VBGMM (Variational Bayesian Gaussian Mixture) を用いてクラスタリング(Python, scikit-learn を使用)
1. エグゼクティブサマリー
VBGMM (Variational Bayesian Gaussian Mixture) では,クラスタ数を指定せずにクラスタリングを行う.本記事では,Python と scikit-learn を使用し,Iris データセットに VBGMM を適用する.VBGMM は最大クラスタ数のうち,データに適合するクラスタのみに大きな重みを割り当て,有効なクラスタ数を自動的に決定する.クラスタリング結果は主成分分析(PCA)で2次元に次元削減し,散布図として可視化する.元の Iris データセットの品種ラベルによるプロットと比較することで,分類精度を視覚的に評価できる.
2. 前準備(必要ソフトウェアの入手)
ここでは、最低限の事前準備について説明する。機械学習や深層学習を行う場合は、NVIDIA CUDA、Visual Studio、Cursorなどを追加でインストールすると便利である。これらについては別ページ https://www.kkaneko.jp/cc/dev/aiassist.htmlで詳しく解説しているので、必要に応じて参照してください。
Python 3.12 のインストール(Windows 上) [クリックして展開]
以下のいずれかの方法で Python 3.12 をインストールする。Python がインストール済みの場合、この手順は不要である。
方法1:winget によるインストール
管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
winget install -e --id Python.Python.3.12 --scope machine --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/quiet InstallAllUsers=1 PrependPath=1 AssociateFiles=1 InstallLauncherAllUsers=1"--scope machine を指定することで、システム全体(全ユーザー向け)にインストールされる。このオプションの実行には管理者権限が必要である。インストール完了後、コマンドプロンプトを再起動すると PATH が自動的に設定される。
方法2:インストーラーによるインストール
- Python 公式サイト(https://www.python.org/downloads/)にアクセスし、「Download Python 3.x.x」ボタンから Windows 用インストーラーをダウンロードする。
- ダウンロードしたインストーラーを実行する。
- 初期画面の下部に表示される「Add python.exe to PATH」に必ずチェックを入れてから「Customize installation」を選択する。このチェックを入れ忘れると、コマンドプロンプトから
pythonコマンドを実行できない。 - 「Install Python 3.xx for all users」にチェックを入れ、「Install」をクリックする。
インストールの確認
コマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。
python --versionバージョン番号(例:Python 3.12.x)が表示されればインストール成功である。「'python' は、内部コマンドまたは外部コマンドとして認識されていません。」と表示される場合は、インストールが正常に完了していない。
AIエディタ Windsurf のインストール(Windows 上) [クリックして展開]
Pythonプログラムの編集・実行には、AIエディタの利用を推奨する。ここでは、Windsurfのインストールを説明する。Windsurf がインストール済みの場合、この手順は不要である。
管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
winget install -e --id Codeium.Windsurf --scope machine --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --custom "/SUPPRESSMSGBOXES /MERGETASKS=!runcode,addtopath,associatewithfiles,!desktopicon"
powershell -Command "$env:Path=[System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','Machine')+';'+[System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','User'); windsurf --install-extension MS-CEINTL.vscode-language-pack-ja --force; windsurf --install-extension ms-python.python --force; windsurf --install-extension Codeium.windsurfPyright --force"--scope machine を指定することで、システム全体(全ユーザー向け)にインストールされる。このオプションの実行には管理者権限が必要である。インストール完了後、コマンドプロンプトを再起動すると PATH が自動的に設定される。
【関連する外部ページ】
Windsurf の公式ページ: https://windsurf.com/
必要なライブラリのインストール [クリックして展開]
管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
python -m pip install -U pip setuptools numpy pandas matplotlib seaborn scikit-learn scikit-learn-intelex
3. 実行のための準備とその確認手順(Windows 前提)
3.1 プログラムファイルの準備
第5章に掲載するソースコードをテキストエディタ(メモ帳,Windsurf 等)に貼り付け,vbgmm_iris.py として保存する(文字コード:UTF-8).
3.2 実行コマンド
コマンドプロンプトでファイルの保存先ディレクトリに移動し,以下を実行する.
