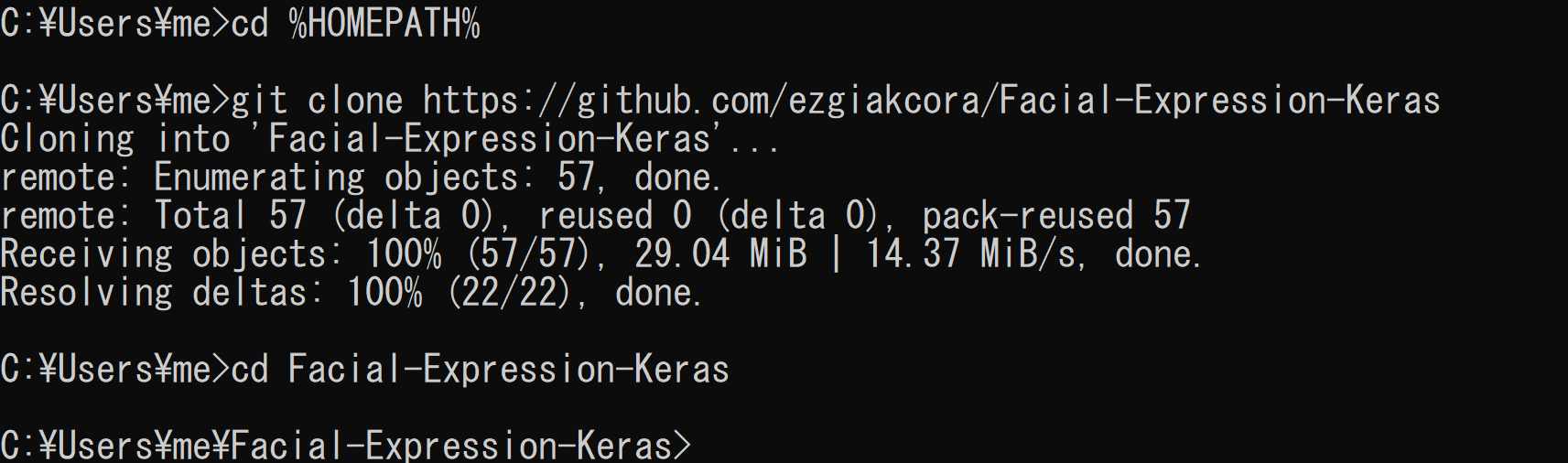
- Dlib 関連のファイルをコピーして使う
cd /d c:%HOMEPATH%\Facial-Expression-Keras copy C:\dlib\python_examples\shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat .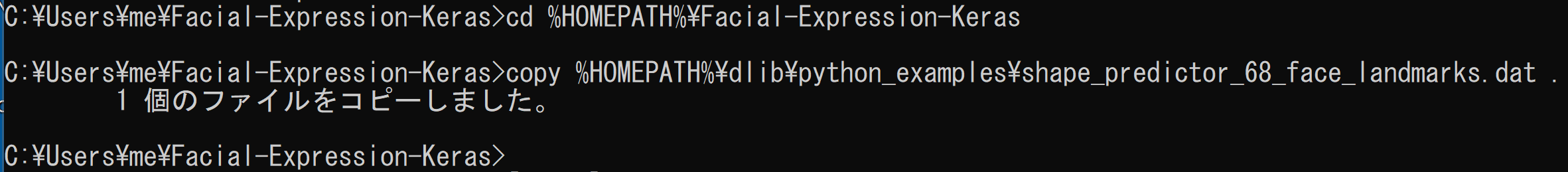
- 表情判定のプログラムを動かしてみる
USB接続できるビデオカメラを準備し,パソコンに接続しておく.
