画像データの拡張,CIFAR 10 の画像分類を行う畳み込みニューラルネットワークの学習(keras の preprocessing を用いて増強,MobileNetV2,TensorFlow データセットのCIFAR-10 データセットを使用)(Google Colaboratroy へのリンク有り)
CIFAR-10 データセット(
教師データとして用いる画像データのデータ拡張を行う.増量では,TensorFlow の機能を使い,画像を縦横にずらす,コントラストを変化させることを行う.
前提として,このページの手順では,増量後の画像データがメモリに入り切る分量であるとしている.
TensorFlow データセットのCIFAR-10 データセットを使用する.
CNN としては,次のものを使用する.
【目次】
【サイト内の関連ページ】
【関連する外部ページ】
1. Google Colaboratory での実行
Google Colaboratory のページ:
次のリンクをクリックすると,Google Colaboratory のノートブックが開く. そして,Google アカウントでログインすると,Google Colaboratory のノートブック内のコード等を編集したり再実行したりができる.編集した場合でも,他の人に影響が出たりということはない.そして,編集後のものを,各自の Google ドライブ内に保存することもできる.
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1osVlD5wpv-pFMrIt2WgXWbTB8t5fKu9f?usp=sharing
2. Windows での実行
Python のインストール(Windows上)
注:既にPython(バージョン3.12を推奨)がインストール済みの場合は,この手順は不要である.
winget(Windowsパッケージマネージャー)を使用してインストールを行う
- Windowsで,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。 - winget(Windowsパッケージマネージャー)が利用可能か確認する:
winget --version
- Pythonのインストール(下のコマンドにより Python 3.12 がインストールされる).
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem" /v LongPathsEnabled /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f REM Python をシステム領域にインストール winget install --scope machine --id Python.Python.3.12 -e --silent REM Python のパス set "INSTALL_PATH=C:\Program Files\Python312" echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%INSTALL_PATH%" >nul if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%INSTALL_PATH%" /M >nul echo "%PATH%" | find /i "%INSTALL_PATH%\Scripts" >nul if errorlevel 1 setx PATH "%PATH%;%INSTALL_PATH%\Scripts" /M >nul
- Python詳細ガイド:Pythonまとめ »
- Windows で,管理者権限でコマンドプロンプトを起動(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー >
cmdと入力 > 右クリック > 「管理者として実行」)。次のコマンドを実行する.
python -m pip install -U numpy matplotlib seaborn scikit-learn pandas pydot
- パッケージのインポート,TensorFlow のバージョン確認など
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras import backend as K K.clear_session() import numpy as np import tensorflow_datasets as tfds from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings
- CIFAR-10 データセットのロード
tensorflow_datasets の loadで, 「batch_size = -1」を指定して,一括読み込みを行っている.
cifar10, cifar10_info = tfds.load('cifar10', with_info = True, shuffle_files=True, as_supervised=True, batch_size = -1)
- データセットの中の画像を表示
MatplotLib を用いて,0 番目の画像を表示する
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings NUM = 0 # NUM 番目の画像を表示 plt.imshow(cifar10['train'][0][NUM])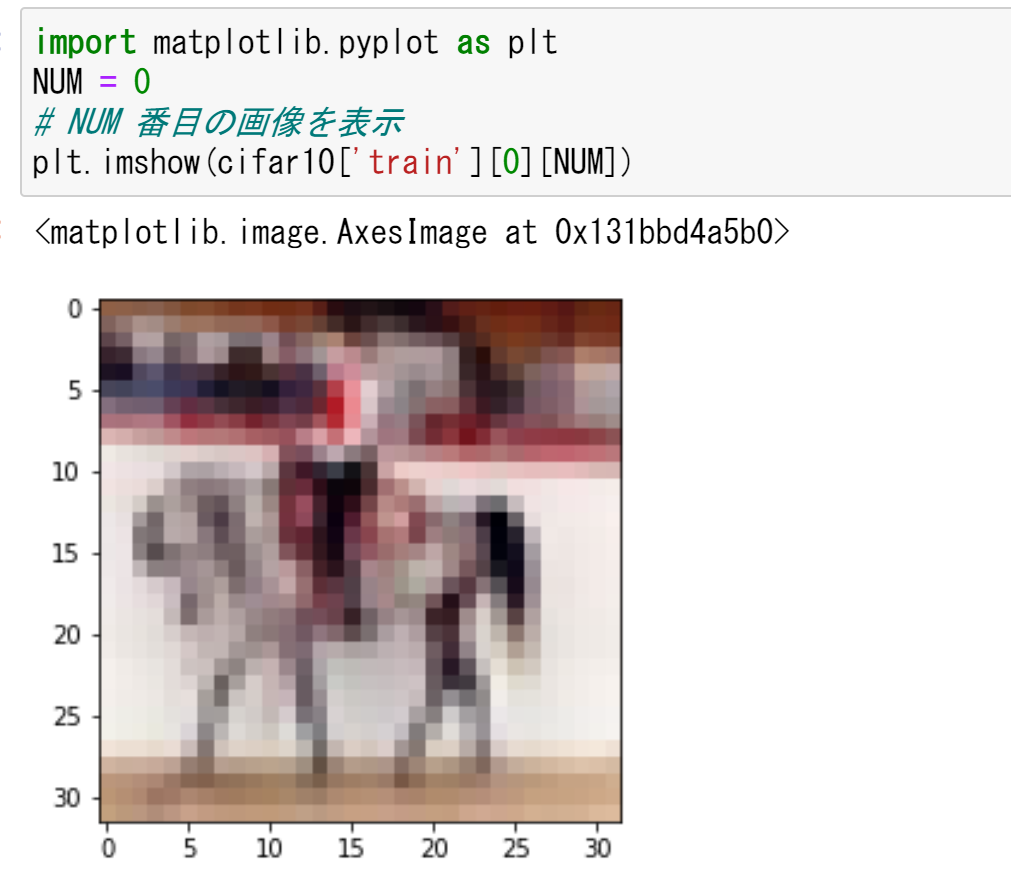
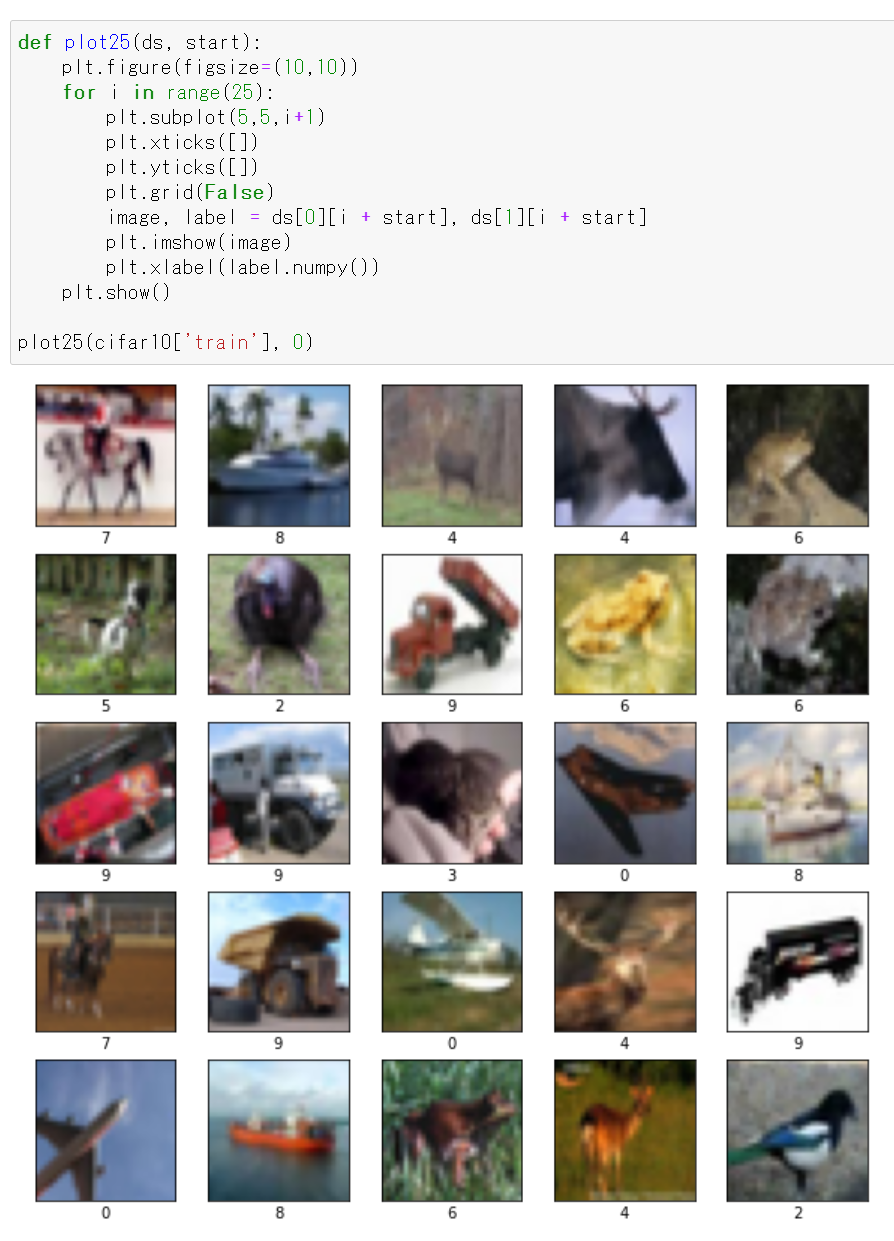
MatplotLib を用いて,複数の画像を並べて表示する.
