CIFAR 10, CIFAR 100, MNIST, Fashion MNIST データセットの主成分分析プロット(Python, matplotlib, seaborn を使用)
【目次】
【関連する外部ページ】
keras に付属のデータセットに関する Web ページ: https://keras.io/ja/datasets/
Google Colaboratory のページ:
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1Blm3l62DN_4dqUoltwhq-sdtsfr7ZaiU?usp=sharing
1. 前準備
Python 3.12 のインストール
以下のいずれかの方法で Python 3.12 をインストールする。
方法1:winget によるインストール
Python がインストール済みの場合、この手順は不要である。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
winget install -e --id Python.Python.3.12 --scope machine --silent --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/quiet InstallAllUsers=1 PrependPath=1 AssociateFiles=1 InstallLauncherAllUsers=1"--scope machine を指定することで、システム全体(全ユーザー向け)にインストールされる。このオプションの実行には管理者権限が必要である。インストール完了後、コマンドプロンプトを再起動すると PATH が自動的に設定される。
方法2:インストーラーによるインストール
- Python 公式サイト(https://www.python.org/downloads/)にアクセスし、「Download Python 3.x.x」ボタンから Windows 用インストーラーをダウンロードする。
- ダウンロードしたインストーラーを実行する。
- 初期画面の下部に表示される「Add python.exe to PATH」に必ずチェックを入れてから「Customize installation」を選択する。このチェックを入れ忘れると、コマンドプロンプトから
pythonコマンドを実行できない。 - 「Install Python 3.xx for all users」にチェックを入れ、「Install」をクリックする。
インストールの確認
コマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。
python --versionバージョン番号(例:Python 3.12.x)が表示されればインストール成功である。「'python' は、内部コマンドまたは外部コマンドとして認識されていません。」と表示される場合は、インストールが正常に完了していない。
AIエディタ Windsurf のインストール
Pythonプログラムの編集・実行には、AIエディタの利用を推奨する。ここでは、Windsurfのインストールを説明する。
Windsurf がインストール済みの場合、この手順は不要である。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで以下を実行する。管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを起動するには、Windows キーまたはスタートメニューから「cmd」と入力し、表示された「コマンドプロンプト」を右クリックして「管理者として実行」を選択する。
winget install -e --id Codeium.Windsurf --scope machine --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements --override "/VERYSILENT /NORESTART /MERGETASKS=!runcode,addtopath,associatewithfiles,!desktopicon"
powershell -Command "$env:Path=[System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','Machine')+';'+[System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','User'); windsurf --install-extension MS-CEINTL.vscode-language-pack-ja --force; windsurf --install-extension ms-python.python --force"--scope machine を指定することで、システム全体(全ユーザー向け)にインストールされる。このオプションの実行には管理者権限が必要である。インストール完了後、コマンドプロンプトを再起動すると PATH が自動的に設定される。
【関連する外部ページ】
Windsurf の公式ページ: https://windsurf.com/
TensorFlow,tensorflow_datasets のインストール
- Windows の場合:
Windows で pip を実行するときは,管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトを使用し,システム領域へのインストールを行う.
python -m pip uninstall -y tensorflow tensorflow-cpu tensorflow-gpu tensorflow-intel tensorflow-text tensorflow-estimator tf-models-official tf_slim tensorflow_datasets tensorflow-hub keras keras-tuner keras-visualizer python -m pip install -U tensorflow tensorflow_datasets - Ubuntu の場合:
次のコマンドを実行.