- Windows のコマンドプロンプトを開く
- Python プログラムの実行
コマンドプロンプトで次を実行
cd /d c:%HOMEPATH%\Facial-Expression-Keras python demo.py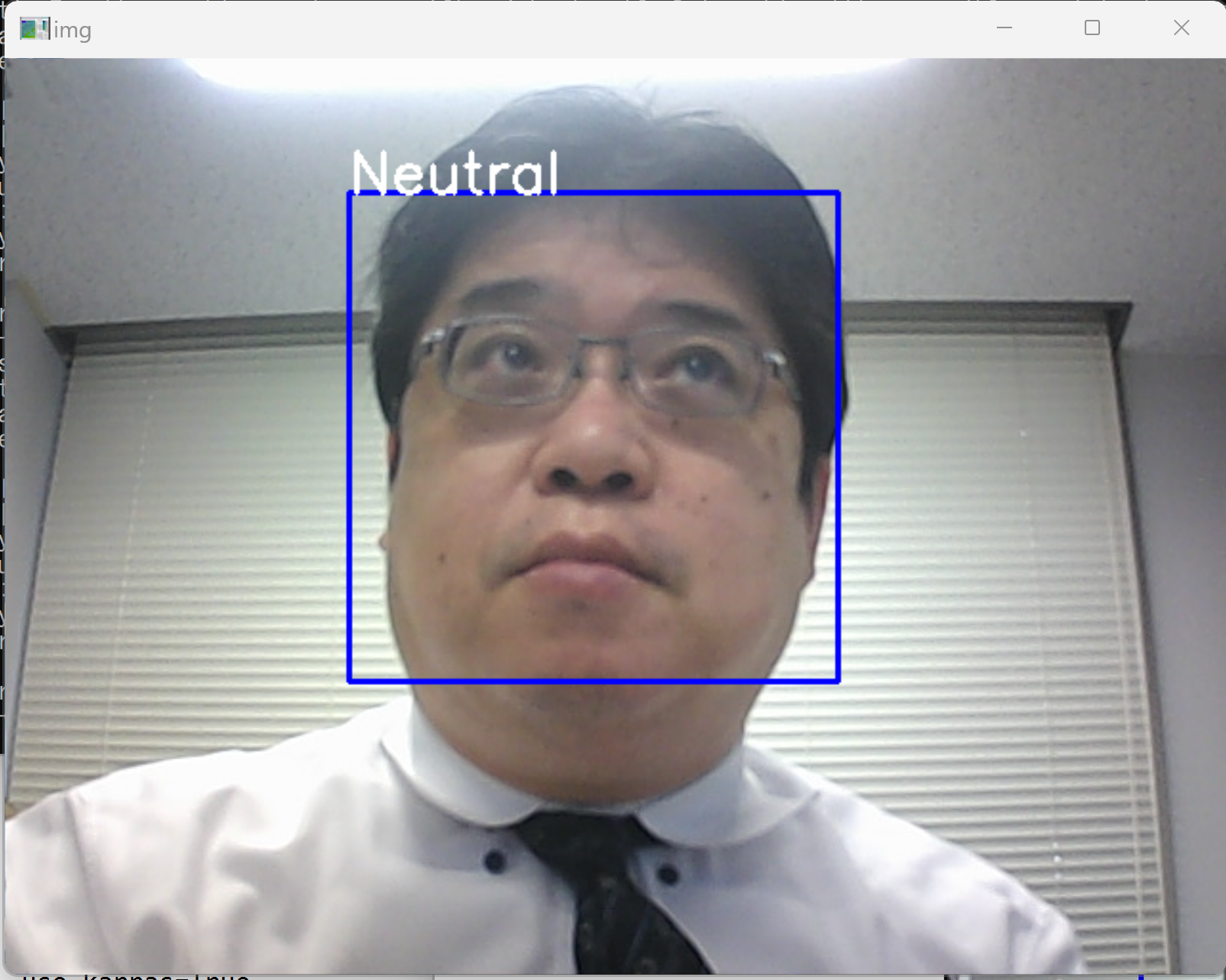
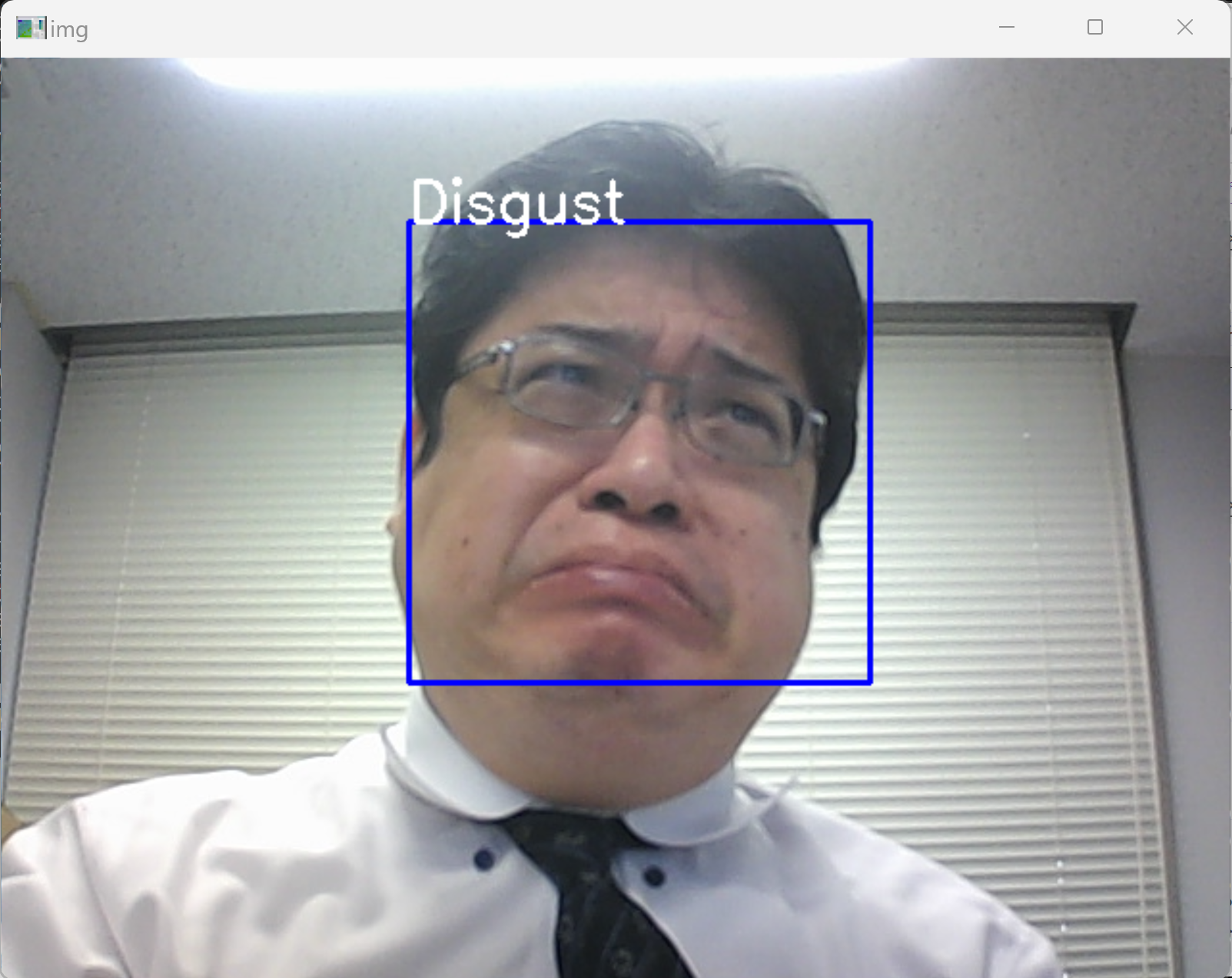
* 途中で止めたいとき,右上の「x」をクリックしない.画面の中をクリックしてから,「q」のキーを押して閉じる
- demo.py を少し書き変えて動かす
import numpy as np import cv2 from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image import dlib from imutils import face_utils import imutils from sklearn import preprocessing import math from keras.models import model_from_json #----------------------------- #opencv initialization face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml') cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) #----------------------------- #face expression recognizer initialization # Using pretrained model model = model_from_json(open("model/model.json", "r").read()) model.load_weights('model/model.h5') #load weights #----------------------------- emotions = ( 'Angry' , 'Disgust' , 'Fear' , 'Happy' , 'Neutral' , 'Sad' , 'Surprise') # initialize dlib's face detector and create a predictor detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector() predictor = dlib.shape_predictor("shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat") def detect_parts(image): distances = [] # resize the image, and convert it to grayscale image = imutils.resize(image, width=200, height=200) gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # detect faces in the grayscale image rects = detector(gray, 1) # loop over the face detections for (i, rect) in enumerate(rects): shape = predictor(gray, rect) shape = face_utils.shape_to_np(shape) distances = euclidean_all(shape) # visualize all facial landmarks with a transparent overlay #output = face_utils.visualize_facial_landmarks(image, shape) #cv2.imshow("Image", output) #cv2.waitKey(0) return distances def euclidean(a, b): dist = math.sqrt(math.pow((b[0] - a[0]), 2) + math.pow((b[1] - a[1]), 2)) return dist # calculates distances between all 68 elements def euclidean_all(a): distances = "" for i in range(0, len(a)): for j in range(0, len(a)): dist = euclidean(a[i], a[j]) dist = "%.2f" % dist; distances = distances + " " + str(dist) return distances def box_label(bgr, x1, y1, x2, y2, label): cv2.rectangle(bgr, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 0), 1, 1) cv2.rectangle(bgr, (int(x1), int(y1-25)), (x2, y1), (255,255,255), -1) cv2.putText(bgr, label, (x1, int(y1-5)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.7, (0,0,0), 1) while(True): ret, img = cap.read() gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 5) for (x,y,w,h) in faces: detected_face = img[int(y):int(y+h), int(x):int(x+w)] #crop detected face distances = detect_parts(detected_face) if(len(distances)!=0): val = distances.split(" ")[1:] val = np.array(val) val = val.astype(np.float) val = np.expand_dims(val, axis = 1) minmax = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler() val = minmax.fit_transform(val) val = val.reshape(1,4624) predictions = model.predict(val) #store probabilities of 6 expressions #find max indexed array ( 'Angry' , 'Disgust' , 'Fear' , 'Happy' , 'Neutral' , 'Sad' , 'Surprise') print ("Angry: %", predictions[0][0]/1.0 * 100) print ("Disgust: %", predictions[0][1]/1.0 * 100) print ("Fear: %", predictions[0][2]/1.0 * 100) print ("Happy: %", predictions[0][3]/1.0 * 100) print ("Neutral: %", predictions[0][4]/1.0 * 100) print ("Sad: %", predictions[0][5]/1.0 * 100) print ("Surprised: %", predictions[0][6]/1.0 * 100) print ("----------------------" ) max_index = np.argmax(predictions[0]) emotion = emotions[max_index] #write emotion text above rectangle box_label(img, x, y, x+w, y+h, emotion+":"+'{:2.2f}'.format(np.max(predictions[0])/1.0 * 100)) cv2.imshow('img',img) if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): #press q to quit break #kill open cv things cap.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows()* 途中で止めたいとき,右上の「x」をクリックしない.画面の中をクリックしてから,「q」のキーを押して閉じる

![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)