def plot25(ds, start): plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) for i in range(25): plt.subplot(5,5,i+1) plt.xticks([]) plt.yticks([]) plt.grid(False) image, label = ds[0][i + start], ds[1][i + start] plt.imshow(image) plt.xlabel(label.numpy()) plt.show() plot25(cifar10['train'], 0)
- データセットの情報を表示
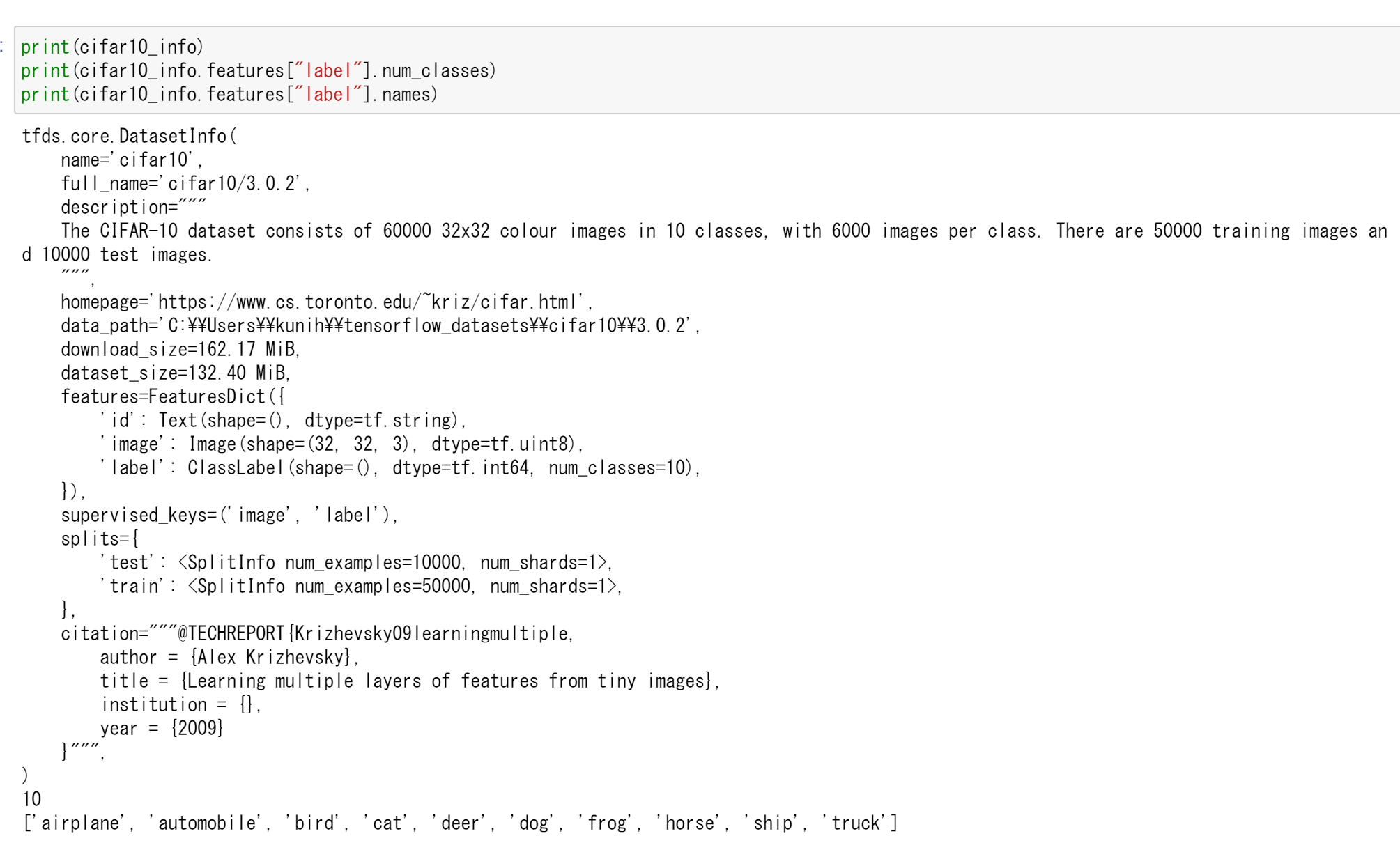
print(cifar10_info) print(cifar10_info.features["label"].num_classes) print(cifar10_info.features["label"].names)
- cifar10['train'] と cifar10['test'] の形と次元を確認
cifar10['train']: サイズ 32 かける 32 の 50000枚のカラー画像,50000枚のカラー画像それぞれのラベル(0 から 9 のどれか)
cifar10['test']: サイズ 32 かける 32 の 10000枚のカラー画像,10000枚のカラー画像それぞれのラベル(0 から 9 のどれか)
print(cifar10['train'][0].shape) print(cifar10['train'][1].shape) print(cifar10['test'][0].shape) print(cifar10['test'][1].shape)
- データセットの生成
ds_train, ds_test = cifar10['train'], cifar10['test']

- ニューラルネットワークを使うために,データの前処理
値は,もともと int で 0 から 255 の範囲であるのを, float32 で 0 から 1 の範囲になるように前処理を行う.
ds_train = (ds_train[0].numpy().astype("float32") / 255., ds_train[1]) ds_test = (ds_test[0].numpy().astype("float32") / 255., ds_test[1])
- 画像データのデータ拡張を行ってみる
画像データのデータ拡張を行う. 画像データは,ds_train[0] にある. TensorFlow の機能を使い,画像を縦横にずらす,コントラストを変化させることを行う. ds_train[1] にはラベルのデータが入っているとする.
結果の入る augmented_ds_train はタップル.うち1つ目は,numpy の配列.2つ目は,要素が tf.Tensor の配列.