sudo pip3 uninstall -y tensorflow tensorflow-cpu tensorflow-gpu tensorflow-intel tensorflow-text tensorflow-estimator tf-models-official tf_slim tensorflow_datasets tensorflow-hub keras keras-tuner keras-visualizer sudo pip3 uninstall -y six wheel astunparse tensorflow-estimator numpy keras-preprocessing absl-py wrapt gast flatbuffers grpcio opt-einsum protobuf termcolor typing-extensions google-pasta h5py tensorboard-plugin-wit markdown werkzeug requests-oauthlib rsa cachetools google-auth google-auth-oauthlib tensorboard tensorflow sudo apt -y install python3-six python3-wheel python3-numpy python3-grpcio python3-protobuf python3-termcolor python3-typing-extensions python3-h5py python3-markdown python3-werkzeug python3-requests-oauthlib python3-rsa python3-cachetools python3-google-auth sudo pip3 install -U tensorflow-gpu tensorflow_datasets
Python の numpy, pandas, seaborn, matplotlib, scikit-learn のインストール
以下のコマンドを管理者権限のコマンドプロンプトで実行する
(手順:Windowsキーまたはスタートメニュー → cmd と入力 → 右クリック → 「管理者として実行」)。
python -m pip install -U pip setuptools numpy pandas matplotlib seaborn scikit-learn scikit-learn-intelex
2. データセットの準備とデータセットの主成分分析プロット
主成分分析プロットの前準備
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
sns.set()
import numpy as np
import sklearn.decomposition
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings
# 主成分分析
def prin(A, n):
pca = sklearn.decomposition.PCA(n_components=n)
return pca.fit_transform(A)
# 主成分分析で2つの成分を得る
def prin2(A):
return prin(A, 2)
# M の最初の2列を,b で色を付けてプロット
def scatter_plot(M, b, alpha):
a12 = pd.DataFrame( M[:,0:2], columns=['a1', 'a2'] )
a12['target'] = b
sns.scatterplot(x='a1', y='a2', hue='target', data=a12, palette=sns.color_palette("hls", np.max(b) + 1), legend="full", alpha=alpha)
# 主成分分析プロット
def pcaplot(A, b, alpha):
scatter_plot(prin2(A), b, alpha)

CIFAR10 データセット
- CIFAR10 データセットのロード
