MNIST データセットによる学習と分類(TensorFlow データセット,TensorFlow,Python を使用)(Windows 上,Google Colaboratroy の両方を記載)
【目次】
- Google Colaboratory での実行
- Windows での実行
- MNIST データセットのロード
- MNIST データセットの確認
- Keras を用いたニューラルネットワークの作成
- ニューラルネットワークの学習と検証
説明資料: [パワーポイント]
* MNIST データセット
MNIST データセットは,公開されているデータセット(オープンデータ)である.
0 から 9 までの 10 種類の手書き文字についての, モノクロ画像と,各画像に付いた「0から9までの数値」のラベルから構成されるデータセットである.
- 画像の枚数:合計 70000枚.
(内訳)70000枚の内訳は次の通りである
60000枚:教師データ
10000枚:検証データ
- 画像のサイズ: 28x28 である.
- 画素はグレースケールであり,画素値は0~255である.0が白,255が黒.
【文献】
Y. Lecun, L. Bottou, Y. Bengio and P. Haffner, Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition, vol. 86, no. 11, pp. 2278-2324, 1998.
【サイト内の関連ページ】
- MNIST データセットを扱う Python プログラム: 別ページ で説明している.
- MNIST データセットによる学習と分類(TensorFlow データセット,TensorFlow,Python を使用)(Windows 上,Google Colaboratroy の両方を記載)
【関連する外部ページ】
- MNIST データセット の詳細は, THE MNIST DATABASE of handwritten digits のページで説明されている.その URL は次の通り.
- TensorFlow データセットの MNIST データセット: https://www.tensorflow.org/datasets/catalog/mnist
1. Google Colaboratory での実行
Google Colaboratory のページ:
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1IfArIvhh-FsvJIE9YTNO8T44Qhpi0rIJ?usp=sharing
2. Windows での実行
Python 3.12 のインストール
以下のいずれかの方法で Python 3.12 をインストールする。
方法1:winget によるインストール
Python がインストール済みの場合、この手順は不要である。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
winget install -e --id Python.Python.3.12 --scope machine --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/quiet InstallAllUsers=1 PrependPath=1 AssociateFiles=1 InstallLauncherAllUsers=1"--scope machine を指定することで、システム全体(全ユーザー向け)にインストールされる。このオプションの実行には管理者権限が必要である。インストール完了後、コマンドプロンプトを再起動すると PATH が自動的に設定される。
方法2:インストーラーによるインストール
- Python 公式サイト(https://www.python.org/downloads/)にアクセスし、「Download Python 3.x.x」ボタンから Windows 用インストーラーをダウンロードする。
- ダウンロードしたインストーラーを実行する。
- 初期画面の下部に表示される「Add python.exe to PATH」に必ずチェックを入れてから「Customize installation」を選択する。このチェックを入れ忘れると、コマンドプロンプトから
pythonコマンドを実行できない。 - 「Install Python 3.xx for all users」にチェックを入れ、「Install」をクリックする。
インストールの確認
コマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。
python --versionバージョン番号(例:Python 3.12.x)が表示されればインストール成功である。「'python' は、内部コマンドまたは外部コマンドとして認識されていません。」と表示される場合は、インストールが正常に完了していない。
Git のインストール
以下のコマンドを管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー → cmd と入力 → 右クリック → 「管理者として実行」)。管理者権限は、wingetの--scope machineオプションでシステム全体にソフトウェアをインストールするために必要となる。
REM Git をシステム領域にインストール
winget install --scope machine --id Git.Git -e --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements
REM Git のパス設定
set "GIT_PATH=C:\Program Files\Git\cmd"
for /f "skip=2 tokens=2*" %a in ('reg query "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" /v Path') do set "SYSTEM_PATH=%b"
if exist "%GIT_PATH%" (
echo "%SYSTEM_PATH%" | find /i "%GIT_PATH%" >nul
if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%GIT_PATH%;%SYSTEM_PATH%" /M >nul
)
【関連する外部ページ】
- Git の公式ページ: https://git-scm.com/
TensorFlow 2.10.1 のインストール(Windows 上)
- 以下の手順を管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー →
cmdと入力 → 右クリック → 「管理者として実行」)。 - TensorFlow 2.10.1 のインストール(Windows 上)
次のコマンドを実行することにより,TensorFlow 2.10.1 および関連パッケージ(tf_slim,tensorflow_datasets,tensorflow-hub,Keras,keras-tuner,keras-visualizer)がインストール(インストール済みのときは最新版に更新)される. そして,Pythonパッケージ(Pillow, pydot, matplotlib, seaborn, pandas, scipy, scikit-learn, scikit-learn-intelex, opencv-python, opencv-contrib-python)がインストール(インストール済みのときは最新版に更新)される.
python -m pip uninstall -y protobuf tensorflow tensorflow-cpu tensorflow-gpu tensorflow-intel tensorflow-text tensorflow-estimator tf-models-official tf_slim tensorflow_datasets tensorflow-hub keras keras-tuner keras-visualizer python -m pip install -U protobuf tensorflow==2.10.1 tf_slim tensorflow_datasets==4.8.3 tensorflow-hub tf-keras keras keras_cv keras-tuner keras-visualizer python -m pip install git+https://github.com/tensorflow/docs python -m pip install git+https://github.com/tensorflow/examples.git python -m pip install git+https://www.github.com/keras-team/keras-contrib.git python -m pip install -U pillow pydot matplotlib seaborn pandas scipy scikit-learn scikit-learn-intelex opencv-python opencv-contrib-python
Graphviz のインストール
Windows での Graphviz のインストール: 別ページ »で説明
numpy,matplotlib, seaborn, scikit-learn, pandas, pydot のインストール
- 次のコマンドを管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー →
cmdと入力 → 右クリック → 「管理者として実行」)。 する.
python -m pip install -U numpy matplotlib seaborn scikit-learn pandas pydot
MNIST データセットのロード
Python は,次のコマンドで起動できる.
Python 開発環境(Jupyter Qt Console, Jupyter ノートブック (Jupyter Notebook), Jupyter Lab, Nteract, Spyder, PyCharm, PyScripterなど)も便利である.