INPUT_SHAPE = [32, 32, 3] CROP_SIZE = 3 # 関数オブジェクトを生成 def gen_data_augmentation(seed): data_augmentation = tf.keras.Sequential( [ tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.RandomFlip("horizontal", input_shape=INPUT_SHAPE, seed=seed), # tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.RandomContrast(factor=(0.1, 0.1), seed=seed), # tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.RandomRotation(factor=(-0.2, 0.2), seed=seed), tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.RandomZoom(height_factor=(-0.1, 0.1), width_factor=(-0.1, 0.1), seed=seed), tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.RandomTranslation(height_factor=(-0.1, 0.1), width_factor=(-0.1, 0.1), fill_mode='wrap', seed=seed) ] ) return data_augmentation # 複数画像を一括して増強 def augment_images(images, seed): data_augmentation = gen_data_augmentation(seed) a = [*map(lambda x: np.squeeze(data_augmentation(x[np.newaxis, ...], training=True), 0), images)] result = np.array(a) return result augmented_ds_train = (augment_images(ds_train[0], seed = 0), ds_train[1]) plot25(augmented_ds_train, 0)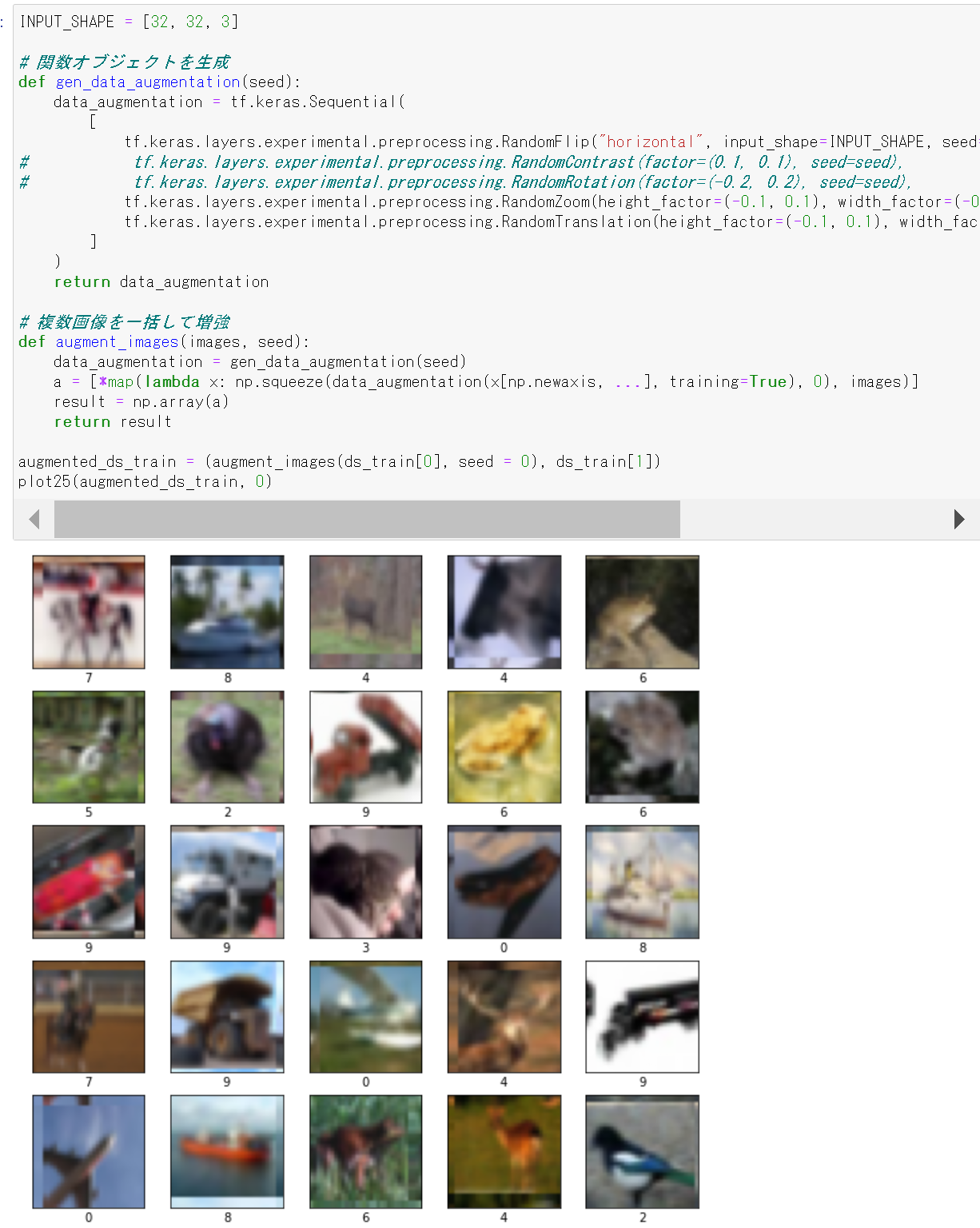