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import tensorflow_datasets as tfds %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings cifar10, cifar10_metadata = tfds.load('cifar10', with_info = True, shuffle_files=True, as_supervised=True, batch_size = -1) x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = cifar10['train'][0], cifar10['train'][1], cifar10['test'][0], cifar10['test'][1] print(cifar10_metadata) # 【x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test の numpy ndarray への変換と,値の範囲の調整(値の範囲が 0 ~ 255 であるのを,0 ~ 1 に調整)する】 print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test)) # numpy に変換 x_train = x_train.numpy().astype("float32") / 255.0 x_test = x_test.numpy().astype("float32") / 255.0 y_train = y_train.numpy() y_test = y_test.numpy() print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test))
- CIFAR10 データセットの主成分分析プロット
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], -1) # サブフラット化 x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], -1) # サブフラット化 print(x_train.shape) print(x_test.shape) pcaplot(np.concatenate( (x_train, x_test) ), np.concatenate( (y_train, y_test) ), 0.1)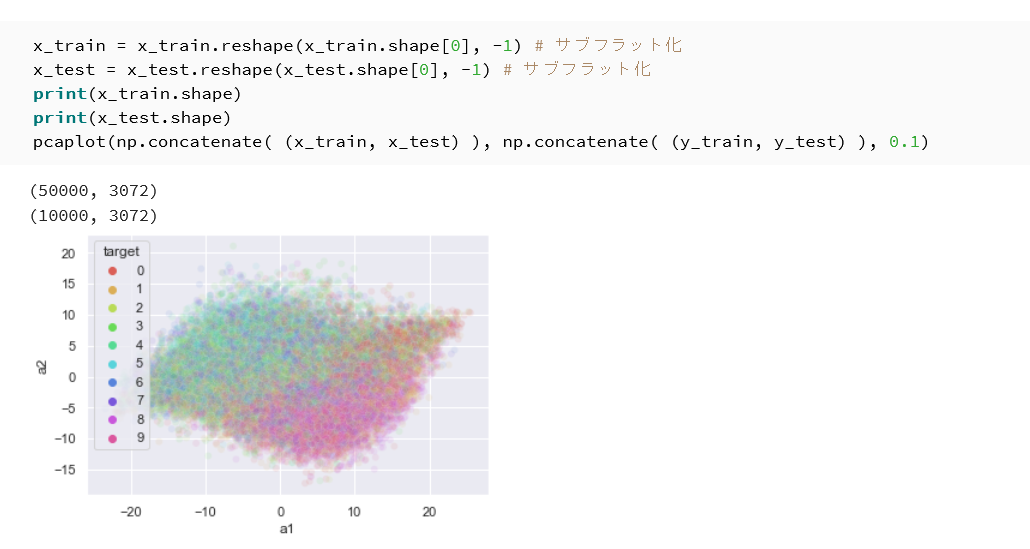
CIFAR 100データセット
- CIFAR100 データセットのロード
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import tensorflow_datasets as tfds %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings cifar100, cifar100_metadata = tfds.load('cifar100', with_info = True, shuffle_files=True, as_supervised=True, batch_size = -1) x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = cifar100['train'][0], cifar100['train'][1], cifar100['test'][0], cifar100['test'][1] print(cifar100_metadata) # 【x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test の numpy ndarray への変換と,値の範囲の調整(値の範囲が 0 ~ 255 であるのを,0 ~ 1 に調整)する】 print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test)) # numpy に変換 x_train = x_train.numpy().astype("float32") / 255.0 x_test = x_test.numpy().astype("float32") / 255.0 y_train = y_train.numpy() y_test = y_test.numpy() print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test))
- CIFAR100 データセットの主成分分析プロット
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], -1) # サブフラット化 x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], -1) # サブフラット化 print(x_train.shape) print(x_test.shape) pcaplot(np.concatenate( (x_train, x_test) ), np.concatenate( (y_train, y_test) ), 0.1)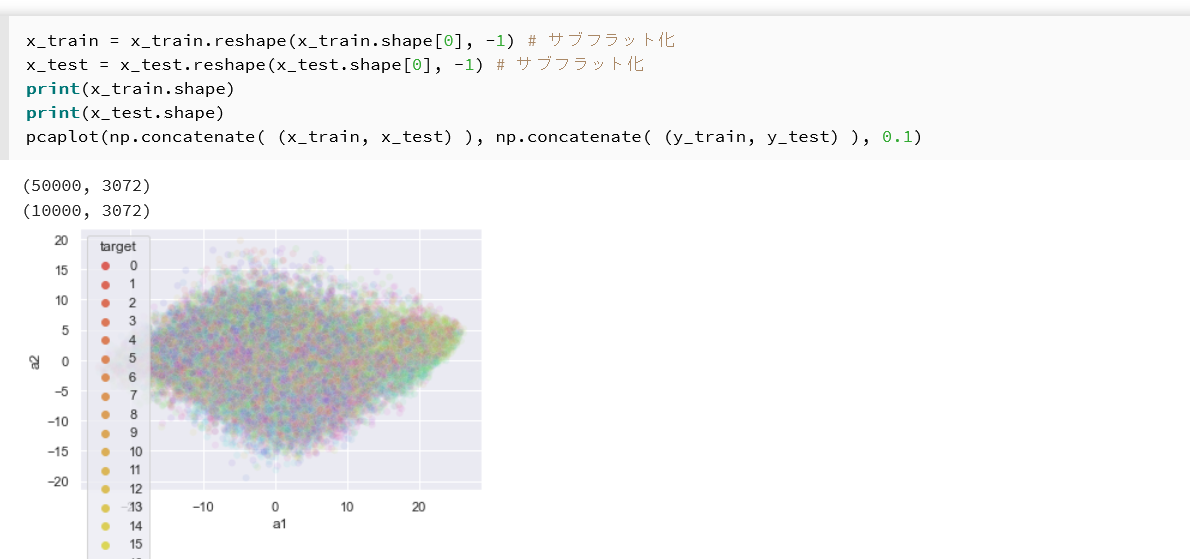
MNIST データセットのロード
次の Python プログラムを用いて,MNIST データセットのロードを行う.