Python のまとめ: 別ページ »にまとめ
- 以下の操作をコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー →
cmdと入力 →「コマンドプロンプト」を選択)。 - jupyter qtconsole の起動
これ以降の操作は,jupyter qtconsole で行う.
jupyter qtconsolePython 開発環境として,Jupyter Qt Console, Jupyter ノートブック (Jupyter Notebook), Jupyter Lab, Nteract, spyder のインストールWindows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。し,次のコマンドを実行する.次のコマンドを実行することにより,pipとsetuptoolsを更新する,Jupyter Notebook,PyQt5、Spyderなどの主要なPython環境がインストールされる.
python -m pip install -U pip setuptools requests notebook==6.5.7 jupyterlab jupyter jupyter-console jupytext PyQt5 nteract_on_jupyter spyder- パッケージのインポート,TensorFlow のバージョン確認など
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras import layers from tensorflow.keras import backend as K K.clear_session() import numpy as np import tensorflow_datasets as tfds %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings
- TensorFlow データセット から MNIST データセット をロード
- x_train: サイズ 28 × 28 の 60000枚の濃淡画像
- y_train: 60000枚の濃淡画像それぞれの,種類番号(0 から 9 のどれか)
- x_test: サイズ 28 × 28 の 10000枚の濃淡画像
- y_test: 10000枚の濃淡画像それぞれの,種類番号(0 から 9 のどれか)
結果は,TensorFlow の Tensor である.
type は型,shape はサイズ,np.max と np.mi は最大値と最小値.
tensorflow_datasets の loadで, 「batch_size = -1」を指定して,一括読み込みを行っている.
