一定間隔で処理の繰り返し
前準備
Python 3.12 のインストール
以下のいずれかの方法で Python 3.12 をインストールする。
方法1:winget によるインストール
Python がインストール済みの場合、この手順は不要である。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
winget install -e --id Python.Python.3.12 --scope machine --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/quiet InstallAllUsers=1 PrependPath=1 AssociateFiles=1 InstallLauncherAllUsers=1"--scope machine を指定することで、システム全体(全ユーザー向け)にインストールされる。このオプションの実行には管理者権限が必要である。インストール完了後、コマンドプロンプトを再起動すると PATH が自動的に設定される。
方法2:インストーラーによるインストール
- Python 公式サイト(https://www.python.org/downloads/)にアクセスし、「Download Python 3.x.x」ボタンから Windows 用インストーラーをダウンロードする。
- ダウンロードしたインストーラーを実行する。
- 初期画面の下部に表示される「Add python.exe to PATH」に必ずチェックを入れてから「Customize installation」を選択する。このチェックを入れ忘れると、コマンドプロンプトから
pythonコマンドを実行できない。 - 「Install Python 3.xx for all users」にチェックを入れ、「Install」をクリックする。
インストールの確認
コマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。
python --versionバージョン番号(例:Python 3.12.x)が表示されればインストール成功である。「'python' は、内部コマンドまたは外部コマンドとして認識されていません。」と表示される場合は、インストールが正常に完了していない。
AIエディタ Windsurf のインストール
Pythonプログラムの編集・実行には、AIエディタの利用を推奨する。ここでは、Windsurfのインストールを説明する。
Windsurf がインストール済みの場合、この手順は不要である。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
winget install -e --id Codeium.Windsurf --scope machine --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/VERYSILENT /NORESTART /MERGETASKS=!runcode,addtopath,associatewithfiles,!desktopicon"
powershell -Command "$env:Path=[System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','Machine')+';'+[System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','User'); windsurf --install-extension MS-CEINTL.vscode-language-pack-ja --force; windsurf --install-extension ms-python.python --force"--scope machine を指定することで、システム全体(全ユーザー向け)にインストールされる。このオプションの実行には管理者権限が必要である。インストール完了後、コマンドプロンプトを再起動すると PATH が自動的に設定される。
【関連する外部ページ】
Windsurf の公式ページ: https://windsurf.com/
Python の公式ページ: https://www.python.org/
ソースコードの例と実行結果の例
- 「5秒」毎に処理を繰り返す.
- 「5秒」以内に処理が終わらなかったときは,さらに5秒待つ
import time
import threading
def worker():
print(time.gmtime())
time.sleep(8)
def mainloop(time_interval, f):
now = time.time()
while True:
t = threading.Thread(target=f)
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
t.join()
wait_time = time_interval - ( (time.time() - now) % time_interval )
time.sleep(wait_time)
mainloop(5, worker)
Python プログラムの実行
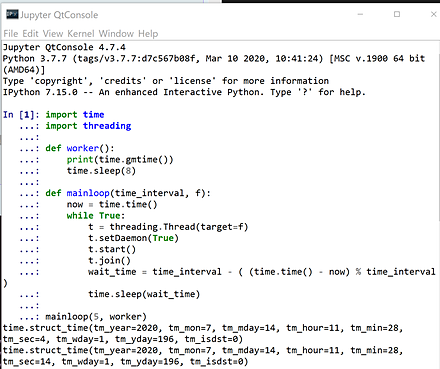
5秒毎に処理を繰り返す。別スレッドでその結果を表示
次のことは、先ほどと同じ
- 「5秒」毎に処理を繰り返す.
- 「5秒」以内に処理が終わらなかったときは,さらに5秒待つ
import time
import threading
c=0
c2=0
# ずっと動き続けるスレッド
def another():
global c
global c2
while True:
c = c + 1
print("hello, %d, %d" % (c, c2))
time.sleep(1)
# 定期的に繰り返すスレッド
def worker():
global c2
c2 = c2 + 1
print(time.gmtime())
time.sleep(8)
def mainloop(time_interval, f, another):
now = time.time()
t0 = threading.Thread(target=another)
t0.setDaemon(True)
t0.start()
while True:
t = threading.Thread(target=f)
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
t.join()
wait_time = time_interval - ( (time.time() - now) % time_interval )
time.sleep(wait_time)
if __name__ == '__main__':
mainloop(5, worker, another)
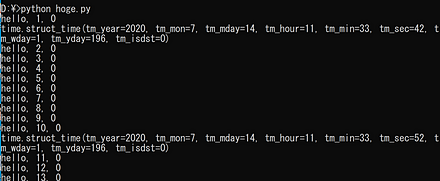
hoge.py のような名前で保存し、「python hoge.py」のようにして実行(Ubuntu の場合は「python3 hoge.py」)
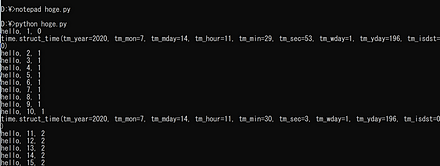
上と同じ機能だが、別の書き方
import time
import threading
c=0
c2=0
# ずっと動き続ける処理
def another():
global c
global c2
while True:
c = c + 1
print("hello, %d, %d" % (c, c2))
time.sleep(1)
# 定期的に繰り返すスレッド
def worker():
print(time.gmtime())
time.sleep(8)
def mainloop():
time_interval = 5
now = time.time()
while True:
t = threading.Thread(target=worker)
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
t.join()
wait_time = time_interval - ( (time.time() - now) % time_interval )
time.sleep(wait_time)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t0 = threading.Thread(target=mainloop)
t0.setDaemon(True)
t0.start()
another()
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)