- データセットの準備
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import tensorflow_datasets as tfds %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings mnist, mnist_metadata = tfds.load('mnist', with_info = True, shuffle_files=True, as_supervised=True, batch_size = -1) x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = mnist['train'][0], mnist['train'][1], mnist['test'][0], mnist['test'][1] print(mnist_metadata) # 【x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test の numpy ndarray への変換と,値の範囲の調整(値の範囲が 0 ~ 255 であるのを,0 ~ 1 に調整)する】 print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test)) # numpy に変換 x_train = x_train.numpy().astype("float32") / 255.0 x_test = x_test.numpy().astype("float32") / 255.0 y_train = y_train.numpy() y_test = y_test.numpy() print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test))
- MNISTデータセットの主成分分析プロット
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], -1) # サブフラット化 x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], -1) # サブフラット化 print(x_train.shape) print(x_test.shape) pcaplot(np.concatenate( (x_train, x_test) ), np.concatenate( (y_train, y_test) ), 0.1)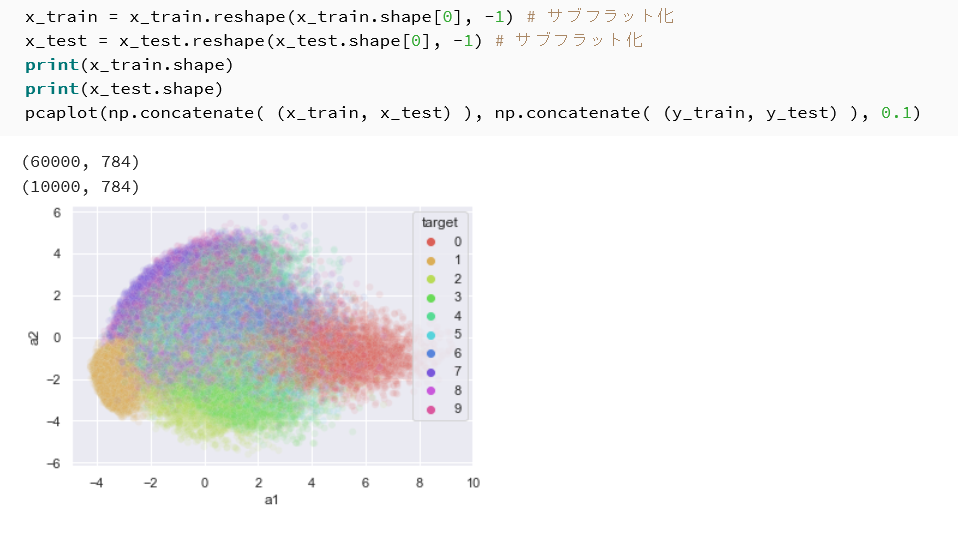
Fashion MNIST データセット
- Fashion MNIST データセットのロード