mnist, mnist_metadata = tfds.load('mnist', with_info = True, shuffle_files=True, as_supervised=True, batch_size = -1) x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = mnist['train'][0], mnist['train'][1], mnist['test'][0], mnist['test'][1] print(mnist_metadata)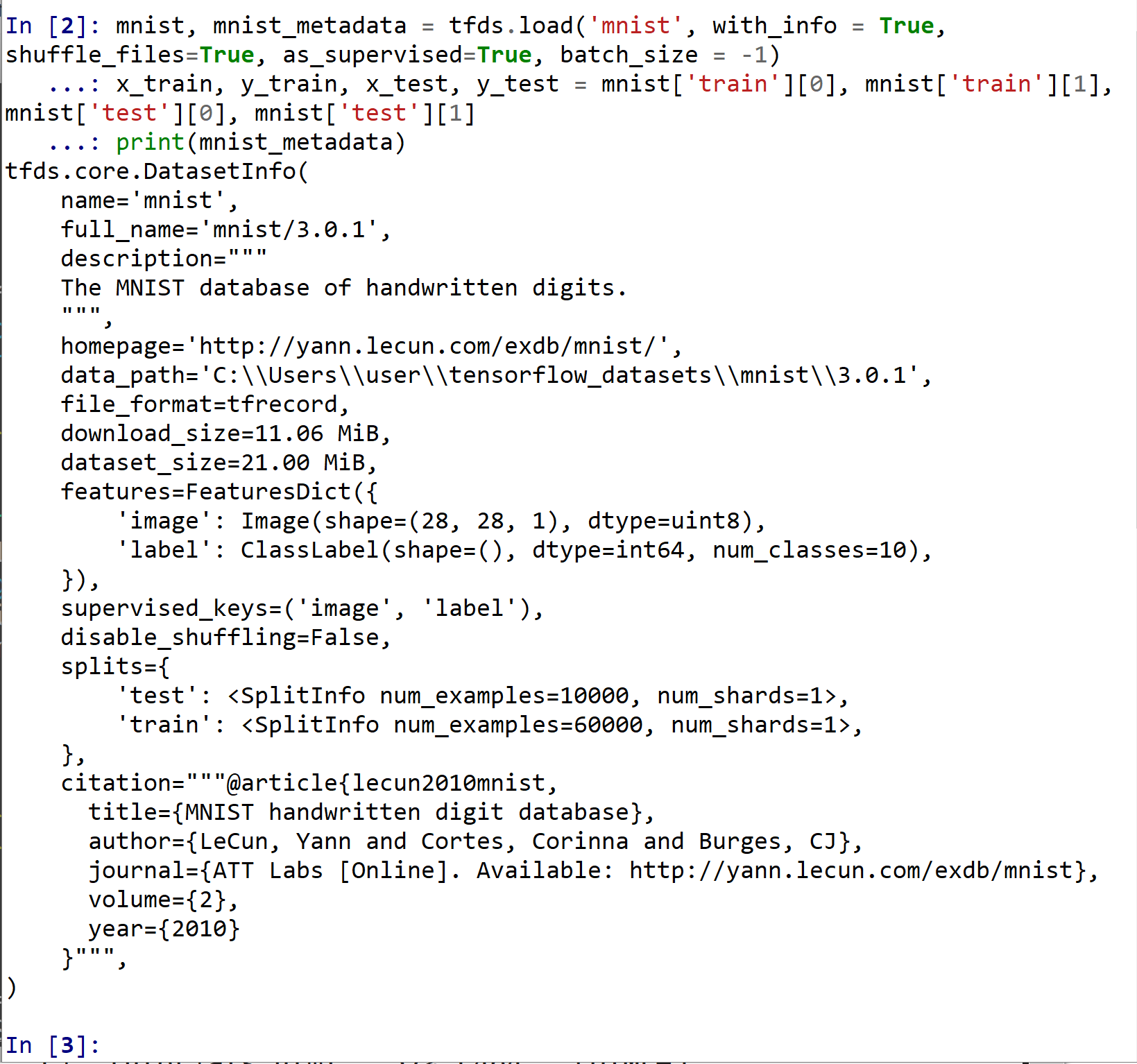
MNIST データセットの確認
- データセットの中の画像を表示
MatplotLib を用いて,0 番目の画像を表示する
NUM = 0 plt.figure() plt.imshow(x_train[NUM,:,:,0], cmap='gray') plt.colorbar() plt.gca().grid(False) plt.show()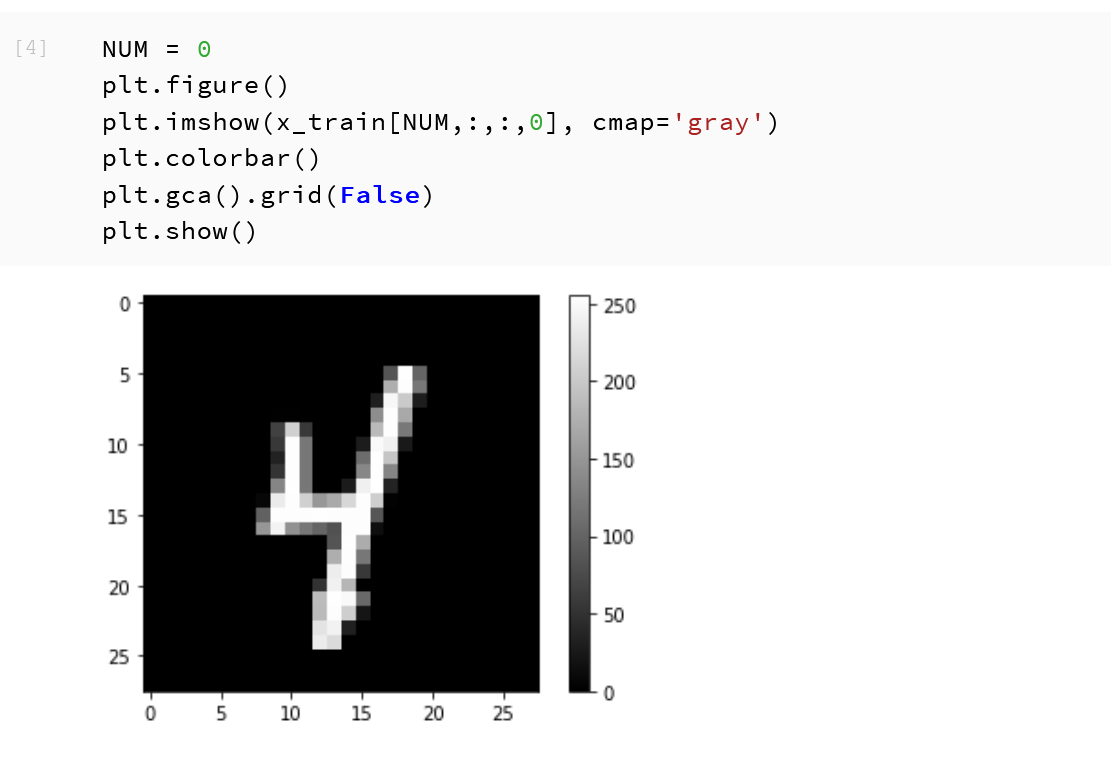
- データセットの情報を表示
print(mnist_metadata) print(mnist_metadata.features["label"].num_classes) print(mnist_metadata.features["label"].names)
- 型と形と最大値と最小値の確認
print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test))
- 主成分分析の結果である主成分スコアのプロット
x_train, x_test は主成分分析で2次元にマッピング, y_train, y_test は色.
import pandas as pd import seaborn as sns sns.set() import sklearn.decomposition # 主成分分析 def prin(A, n): pca = sklearn.decomposition.PCA(n_components=n) return pca.fit_transform(A) # 主成分分析で2つの成分を得る def prin2(A): return prin(A, 2) # M の最初の2列を,b で色を付けてプロット def scatter_plot(M, b, alpha): a12 = pd.DataFrame( M[:,0:2], columns=['a1', 'a2'] ) a12['target'] = b sns.scatterplot(x='a1', y='a2', hue='target', data=a12, palette=sns.color_palette("hls", np.max(b) + 