- 増量できたことの確認
print(augmented_ds_train[0].shape)
- 今度は,画像データのデータ拡張を行いながら,画像データを 5倍に増やす.
ここで増やした画像データは,あとで使用する
def increase_image_data(ds_train, t): # t 倍に増やす x1 = augment_images(ds_train[0], 1) y1 = ds_train[1] if t > 1: for i in range(t - 1): x2 = augment_images(ds_train[0], i + 1) # 画像は nparray, ラベルは tf.Tensorを要素とする配列にする x1 = np.concatenate([x1, x2]) y1 = tf.concat([y1, ds_train[1]], axis = 0) result = (x1, y1) return result augmented_ds_train = increase_image_data(ds_train, 5) plot25(augmented_ds_train, 0)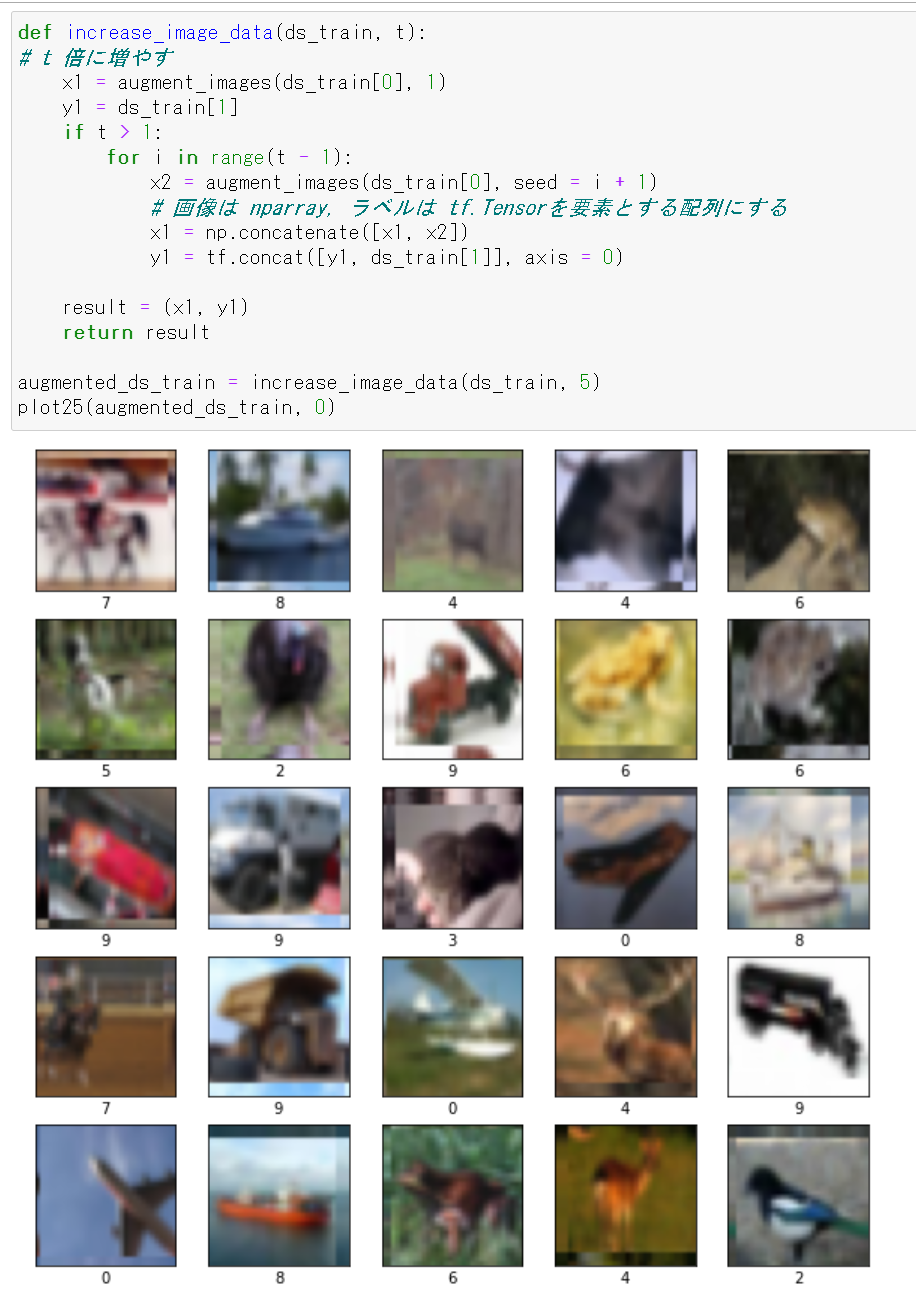
- ニューラルネットワークの作成と確認とコンパイル
Keras の MobileNet を使う. 「weights=None」を指定することにより,最初,重みはランダムに設定する.
NUM_CLASSES = 10 INPUT_SHAPE = [32, 32, 3] m1 = tf.keras.applications.mobilenet.MobileNet(input_shape=INPUT_SHAPE, weights=None, classes=NUM_CLASSES) m1.summary() m1.compile( optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001), loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['sparse_categorical_crossentropy', 'accuracy'] )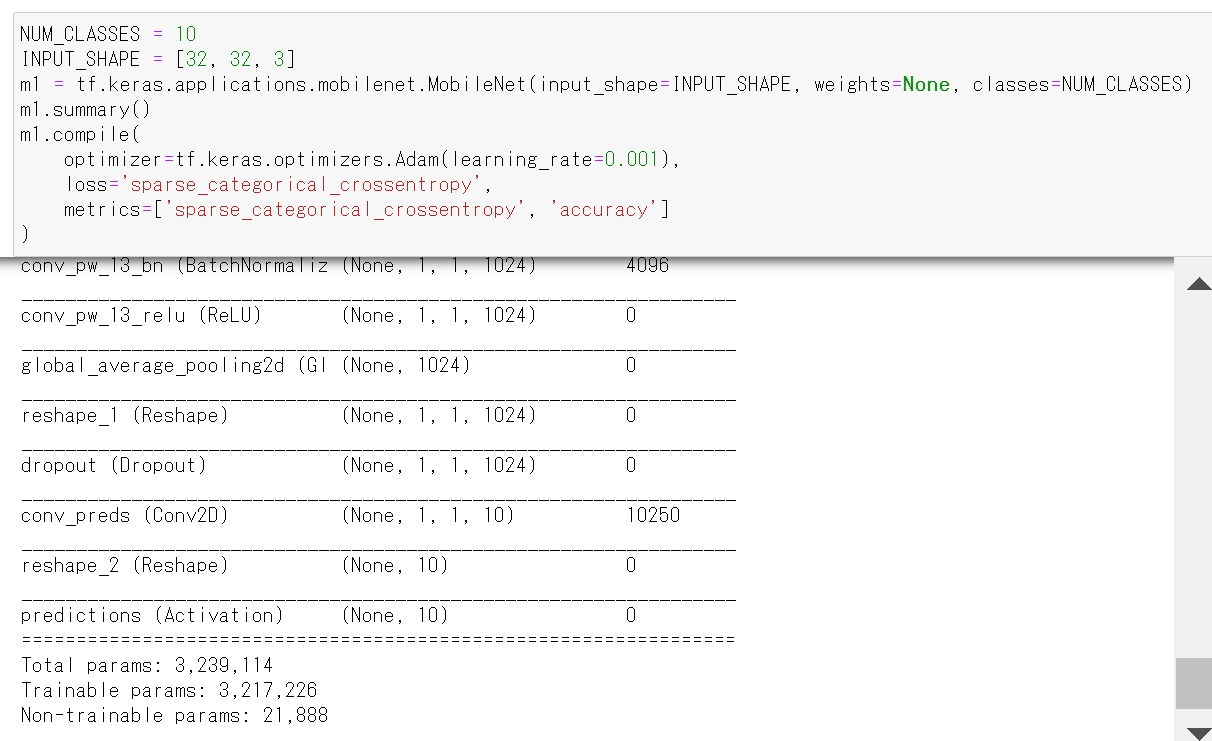
- モデルのビジュアライズ
Keras のモデルのビジュアライズについては: https://keras.io/ja/visualization/
ここでの表示で,エラーメッセージが出る場合でも,モデル自体は問題なくできていると考えられる.続行する.