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import tensorflow_datasets as tfds %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # Suppress Matplotlib warnings fashion_mnist, fashion_mnist_metadata = tfds.load('fashion_mnist', with_info = True, shuffle_files=True, as_supervised=True, batch_size = -1) x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = fashion_mnist['train'][0], fashion_mnist['train'][1], fashion_mnist['test'][0], fashion_mnist['test'][1] print(fashion_mnist_metadata) # 【x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test の numpy ndarray への変換と,値の範囲の調整(値の範囲が 0 ~ 255 であるのを,0 ~ 1 に調整)する】 print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test)) # numpy に変換 x_train = x_train.numpy().astype("float32") / 255.0 x_test = x_test.numpy().astype("float32") / 255.0 y_train = y_train.numpy() y_test = y_test.numpy() print(type(x_train), x_train.shape, np.max(x_train), np.min(x_train)) print(type(x_test), x_test.shape, np.max(x_test), np.min(x_test)) print(type(y_train), y_train.shape, np.max(y_train), np.min(y_train)) print(type(y_test), y_test.shape, np.max(y_test), np.min(y_test))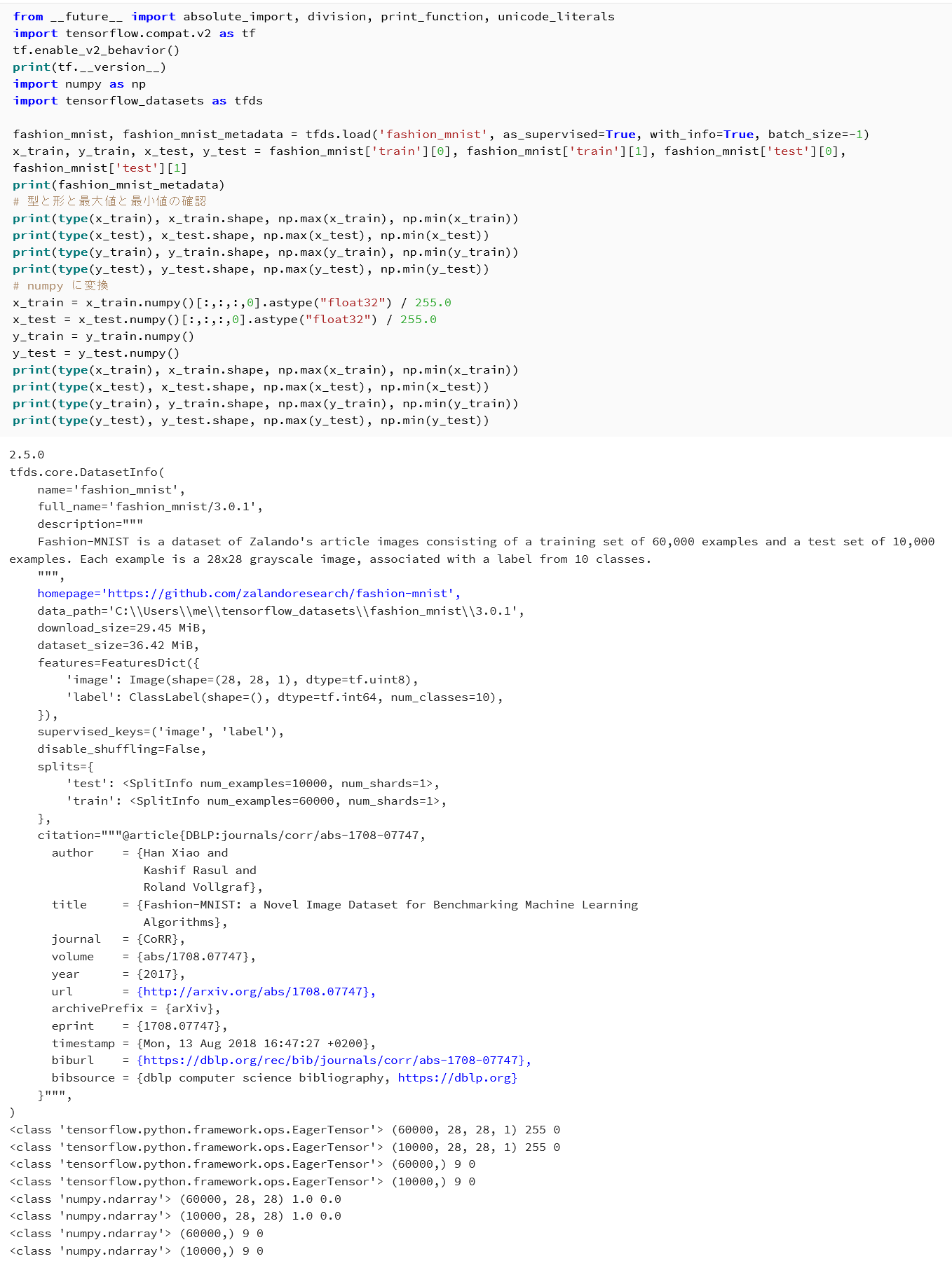
- Fashion MNIST データセットの主成分分析プロット
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], -1) # サブフラット化 x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], -1) # サブフラット化 print(x_train.shape) print(x_test.shape) pcaplot(np.concatenate( (x_train, x_test) ), np.concatenate( (y_train, y_test) ), 0.1)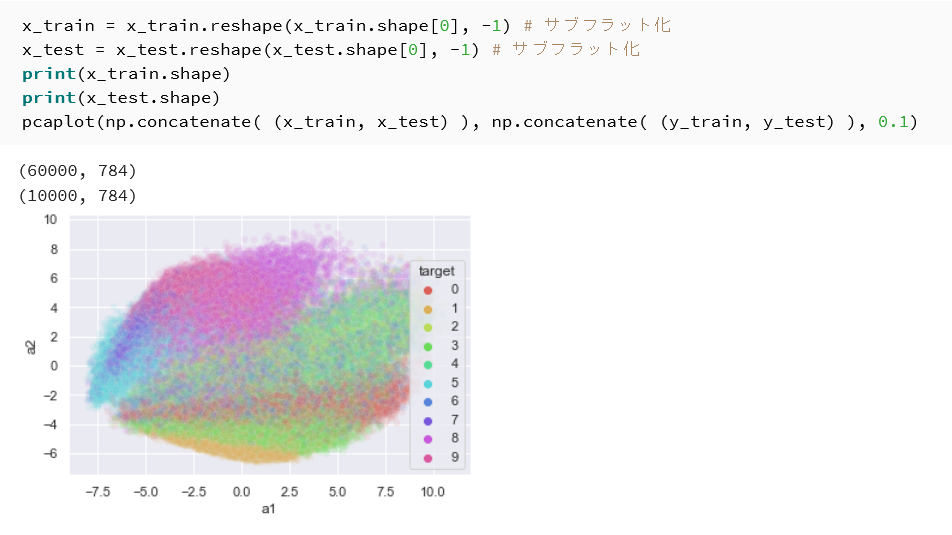
![[kaneko lab.]](https://www.kkaneko.jp/info/logo_png.png)