1), legend="full", alpha=alpha) # 主成分分析プロット def pcaplot(A, b, alpha): scatter_plot(prin2(A), b, alpha) pcaplot(np.reshape(x_train, (x_train.shape[0], -1)), y_train, 0.1)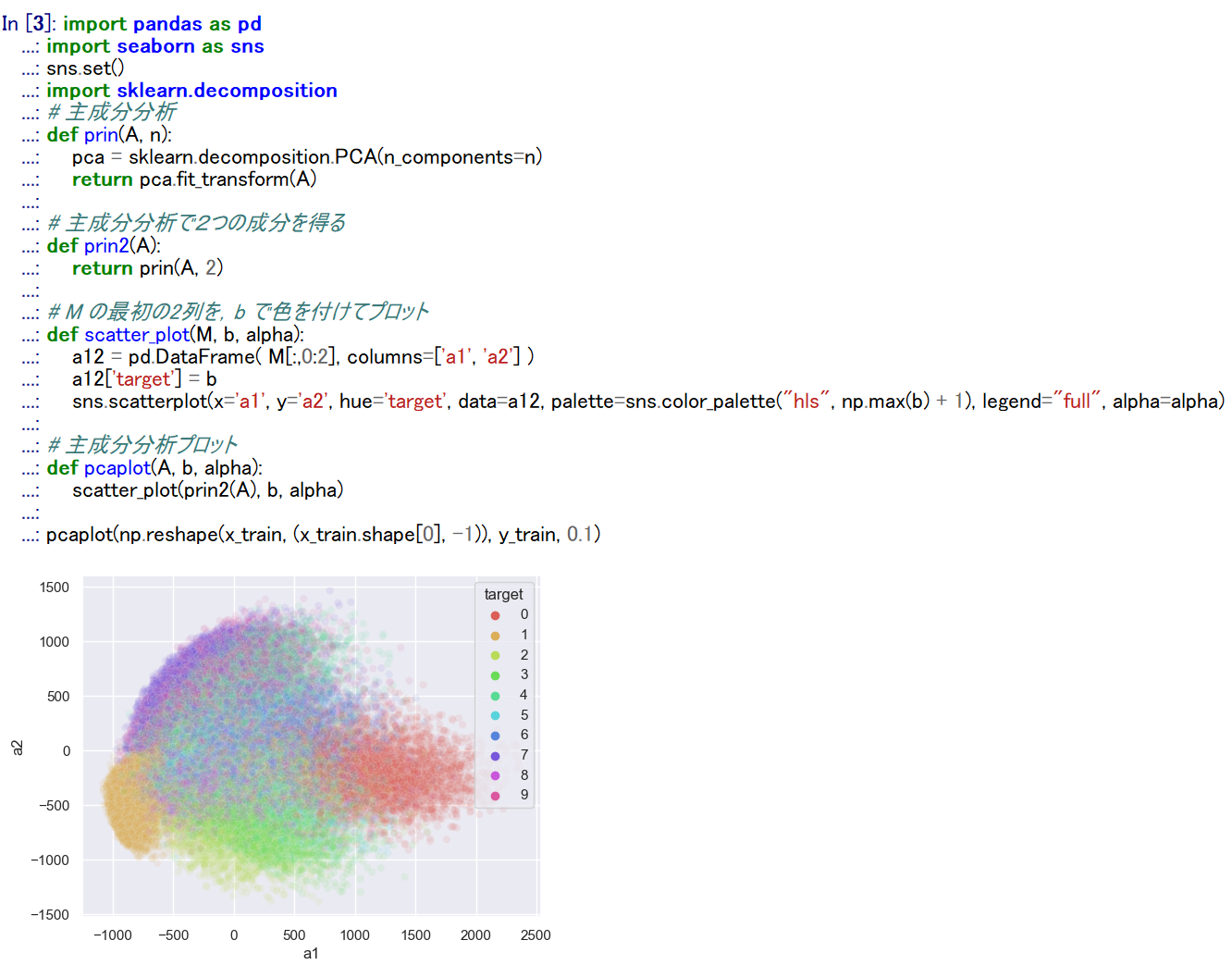
pcaplot(np.reshape(x_test, (x_test.shape[0], -1)), y_test, 0.1)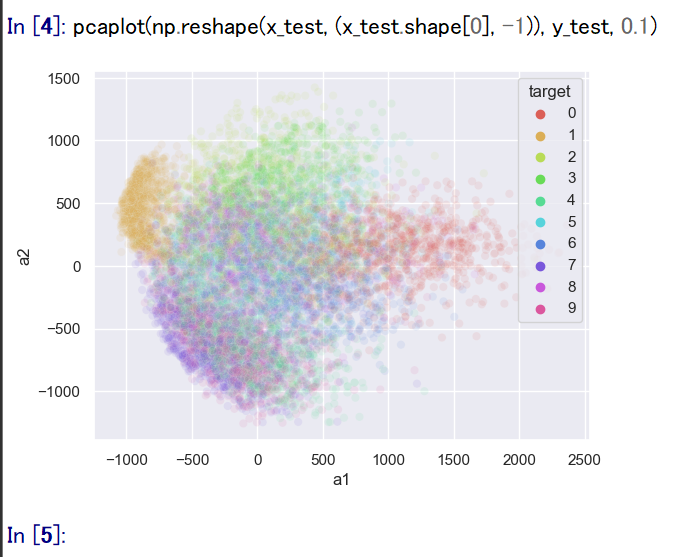
- データの確認表示
MatplotLib を用いて,複数の画像を並べて表示する.
class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat', 'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot'] plt.style.use('default') plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) for i in range(25): plt.subplot(5,5,i+1) plt.xticks([]) plt.yticks([]) plt.grid(False) plt.imshow(x_train[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary) plt.xlabel(class_names[y_train[i]]) plt.show()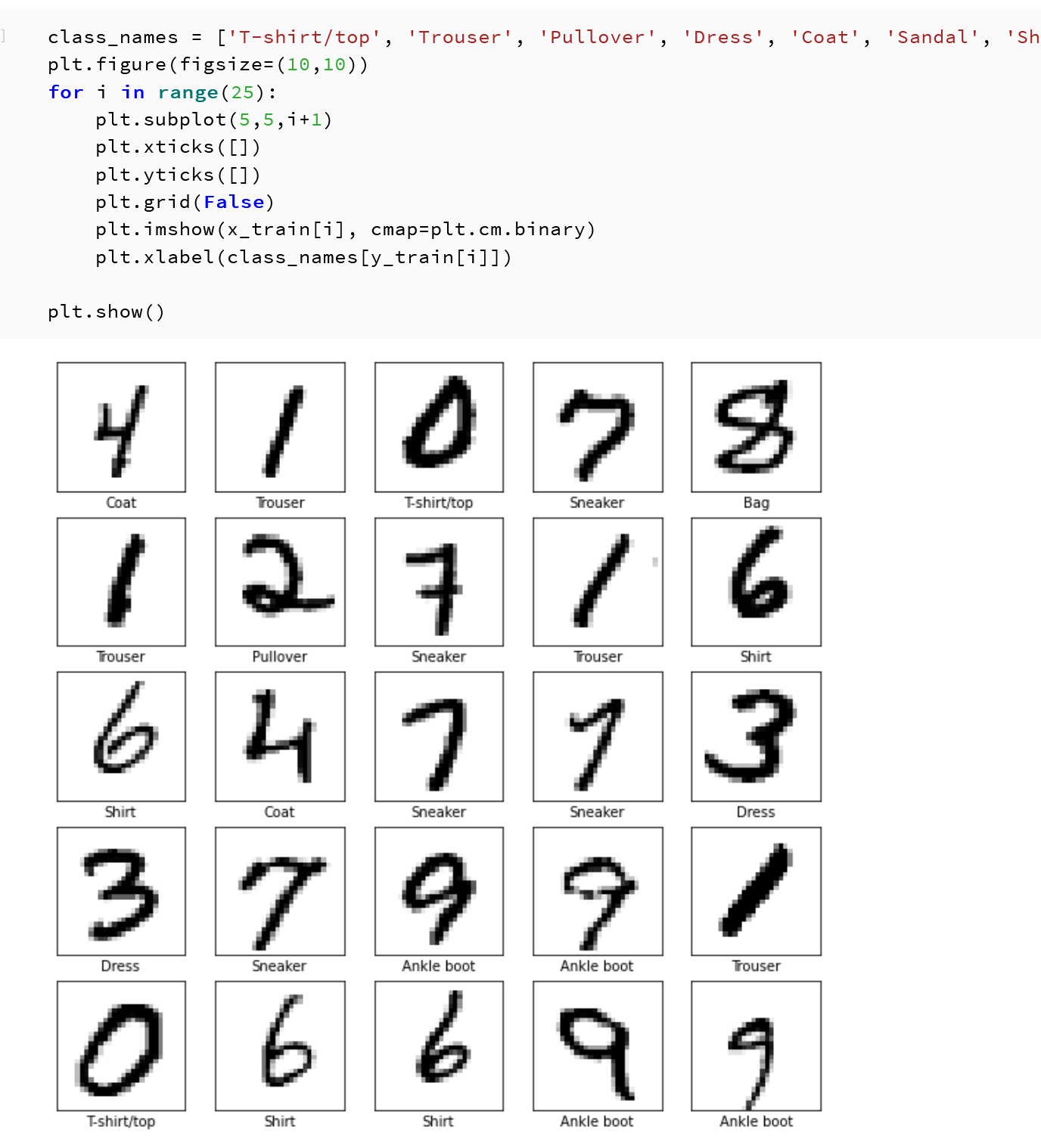
Keras を用いたニューラルネットワークの作成
- x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test の numpy ndarray への変換と,値の範囲の調整(値の範囲が 0 〜 255 であるのを,0 〜 1 に調整)
x_train = x_train.numpy().astype("float32") / 255.0 x_test = x_test.numpy().astype("float32") / 255.0 y_train = y_train.numpy() y_test = y_test.numpy() print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test))
- ニューラルネットワークの作成と確認とコンパイル
- Flatten の層: 画像(28かける28)を 1次元の配列に変換する.