from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model import pydot plot_model(m1)
7. ニューラルネットワークの学習(MobileNetV2 を使用)
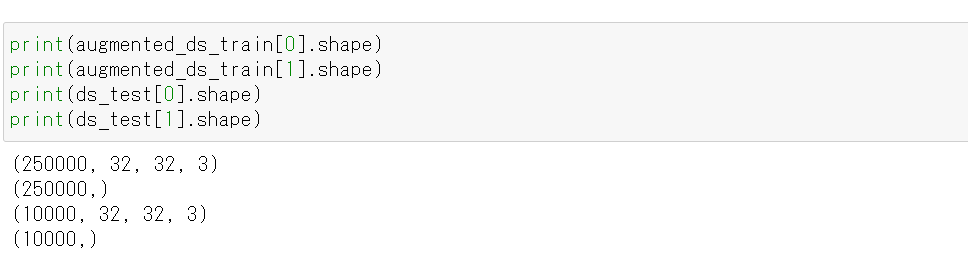
- 使用するデータの確認
print(augmented_ds_train[0].shape) print(augmented_ds_train[1].shape) print(ds_test[0].shape) print(ds_test[1].shape)
- ニューラルネットワークの学習を行う
ニューラルネットワークの学習は fit メソッドにより行う. 教師データを使用する. 教師データを投入する.
epochs = 20 history = m1.fit(augmented_ds_train[0], augmented_ds_train[1], epochs=epochs, validation_data=(ds_test[0], ds_test[1]), verbose=1)
- CNN による画像分類
ds_test を分類してみる.
print(m1.predict(ds_test[0]))
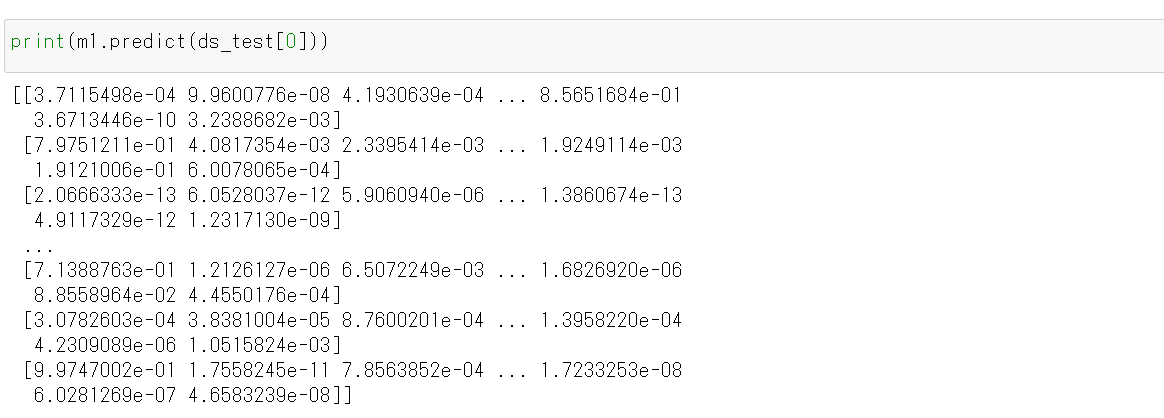
それぞれの数値の中で、一番大きいものはどれか?
m1.predict(ds_test[0]).argmax(axis=1)
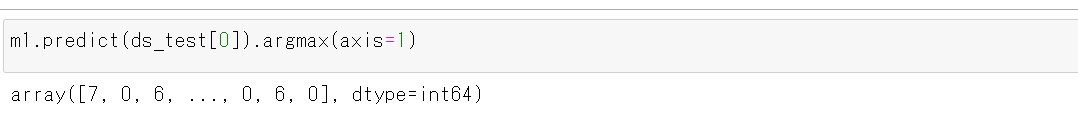