python vbgmm_iris.py3.3 動作確認チェックリスト
| 確認項目 | 期待される結果 |
|---|---|
| Iris データセットの読み込み | iris.head() により先頭5行が表示される |
| データの形と次元の確認 | iris.shape が (150, 5),iris.ndim が 2 と表示される |
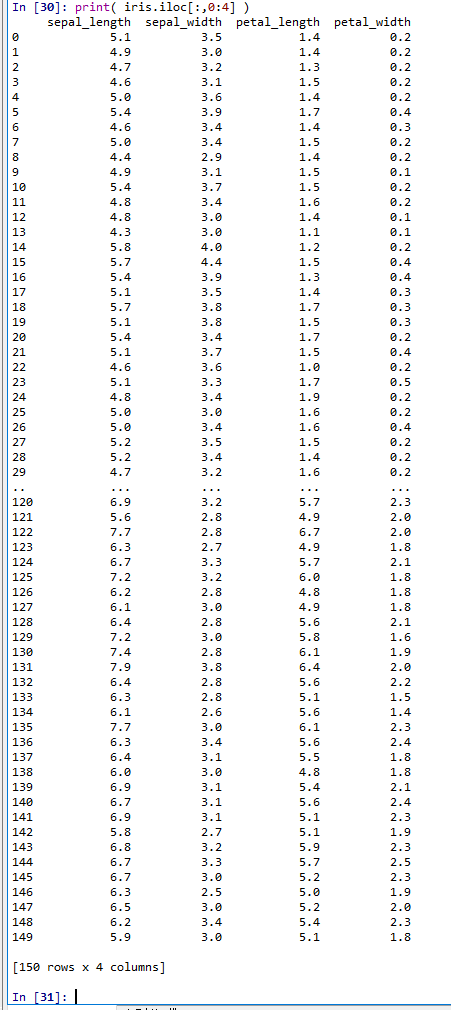
| 0〜3 列目の表示 | iris.iloc[:,0:4] により 150 行 × 4 列の数値データが表示される |
| VBGMM によるクラスタリング | bgmm.predict(X) により 150 個のクラスタラベル(整数)が表示される |
| 各クラスタの重みの確認 | 重みが 0.01 を超えるクラスタのみが番号と重み付きで表示される |
| クラスタリング結果のプロット | PCA による2次元散布図が表示され,クラスタごとに色分けされている |
| Iris データセットのプロット(比較用) | PCA による2次元散布図が表示され,品種(species)ごとに色分けされている |
4. 概要・使い方・実行上の注意
4.1 Iris データセット
Iris データセットは seaborn の load_dataset 関数で読み込む.サイズは 150 × 5,次元数は 2 である.最後の列(species)は花の種類を表す.クラスタリングには 0〜3 列目(sepal_length, sepal_width, petal_length, petal_width)を使用する.
4.2 VBGMM によるクラスタリング
BayesianGaussianMixture に最大クラスタ数(n_components=10)を指定し,fit でモデルを学習させた後,predict で各データ点のクラスタラベルを取得する.random_state=42 を指定し,実行結果の再現性を確保している.
4.3 クラスタの重みの確認
VBGMM は,データに適合するクラスタのみに大きな重みを割り当てる.bgmm.weights_ を参照し,重みが 0.01 を超えるクラスタを表示することで,有効クラスタ数を確認できる.
4.4 主成分分析による可視化
クラスタリング結果は,PCA で2次元に次元削減し散布図で可視化する.pcaplot 関数は,PCA を適用し第1・第2主成分を軸とする散布図を描画する.ラベルごとに色分けし凡例を表示する.クラスタリング結果と元の品種ラベルのプロットを比較することで,VBGMM の分類精度を視覚的に評価できる.
5. ソースコード
5.1 Iris データセットの読み込みと確認
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.mixture import BayesianGaussianMixture
sns.set()
iris = sns.load_dataset('iris')
データの確認を行う.
print(iris.head())
形と次元を確認する.サイズは 150 × 5,次元数は 2.最後の列(species)は花の種類を表すデータである.
print(iris.shape)
print(iris.ndim)
Iris データセットの 0, 1, 2, 3 列目を表示する.
print( iris.iloc[:,0:4] )
5.2 散布図に主成分分析プロットの準備
# 主成分分析で n 個の成分を得る
def prin(A, n):
return PCA(n_components=n).fit_transform(A)
# M の最初の 2 列を,b で色分けしてプロット.b はラベル
def scatter_label_plot(M, b, alpha):
a12 = pd.DataFrame(M[:, 0:2], columns=['a1', 'a2'])
f = pd.factorize(b)
a12['target'] = f[0]
g = sns.scatterplot(x='a1', y='a2', hue='target', data=a12, palette=sns.color_palette("hls", np.max(f[0]) + 1), legend="full", alpha=alpha)
for i, label in enumerate(f[1]):
g.legend_.get_texts()[i].set_text(label)
plt.show()
# 主成分分析プロット
def pcaplot(A, b, alpha):
scatter_label_plot(prin(A, 2), b, alpha)
5.3 VBGMM によるクラスタリングと結果の表示
Iris データセットの 0〜3 列目について,VBGMM でクラスタリングを行う.
X = iris.iloc[:, 0:4].values
bgmm = BayesianGaussianMixture(n_components=10, random_state=42).fit(X)
c = bgmm.predict(X)
print(c)
各クラスタの重みを確認する.
for i, w in enumerate(bgmm.weights_):
if w > 0.01:
print(f"クラスタ {i}: 重み {w:.4f}")
結果をプロットする.
pcaplot(X, c, 1)
比較のため,Iris データセットを品種ラベルでプロットする.
pcaplot(X, iris.iloc[:, 4], 1)
6. まとめ
6.1 VBGMM によるクラスタ数の自動推定
VBGMM では,クラスタ数を指定せずにクラスタリングを行う.最大クラスタ数を指定しておくと,データに適合するクラスタのみに大きな重みが割り当てられ,有効なクラスタ数が自動的に決定される.
6.2 クラスタの重みによる有効クラスタの判定
bgmm.weights_ を参照することで各クラスタの重みを確認できる.重みが 0 に近いクラスタは実質的に使用されておらず,これにより有効クラスタ数を把握できる.
6.3 主成分分析(PCA)による可視化
PCA で2次元に次元削減した散布図により,クラスタリング結果を可視化する.元の品種ラベルによるプロットと比較することで,VBGMM の分類精度を視覚的に評価できる.
6.4 再現性の確保
BayesianGaussianMixture に random_state=42 を指定することで,実行結果の再現性を確保している.
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)