- 1層目: Dense(全結合),ニューロン(ユニット)の個数: 128
- 2層目: Dense(全結合),ニューロン(ユニット)の個数: 10
- 2層目のニューロン(ユニット)の種類: softmax
- 1番目のDense の層と2番目のDense の層の間の結合については,ドロップアウトを行う.
ADAM を使う場合のプログラム例
NUM_CLASSES = 10 m = tf.keras.Sequential() m.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28, 1))) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=128, activation='relu')) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate=0.5)) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=NUM_CLASSES, activation='softmax')) m.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001), loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
SGD を使う場合のプログラム例
NUM_CLASSES = 10 m = tf.keras.Sequential() m.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28, 1))) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=128, activation='relu')) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate=0.5)) m.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=NUM_CLASSES, activation='softmax')) m.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True), loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) - ニューラルネットワークの確認表示
print(m.summary())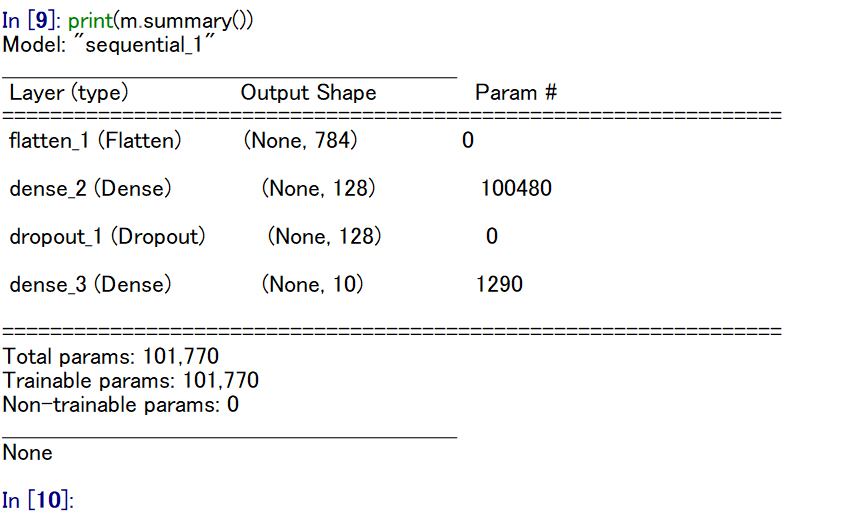
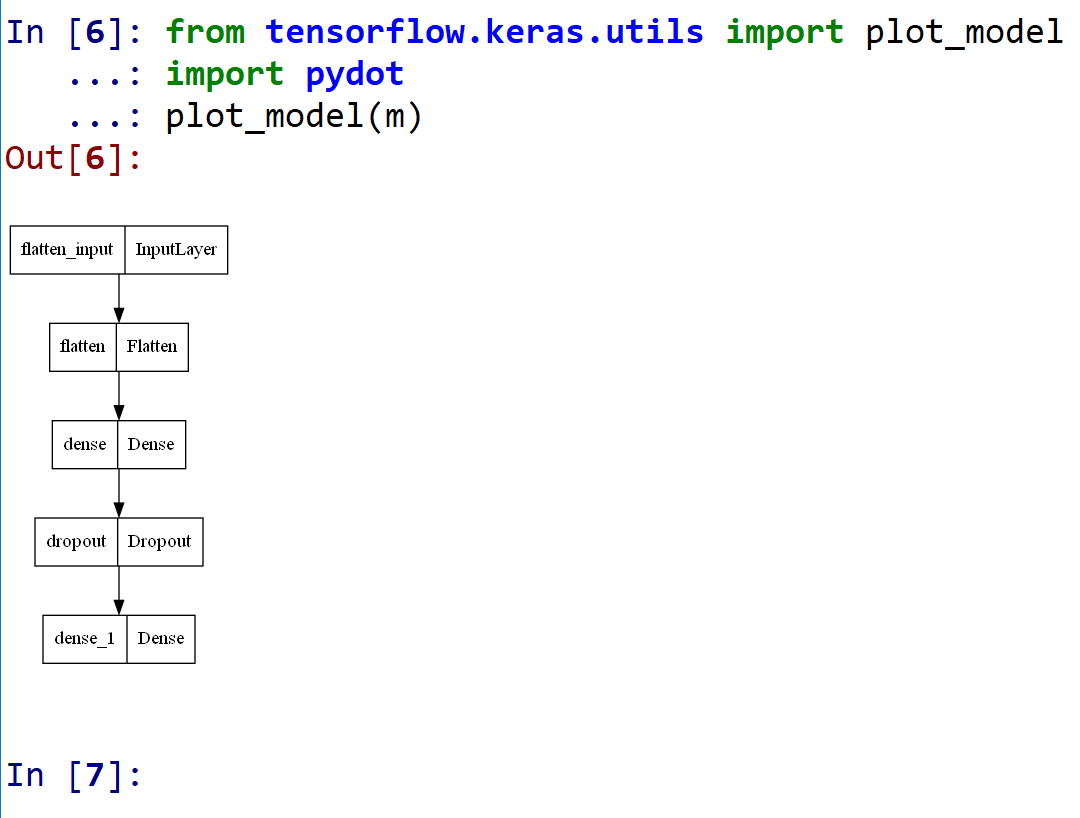
- モデルのビジュアライズ
Keras のモデルのビジュアライズについては: https://keras.io/ja/visualization/
ここでの表示で,エラーメッセージが出る場合でも,モデル自体は問題なくできていると考えられる.続行する.
from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model import pydot plot_model(m)
ニューラルネットワークの学習と検証
- ニューラルネットワークの学習を行う
ニューラルネットワークの学習は fit メソッドにより行う. 教師データを使用する.