y_test 内にある正解のラベル(クラス名)を表示する(上の結果と比べるため)
print(y_test[1])
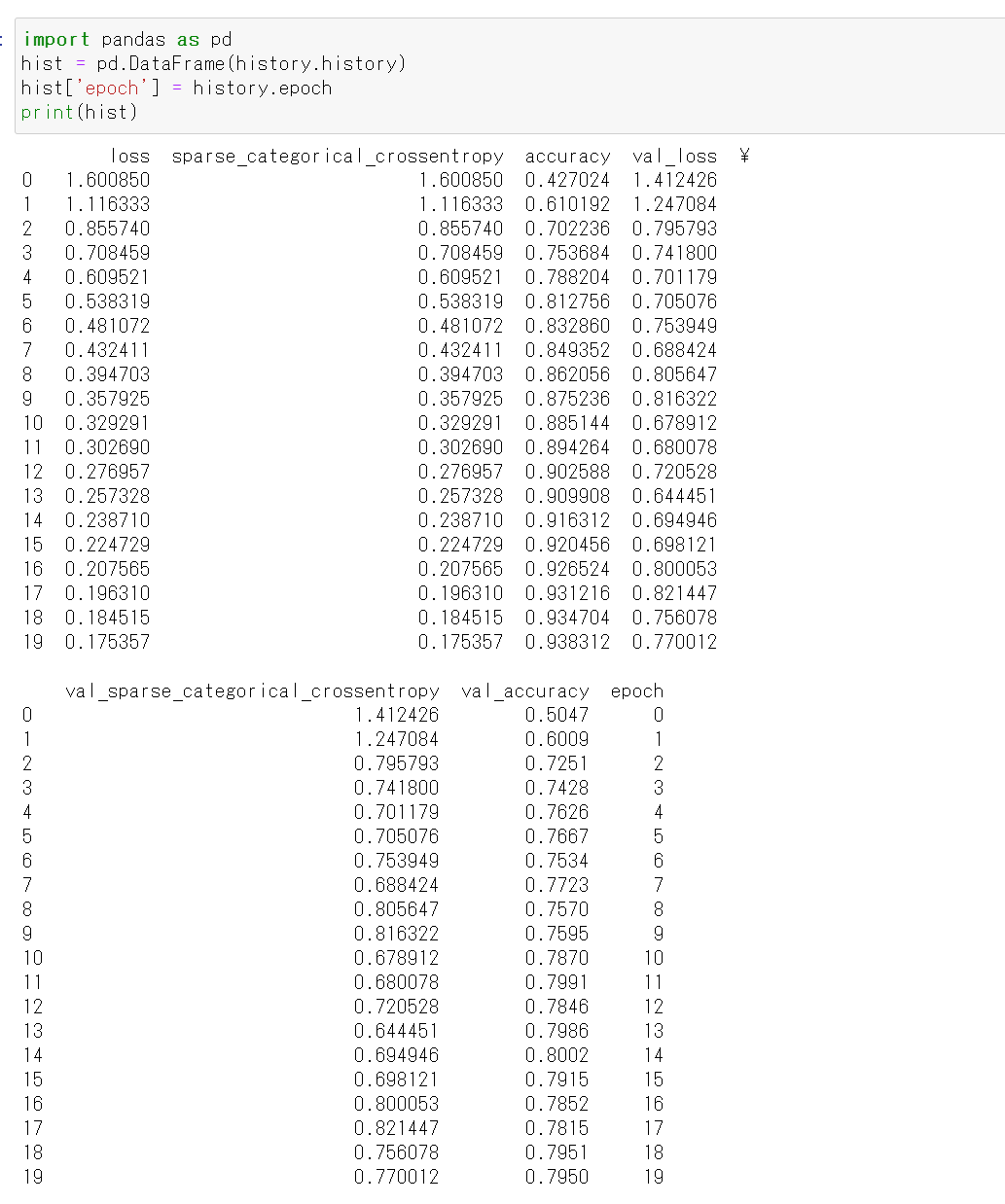
- 学習曲線の確認
過学習や学習不足について確認.
import pandas as pd hist = pd.DataFrame(history.history) hist['epoch'] = history.epoch print(hist)
- 学習曲線のプロット
過学習や学習不足について確認.
https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/keras/overfit_and_underfit?hl=ja で公開されているプログラムを使用
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings def plot_history(histories, key='binary_crossentropy'): plt.figure(figsize=(16,10)) for name, history in histories: val = plt.plot(history.epoch, history.history['val_'+key], '--', label=name.title()+' Val') plt.plot(history.epoch, history.history[key], color=val[0].get_color(), label=name.title