Iris データセットの次元削減(t-SNE, Isomap, Script Embedding, LLE, kernel approximation 法)(Python, scikit-learn を使用)
1. 前準備
Python の準備(Windows,Ubuntu 上)
- Windows での Python 3.10,関連パッケージ,Python 開発環境のインストール(winget を使用しないインストール): 別ページ »で説明
- Ubuntu では,システム Pythonを使うことができる.Python3 開発用ファイル,pip, setuptools のインストール: 別ページ »で説明
【サイト内の関連ページ】
- Python のまとめ: 別ページ »にまとめ
- Google Colaboratory の使い方など: 別ページ »で説明
【関連する外部ページ】 Python の公式ページ: https://www.python.org/
Python の numpy, pandas, seaborn, matplotlib, scikit-learn のインストール
- Windows の場合
Windows では,コマンドプロンプトを管理者として実行し, 次のコマンドを実行する.
python -m pip install -U pip setuptools numpy pandas matplotlib seaborn scikit-learn scikit-learn-intelex
- Ubuntu の場合
端末で,次のコマンドを実行
# パッケージリストの情報を更新 sudo apt update sudo apt -y install python3-numpy python3-pandas python3-seaborn python3-matplotlib python3-sklearn
2. Iris データセットの準備
- Iris データセットの読み込み
import pandas as pd import seaborn as sns sns.set() iris = sns.load_dataset('iris')
- データの確認
print(iris.head())

- 形と次元を確認
配列(アレイ)の形: サイズは 150 ×5.次元数は 2. 最後の列は,iris.target は花の種類のデータである
print(iris.shape) print(iris.ndim)

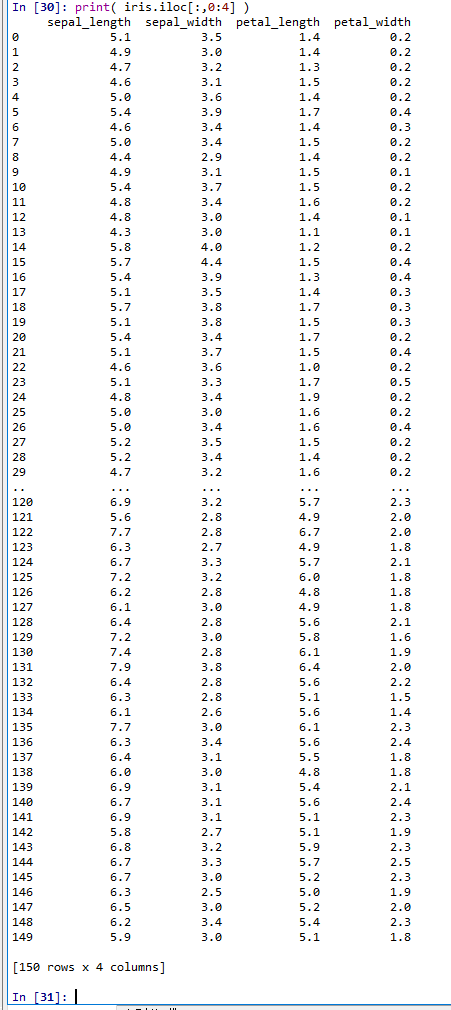
- Iris データセットの0, 1, 2, 3列目を表示
print( iris.iloc[:,0:4] )
3. t-SNE 法による次元削減
- 散布図にプロットの準備
import numpy as np import sklearn.decomposition %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings # M の最初の2列を,b で色を付けてプロット.b はラベル def scatter_label_plot(M, b, alpha): a12 = pd.DataFrame( M[:,0:2], columns=['a1', 'a2'] ) f = pd.factorize(b) a12['target'] = f[0] g = sns.scatterplot(x='a1', y='a2', hue='target', data=a12, palette=sns.color_palette("hls", np.max(f[0]) + 1), legend="full", alpha=alpha) # lenend を書き換え labels=f[1] for i, label in enumerate(labels): g.legend_.get_texts()[i].set_text(label) plt.show() - Iris データセットの0, 1, 2, 3列目について、t-SNE を実行
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE d = TSNE(n_components = 2).fit_transform(iris.iloc[:,0:4]) print(d)
scatter_label_plot(d, iris.iloc[:,4], 1)
4. isomap 法による次元削減
from sklearn.manifold import Isomap
d = Isomap(n_components=2, n_neighbors=10).fit_transform(iris.iloc[:,0:4])
print(d)
scatter_label_plot(d, iris.iloc[:,4], 1)
5. Spectral Embeddeing 法による次元削減
from sklearn.manifold import SpectralEmbedding
d = SpectralEmbedding(n_components=2, n_neighbors=10).fit_transform(iris.iloc[:,0:4])
print(d)
scatter_label_plot(d, iris.iloc[:,4], 1)
6. Locally Linear Embedding (LLE) 法による次元削減
scikit-learn の cheet sheet によれば、isomap, Spectral Embedding が働かないときは
Locally Linear Embedding (LLE)
が候補になっている
from sklearn.manifold import LocallyLinearEmbedding
d = LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_components=2, n_neighbors=10).fit_transform(iris.iloc[:,0:4])
print(d)
scatter_label_plot(d, iris.iloc[:,4], 1)
7. kernel approximation 法による次元削減
scikit-learn の cheet sheet によれば、
データ数が10000以上のときは
kernel approximation が候補になっている.
from sklearn.kernel_approximation import RBFSampler
d = RBFSampler(gamma=1).fit_transform(iris.iloc[:,0:4])
print(d)
scatter_label_plot(d, iris.iloc[:,4], 1)
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)