EPOCHS = 50 history = m.fit(x_train, y_train, validation_data=(x_test, y_test), verbose=2, epochs=EPOCHS)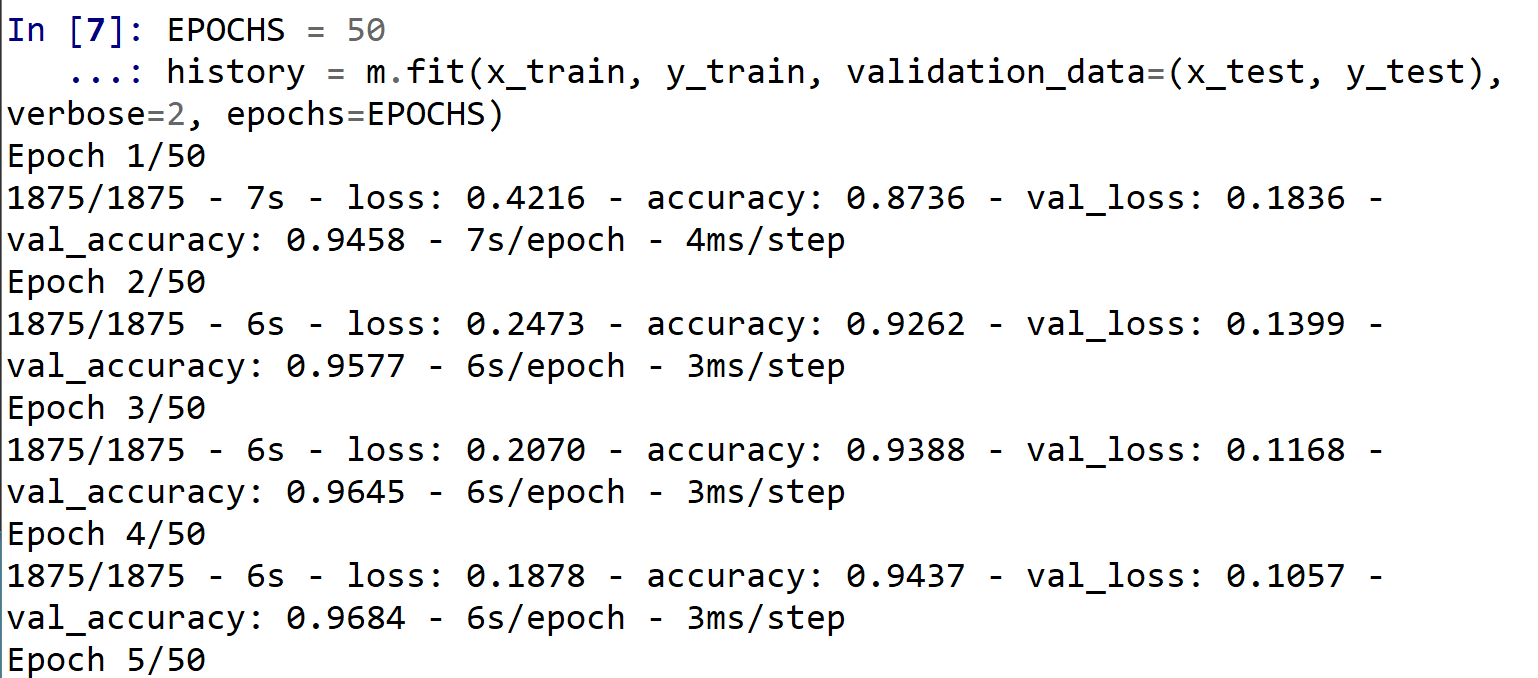
- ニューラルネットワークを使い,分類を行う.
* 訓練(学習)などで乱数が使われるので,下図と違う値になる.
predictions = m.predict(x_test) print(predictions[0])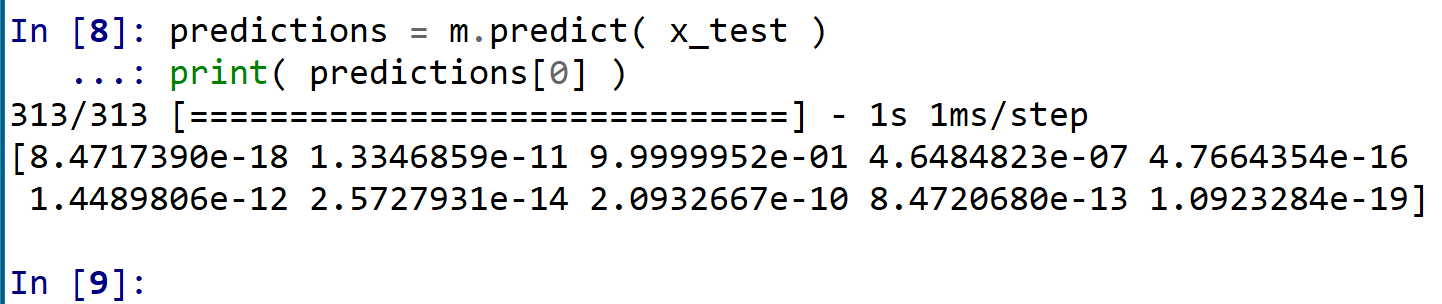
- 正解表示
テスト画像 0 番の正解を表示
print(y_test[0])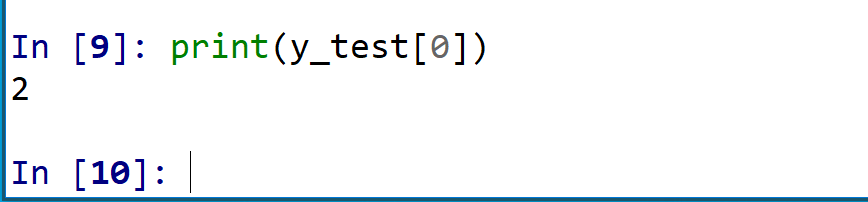
- 学習曲線の確認
過学習や学習不足について確認.