()+' Train') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel(key.replace('_',' ').title()) plt.legend() plt.xlim([0,max(history.epoch)]) plot_history([('history', history)], key='sparse_categorical_crossentropy')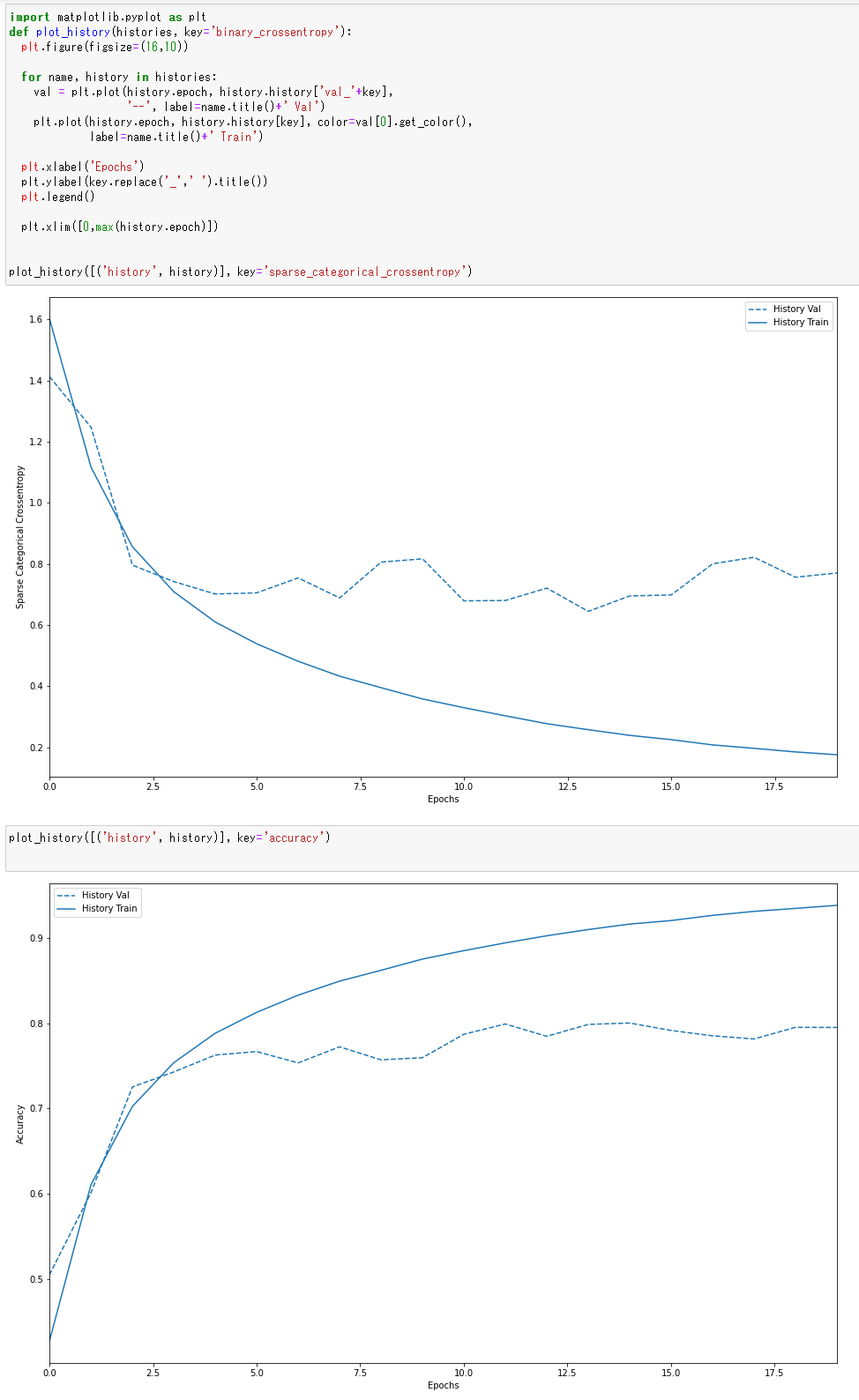
plot_history([('history', history)], key='accuracy')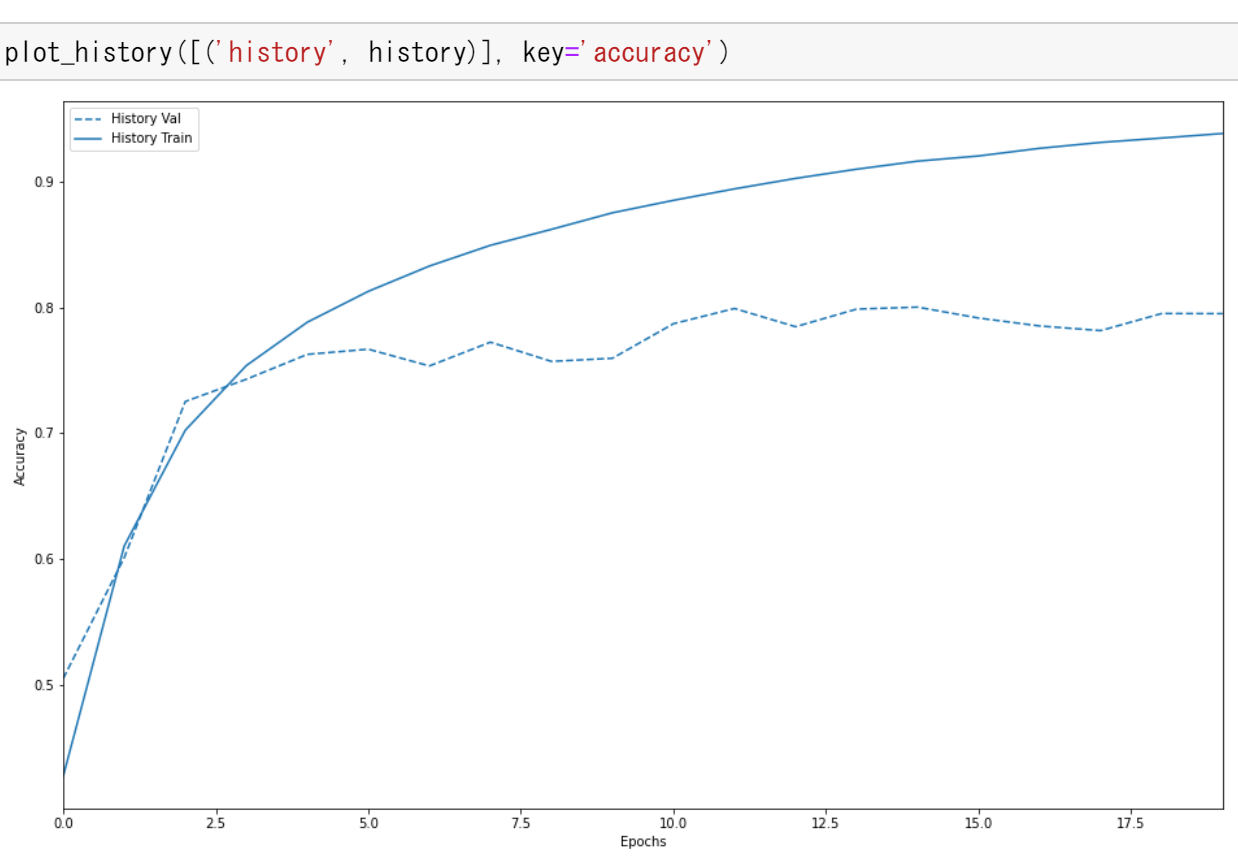
データのデータ拡張を行わない場合の結果(学習曲線など)は, 別ページ »で説明
- 使用するデータの確認
【関連する外部サイト】
【サイト内の関連ページ】
TensorFlow,Keras のインストール
Windows での TensorFlow,Keras のインストール: 別ページ »で説明
(このページで,Build Tools for Visual Studio 2022,NVIDIA ドライバ, NVIDIA CUDA ツールキット, NVIDIA cuDNNのインストールも説明している.)
Graphviz のインストール
Windows での Graphviz のインストール: 別ページ »で説明
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)