import pandas as pd hist = pd.DataFrame(history.history) hist['epoch'] = history.epoch print(hist)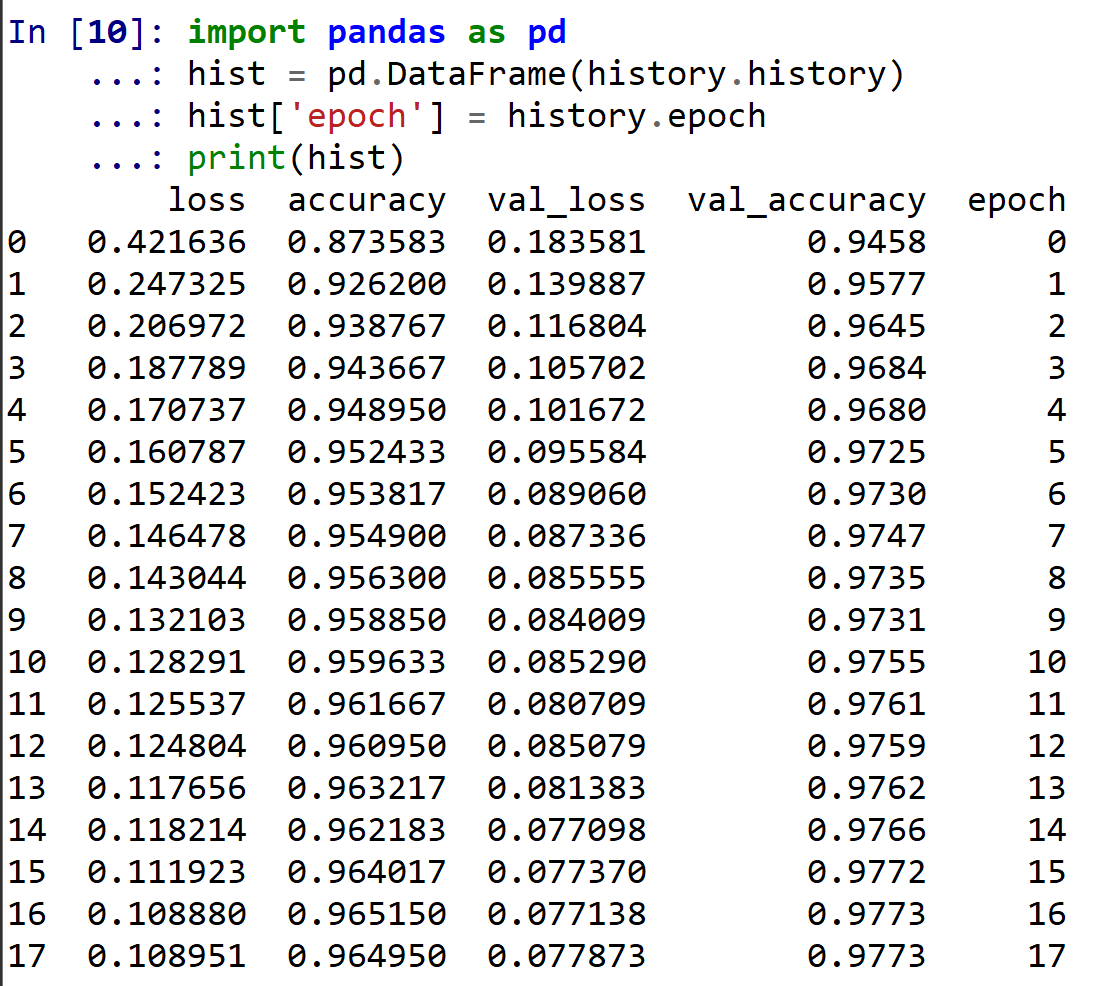
- 学習曲線のプロット
【関連する外部ページ】 訓練の履歴の可視化については,https://keras.io/ja/visualization/
- 学習時と検証時の,損失の違い
acc = history.history['accuracy'] val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy'] loss = history.history['loss'] val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1) # "bo" は青いドット plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss') # ”b" は青い実線 plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss') plt.title('Training and validation loss') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Loss') plt.legend() plt.show()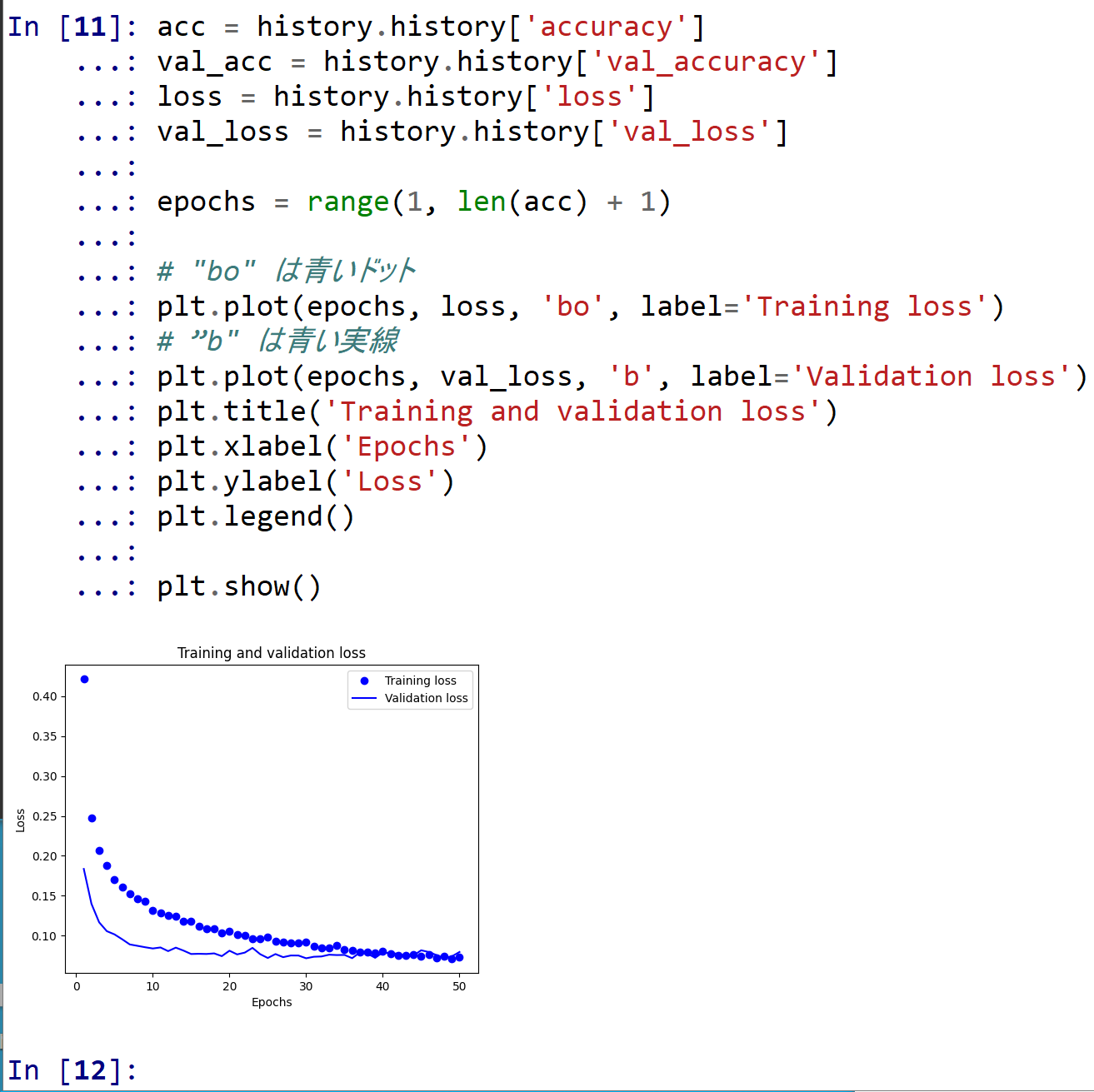
- 学習時と検証時の,精度の違い
acc = history.history['accuracy'] val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy'] loss = history.history['loss'] val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] plt.clf() # 図のクリア plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc') plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc') plt.title('Training and validation accuracy') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.legend() plt.show()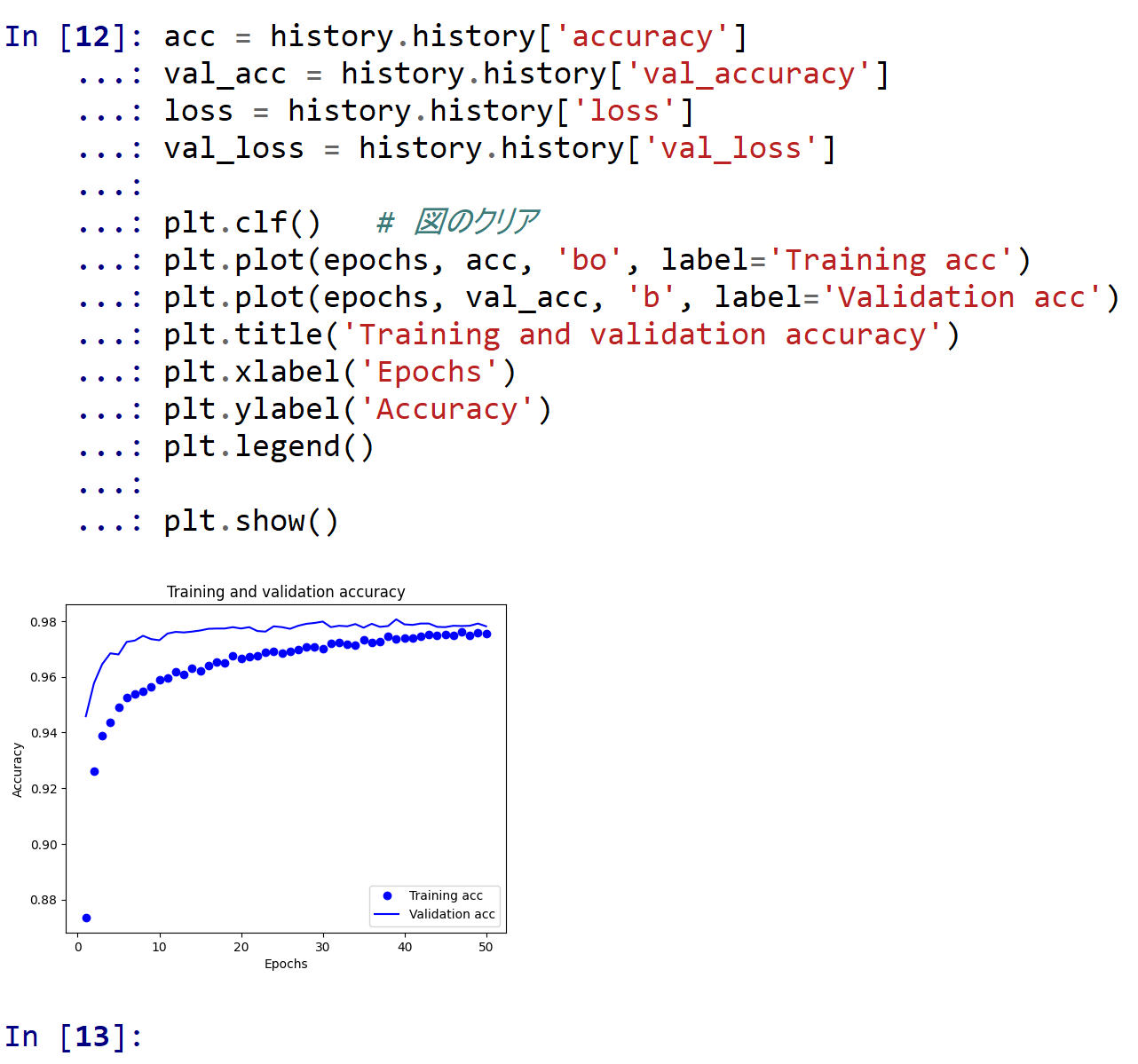
- 学習時と検証時の,損失の違い
- ニューラルネットワークの学習を行う
- パッケージのインポート,TensorFlow のバージョン確認など
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)